In advanced 3D printing technologies, particularly those using Stereolithography (SLA) or Digital Light Processing (DLP), the optics system plays a crucial role. This system is responsible for directing and focusing light to cure photopolymer resins with high precision and accuracy. Understanding the components and functionality of the optics system can significantly enhance the efficiency and quality of 3D prints. This article explores the importance of the optics system in 3D printing, detailing its components, functions, and maintenance for optimal performance.
Importance of the Optics System in 3D Printing
Precision and Resolution: The optics system determines the fineness of detail and overall accuracy of the 3D printed objects by controlling the focus and intensity of the light source.
Speed of Printing: Effective light management can significantly impact the speed of the printing process. A well-optimized optics system ensures rapid and uniform curing of the resin, thus speeding up production.
Material Compatibility: Different photopolymer resins react differently to various wavelengths and intensities of light. The optics system must be adaptable to optimize the curing process for a wide range of materials.
Energy Efficiency: By focusing light precisely where it is needed, the optics system reduces waste and improves the energy efficiency of the printer, which is crucial for both environmental sustainability and operational cost reduction.
Components of the Optics System in 3D Printers
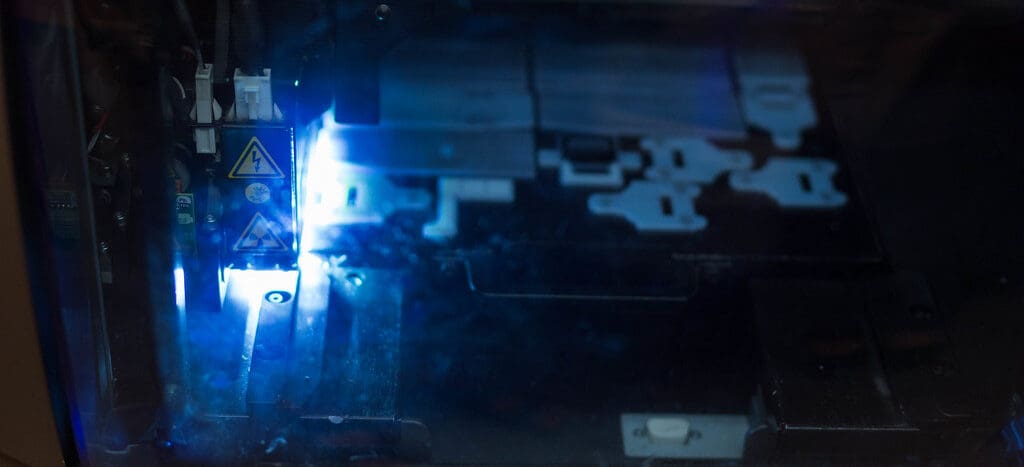
Light Source: The primary component, typically a UV laser in SLA printers or a UV LED array in DLP systems. The choice of light source affects the wavelength of light and, consequently, how the resin cures.
Mirrors and Lenses: These are used to direct and focus the light emitted from the source. In SLA printers, mirrors might be mounted on galvanometers that adjust the mirror angles to steer the laser beam across the build area.
Galvanometers: Used in SLA printers, these precision devices control the mirrors that direct the laser beam. They are crucial for the accurate and swift movement of the laser across the printing surface.
Condensing Lenses: These lenses collect and concentrate light towards a specific area, ensuring that the light is uniformly distributed and intense enough to cure the resin effectively.
Focusing Lenses: These are used to fine-tune the focus of the light on the resin surface, crucial for achieving the desired resolution and depth in the printed object.
Installation and Calibration of the Optics System
Proper Alignment: The alignment of lenses and mirrors is critical for the effective functioning of the optics system. Even minor misalignments can lead to defects in the printed objects.
Calibration: Regular calibration of the optics system, including the adjustment of galvanometers and the focus of the laser or light source, ensures that the system maintains its precision over time.
Cleanliness: The optical components must be kept clean from dust, resin splashes, and other contaminants that could scatter or block the light, leading to print errors.
Maintenance and Optimization of the Optics System
Regular Cleaning: Use lens wipes and appropriate cleaning solutions to keep optical components free of debris. This maintenance is crucial for maintaining clarity and light transmission efficiency.
Component Inspection: Routine inspections can help identify wear and tear on lenses or degradation of mirrors and galvanometers, which might necessitate adjustments or replacements to maintain print quality.
Environmental Considerations: The optics system should be protected from environmental factors such as excessive humidity, which can affect the components’ performance and longevity.
Firmware Updates: Keeping the printer’s firmware up-to-date can ensure that the optics system is operating with the latest software corrections and improvements, which might include better motion control algorithms for the galvanometers.
Challenges and Solutions
Thermal Management: High-powered lasers and LEDs can generate significant heat, which might affect the optics system’s performance. Implementing active cooling systems or heat sinks can mitigate these effects.
Light Intensity Management: Over time, the intensity of lasers and LEDs can diminish, which might affect the curing process. Regularly testing and adjusting the output settings can compensate for these changes.
Wear and Tear: Optical components, especially moving parts like galvanometers, are subject to wear. Setting up regular maintenance schedules can help in early detection and replacement of worn-out parts.
The optics system in 3D printers is a sophisticated assembly that requires careful management to ensure optimal performance. It is instrumental in defining the capabilities and limitations of SLA and DLP 3D printing technologies, directly impacting print quality, speed, and material handling. By understanding and maintaining the optics system, users can significantly enhance their printing processes, resulting in precise, high-quality 3D printed products.