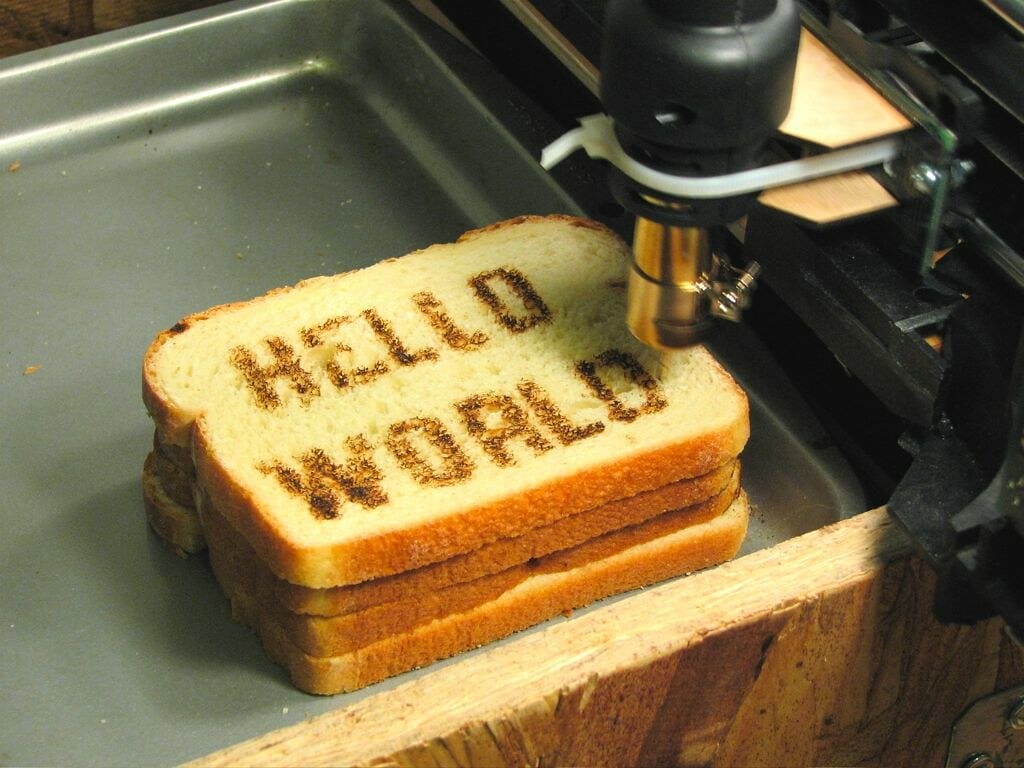
3D printing, a technology once primarily associated with manufacturing and industrial design, is now making its mark on the food industry. This emerging culinary trend is redefining the possibilities of food preparation, allowing for unprecedented customization, intricate design, and efficient use of resources. From high-end restaurants to home kitchens, 3D printing is poised to transform how we think about and prepare food.
Advantages of 3D Printing in Food Production
3D printing offers several compelling advantages in the culinary world:
Customization: One of the most significant benefits of 3D food printing is the ability to customize dishes to individual preferences and dietary needs. Whether adjusting flavors, textures, or nutritional content, 3D printing enables a level of personalization that is difficult to achieve with traditional cooking methods.
Efficiency and Sustainability: This technology can help reduce food waste by precisely using ingredients needed for each dish. Additionally, 3D printing allows for the exploration of alternative and sustainable food sources, such as proteins from insects or plants, which can be transformed into appealing and nutritious foods.
Innovation in Presentation: 3D printing enables chefs to create complex and intricate shapes and designs that were previously not possible or too labor-intensive to be feasible. This innovation opens up new avenues for artistic expression in the culinary arts.
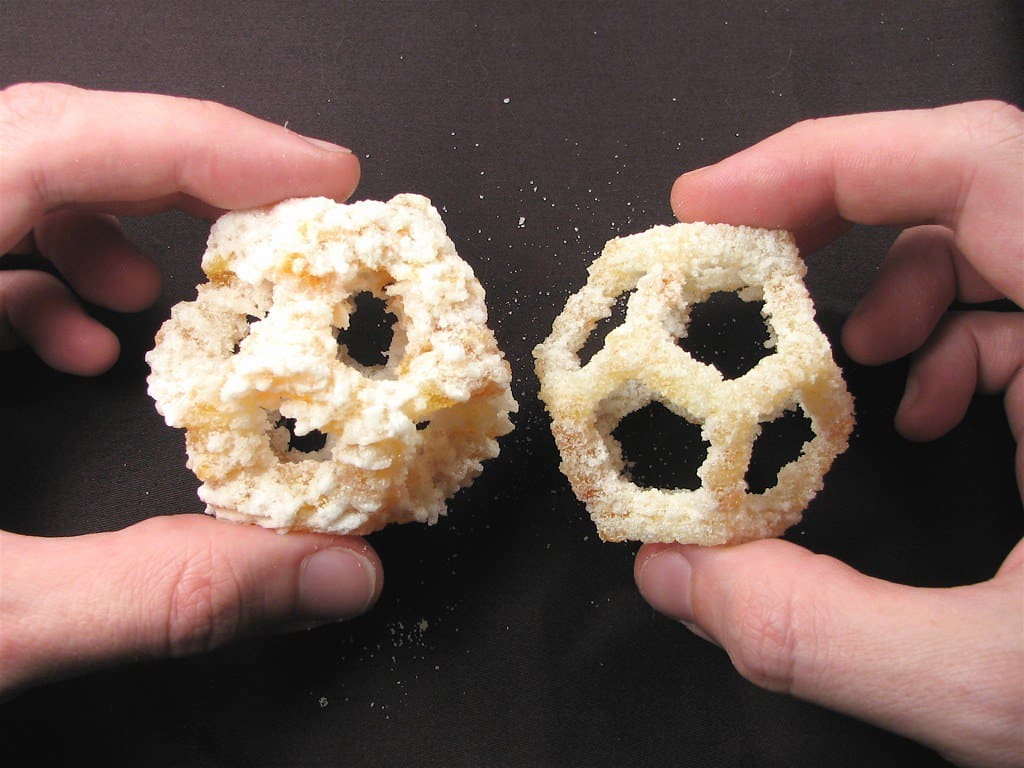
Key Applications of 3D Printing in the Food Industry
The applications of 3D printing in the food sector are diverse and growing:
Custom Dietary Foods: 3D printing is particularly advantageous for producing food that meets specific dietary restrictions, such as gluten-free, vegan, or nutritionally balanced meals for those with health conditions like diabetes.
High-End Restaurants and Culinary Art: In the realm of haute cuisine, chefs use 3D printers to craft dishes that combine complex flavors and shapes to enhance the dining experience. This technology is increasingly seen as a tool for innovation on par with molecular gastronomy.
Confectionery and Bakery Products: The precision of 3D printing is ideal for creating customized candies and chocolates, allowing confectioners to design elaborate and personalized sweets that are as beautiful as they are delicious.
Research and Development: Food scientists are leveraging 3D printing to experiment with new food textures and formulations, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in food science and manufacturing.
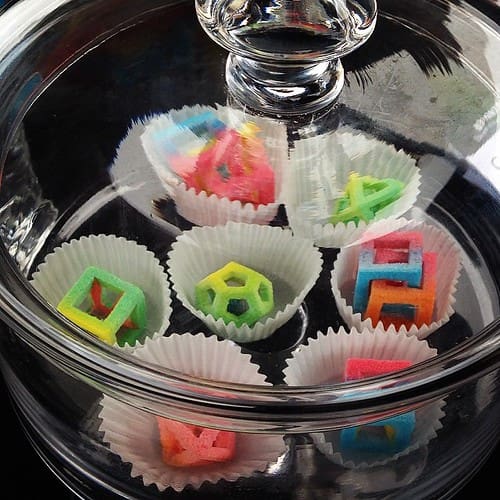
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its potential, 3D printing in the food industry faces several challenges:
Food Safety and Regulation: Ensuring that 3D-printed foods meet existing food safety standards is paramount. This includes using food-grade materials for the printers and ensuring that the printing process does not introduce any contaminants.
Technical Limitations: The current speed and scale of 3D food printers limit their application for large-scale production. Additionally, the texture and taste of printed food continue to be areas needing further development.
Consumer Acceptance: There is still some consumer skepticism regarding 3D-printed foods, particularly concerning their taste and the naturalness of heavily processed ingredients.
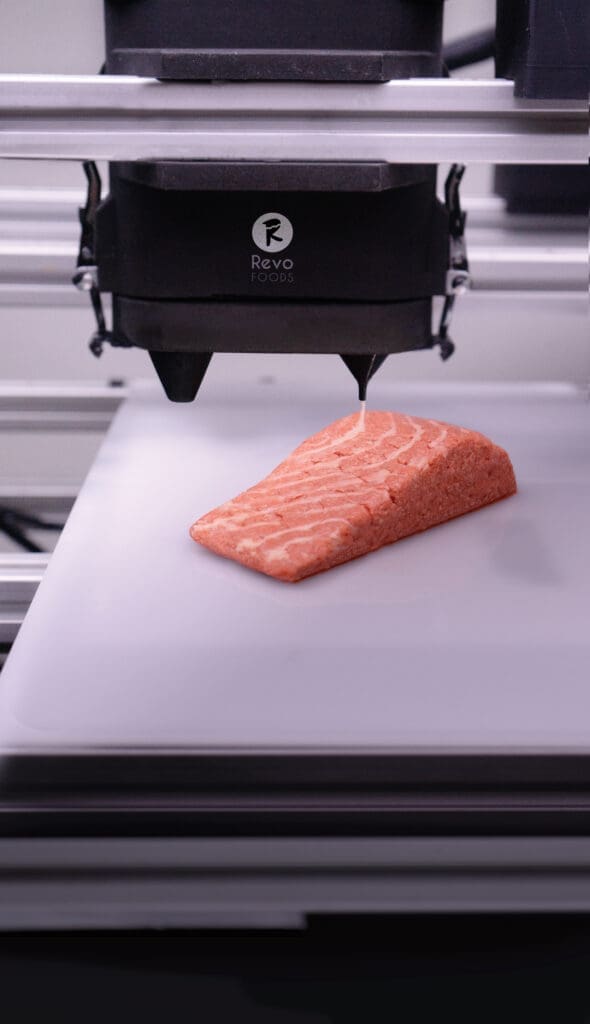

Future Trends in 3D Printing for the Food Industry
Looking ahead, 3D printing in the food industry is likely to see significant technological advancements:
Technological Improvements: Future innovations may increase the speed, efficiency, and variety of food that can be printed, making the technology more practical for both restaurants and home use.
Integration with Nutrition Science: As nutrition science advances, 3D printing could play a crucial role in creating highly customized diets based on individual nutritional needs, potentially revolutionizing health and wellness.
3D printing is set to transform the food industry by enabling more creative, sustainable, and personalized culinary practices. As the technology continues to evolve, it offers exciting possibilities for innovation in food design and production. For culinary professionals and enthusiasts alike, exploring 3D food printing could open up new realms of creativity and efficiency in the kitchen.