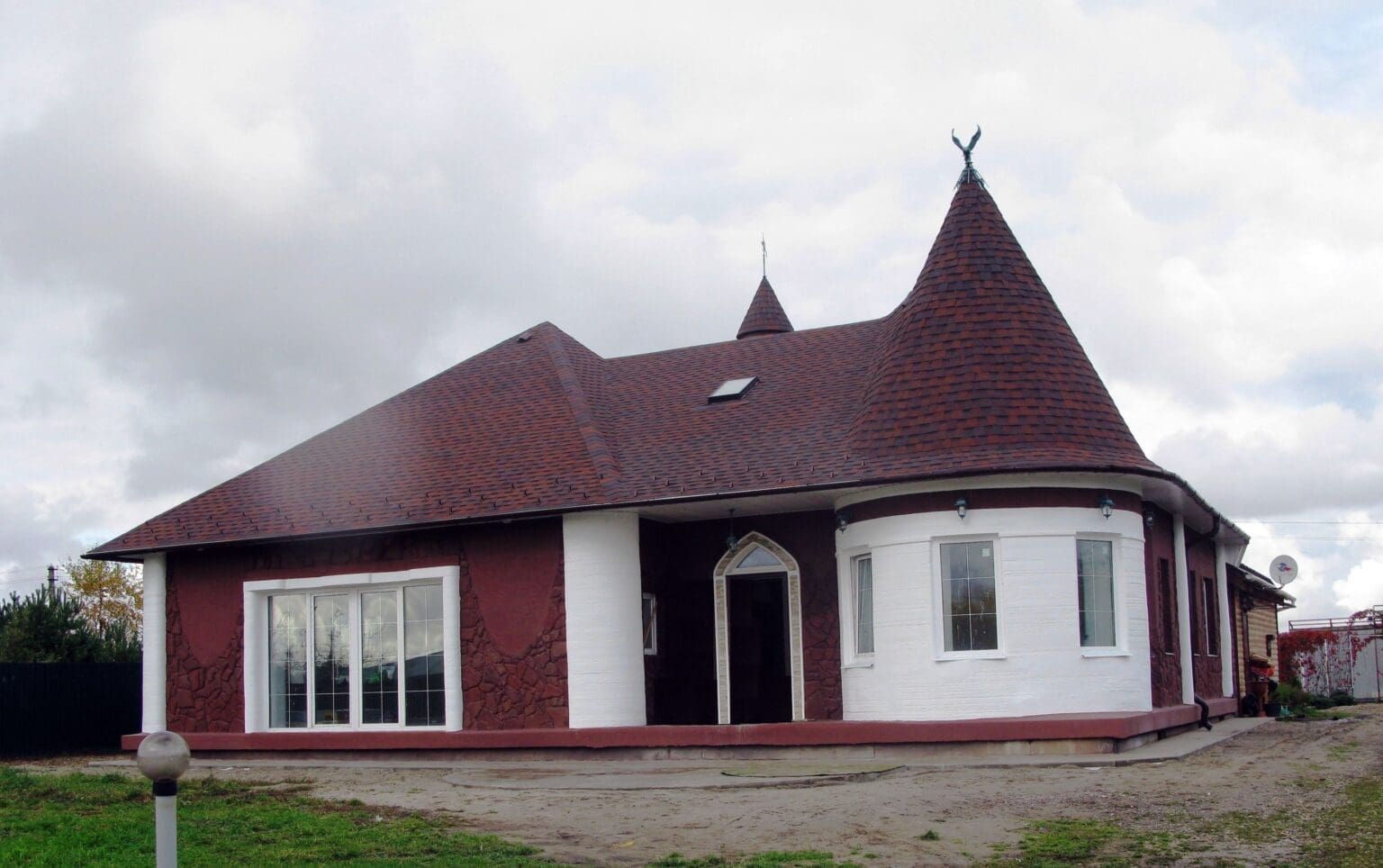
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is rapidly transforming the field of civil engineering. This revolutionary technology offers unprecedented capabilities in building complex, customized, and sustainable structures. By layering materials precisely and efficiently, 3D printing is not only changing the way buildings and infrastructure are constructed but also enhancing the creative possibilities within the civil engineering domain.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Civil Engineering
Initially utilized in the manufacturing and design industries for creating models and prototypes, 3D printing has found a significant application in civil engineering over the past decade. The ability to print large-scale structures directly from digital models has presented a new paradigm in construction, characterized by increased speed, reduced waste, and complex geometric possibilities. From bridges and houses to roads and tunnels, 3D printing is being explored for its potential to improve various aspects of construction.
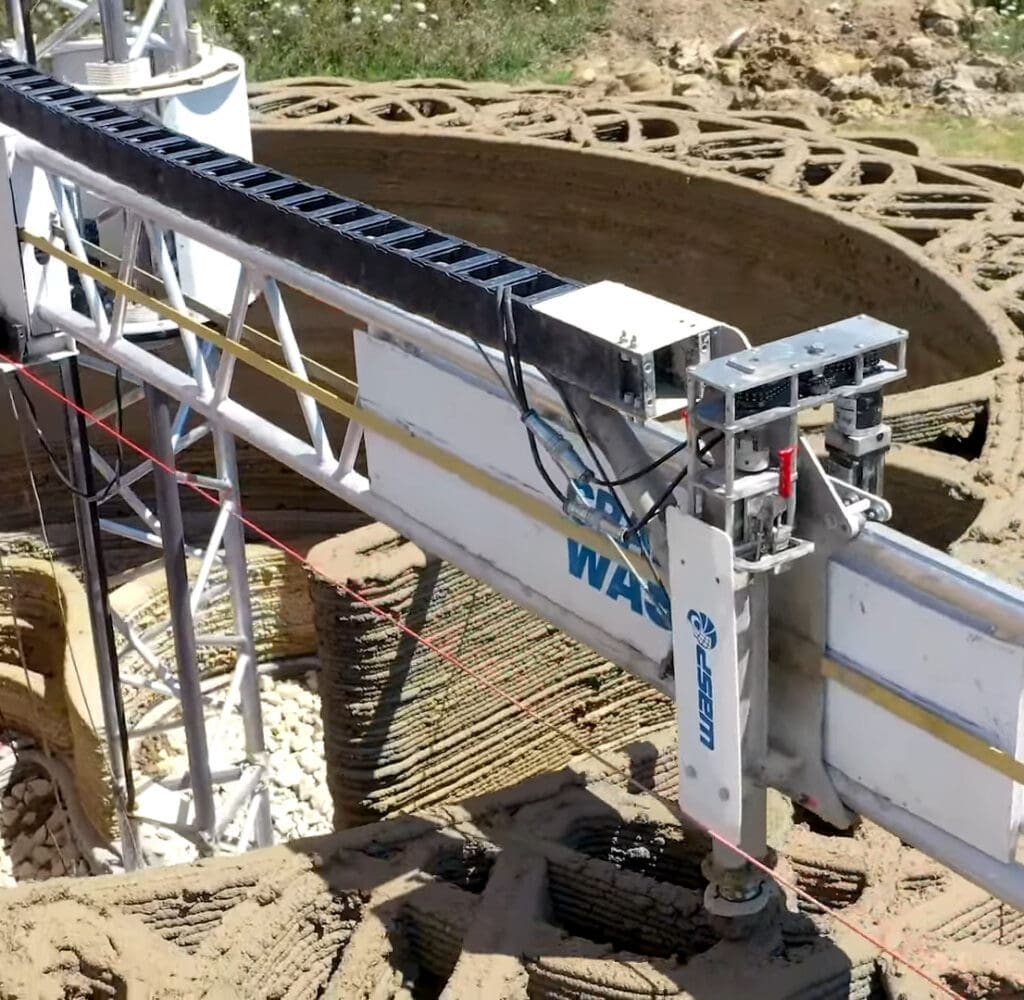

Advantages of 3D Printing in Civil Engineering
Efficiency and Speed: 3D printing significantly accelerates the construction process. Structures that traditionally take weeks or months to build can be completed in a fraction of the time. This rapid construction capability is particularly beneficial in urgent housing needs and disaster recovery scenarios.
Cost-Effectiveness: 3D printing reduces labor costs and material wastage. Traditional construction methods often lead to excess waste due to cut-offs and unused materials, whereas 3D printing uses only the material that is necessary to create the structure, layer by layer.
Design Flexibility: One of the most significant benefits of 3D printing in civil engineering is the ability to create complex designs that are difficult or impossible to achieve with conventional construction methods. This flexibility allows engineers and architects to innovate more freely and integrate complex features into their designs without significant additional costs.
Sustainability: 3D printing promotes sustainable construction practices by minimizing waste and potentially using eco-friendly materials. For instance, some 3D printers use recycled materials or local soil, reducing the environmental impact associated with construction.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Civil Engineering
Building and Housing: Residential buildings are one of the primary applications of 3D printing in civil engineering. Companies around the world are experimenting with 3D-printed homes that can be constructed quickly and cost-effectively, providing affordable housing solutions.
Infrastructure Projects: 3D printing is also used in larger-scale infrastructure projects, including bridges and tunnels. For example, the first 3D-printed concrete bridge was constructed in the Netherlands, showcasing the practical applications and durability of 3D-printed structures.
Custom Components and Repair: 3D printing enables the creation of bespoke components tailored to specific projects, such as unique architectural features or replacement parts for infrastructure repair. This capability is particularly useful in renovation projects where matching the original materials and designs can be challenging.
Disaster Relief and Temporary Structures: In disaster-stricken areas, the speed of 3D printing can play a critical role in providing quick relief. Temporary shelters, clinics, and other essential facilities can be constructed within days, offering immediate aid to affected communities.
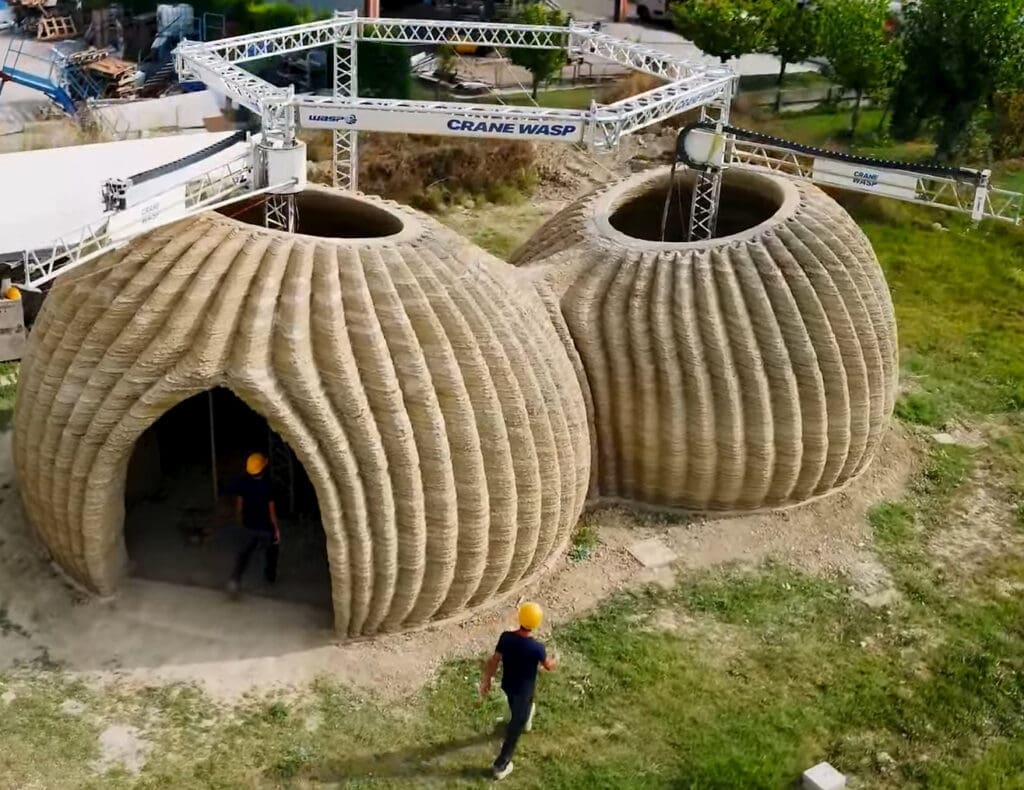

Challenges in 3D Printing for Civil Engineering
Despite its promising applications, 3D printing in civil engineering is not without challenges:
Material Limitations: Currently, most 3D printing in civil engineering uses concrete or similar materials, which may not have the same performance characteristics as traditional construction materials. Further research is needed to enhance the strength, durability, and weather resistance of 3D-printed materials.
Regulatory and Standards Compliance: Building codes and regulations are still catching up with the new technologies. Ensuring that 3D-printed buildings meet all safety and performance standards is crucial for their wider adoption.
Scale and Logistics: Scaling 3D printing technology for larger and more complex construction projects remains a technical and logistical challenge. Additionally, transporting the often large and heavy 3D printing equipment to construction sites can be challenging.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Civil Engineering
The future of 3D printing in civil engineering looks promising, with ongoing advancements in printer technology, materials science, and digital modeling. As the technology continues to mature, it is expected to become more integrated into mainstream construction practices, potentially becoming a standard method for certain types of building and repair work.
3D printing is set to revolutionize civil engineering by providing more efficient, sustainable, and innovative construction methods. As the technology evolves, it offers the potential to significantly alter how civil infrastructure is designed, built, and maintained. Embracing 3D printing in civil engineering not only enhances current construction practices but also paves the way for future advancements that could redefine the global construction industry.