3D printing is rapidly transforming educational landscapes, providing students and educators with tools to bring conceptual learning to life. This technology enhances traditional educational methods by integrating practical, hands-on experiences that encourage creativity, problem-solving, and a deeper understanding of subjects ranging from the sciences to the arts. As educational institutions seek to equip students with skills for the future, 3D printing emerges as a pivotal educational tool.
Advantages of 3D Printing in Education
The inclusion of 3D printing in educational settings offers several significant benefits:
Hands-On Learning: 3D printing converts abstract concepts into tangible objects, enhancing comprehension and retention. For instance, students can physically handle the 3D models they create, which bridges the gap between theoretical learning and practical application.
Innovation and Creativity: This technology encourages students to engage in creative thinking and innovation. By designing, iterating, and printing their creations, students learn through trial and error in a risk-free environment, fostering a growth mindset.
Interdisciplinary Learning: 3D printing is inherently interdisciplinary, blending elements of design, engineering, math, and science. It provides a practical context for students to apply knowledge from different subjects in a cohesive project, enhancing integrative learning.

Key Applications of 3D Printing in Education
3D printing serves various educational purposes across multiple disciplines:
STEM Education: In subjects like physics and biology, teachers use 3D printing to create models of atoms, cells, or engineering components, making complex concepts more accessible and engaging for students.
Arts and Design: Art students can experiment with 3D printing to explore new forms of media and techniques, pushing the boundaries of traditional artistic practices.
Geography and History: Teachers utilize 3D printing to reconstruct historical artifacts or topographical maps, offering students a hands-on approach to historical studies and geography.
Special Education: Custom educational tools and aids designed through 3D printing can significantly assist learners with special needs, providing them with tailored resources to enhance their learning experiences.
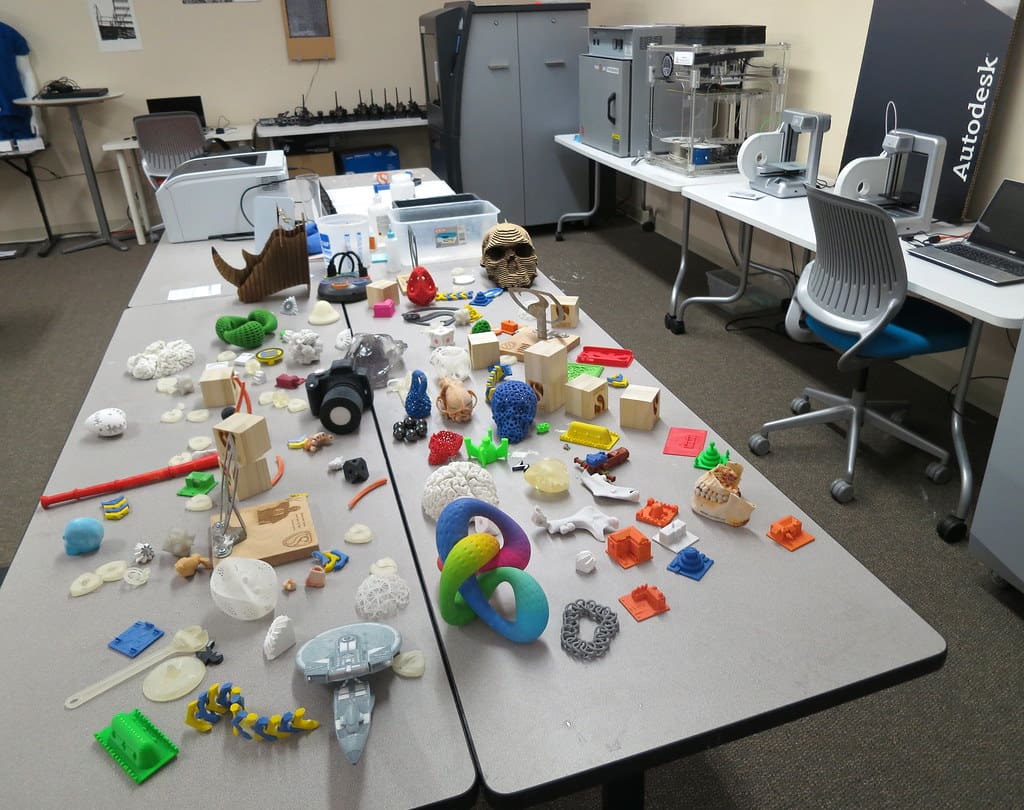

Challenges and Considerations
Despite its benefits, the adoption of 3D printing in education faces several challenges:
Accessibility and Costs: The cost of 3D printers and the materials needed can be prohibitive for some schools, particularly those with limited budgets or in underprivileged areas.
Teacher Training and Curriculum Integration: Effective integration of 3D printing into the curriculum requires teachers to be well-versed in the technology. Adequate professional development and support are crucial to empower educators to utilize 3D printing effectively.
Future Trends in 3D Printing for Education
Looking ahead, the role of 3D printing in education is poised for significant expansion:
Expansion of Use: As the technology becomes more accessible and costs decrease, more schools around the world are expected to incorporate 3D printing into their classrooms.
Advancements in Technology: Ongoing advancements in 3D printing technology will likely introduce more user-friendly printers suitable for educational purposes, enhancing their usability and functionality.
Custom Learning Materials: Future developments may include the ability to produce customized learning materials that adapt to individual learning styles and needs, further personalizing education.
3D printing offers a powerful means of enhancing educational experiences, providing students with valuable opportunities to engage directly with the materials they study. As this technology continues to evolve, its potential to transform classrooms and inspire the next generation of thinkers and innovators is immense. Educators and institutions should consider embracing 3D printing not just as a tool for teaching but as an essential component of modern education.