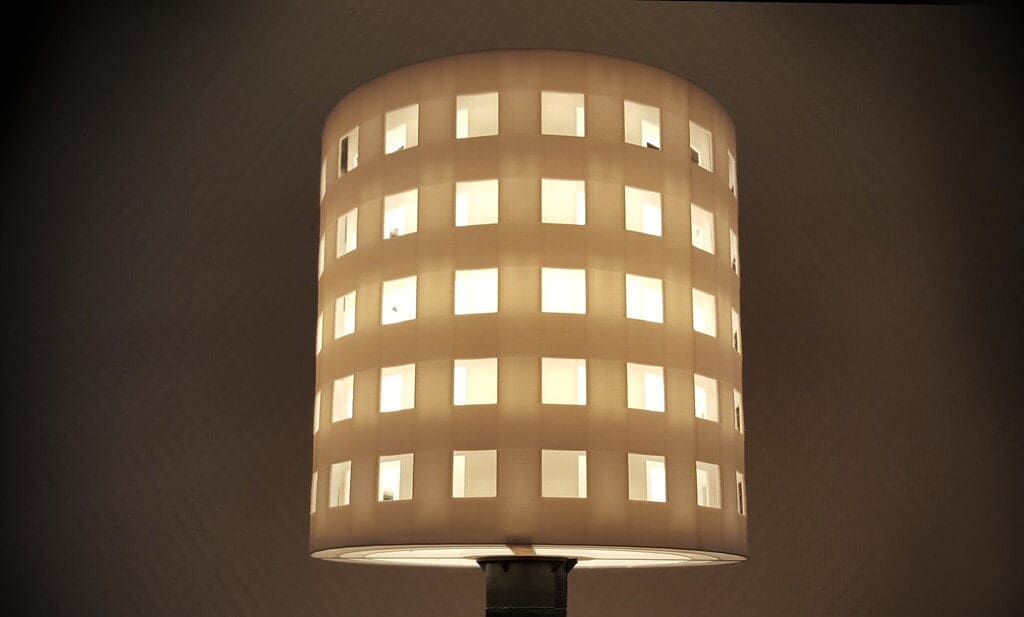
Lighting design plays a crucial role in both the aesthetics and functionality of spaces, impacting ambiance, visibility, and even emotional well-being. The advent of 3D printing technology has revolutionized the field of lighting design, offering unprecedented flexibility and creativity in the production of lighting fixtures. This technology allows designers to experiment with complex forms and tailor solutions to specific environments, enhancing both the efficiency and artistic expression of lighting installations.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Lighting Design
Initially utilized for prototyping, 3D printing has evolved into a key manufacturing process for end-use products, including lighting fixtures. Its ability to create detailed, complex shapes at a reduced cost and time has captured the attention of lighting designers and manufacturers. With advancements in materials and printing technology, 3D printing now enables the production of bespoke lighting designs that align with modern aesthetic and functional demands.
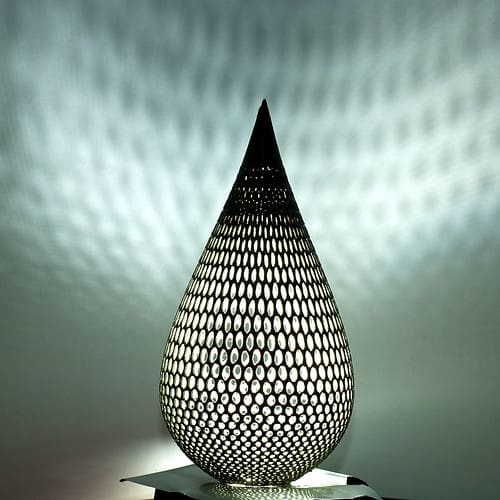

Advantages of 3D Printing in Lighting Design
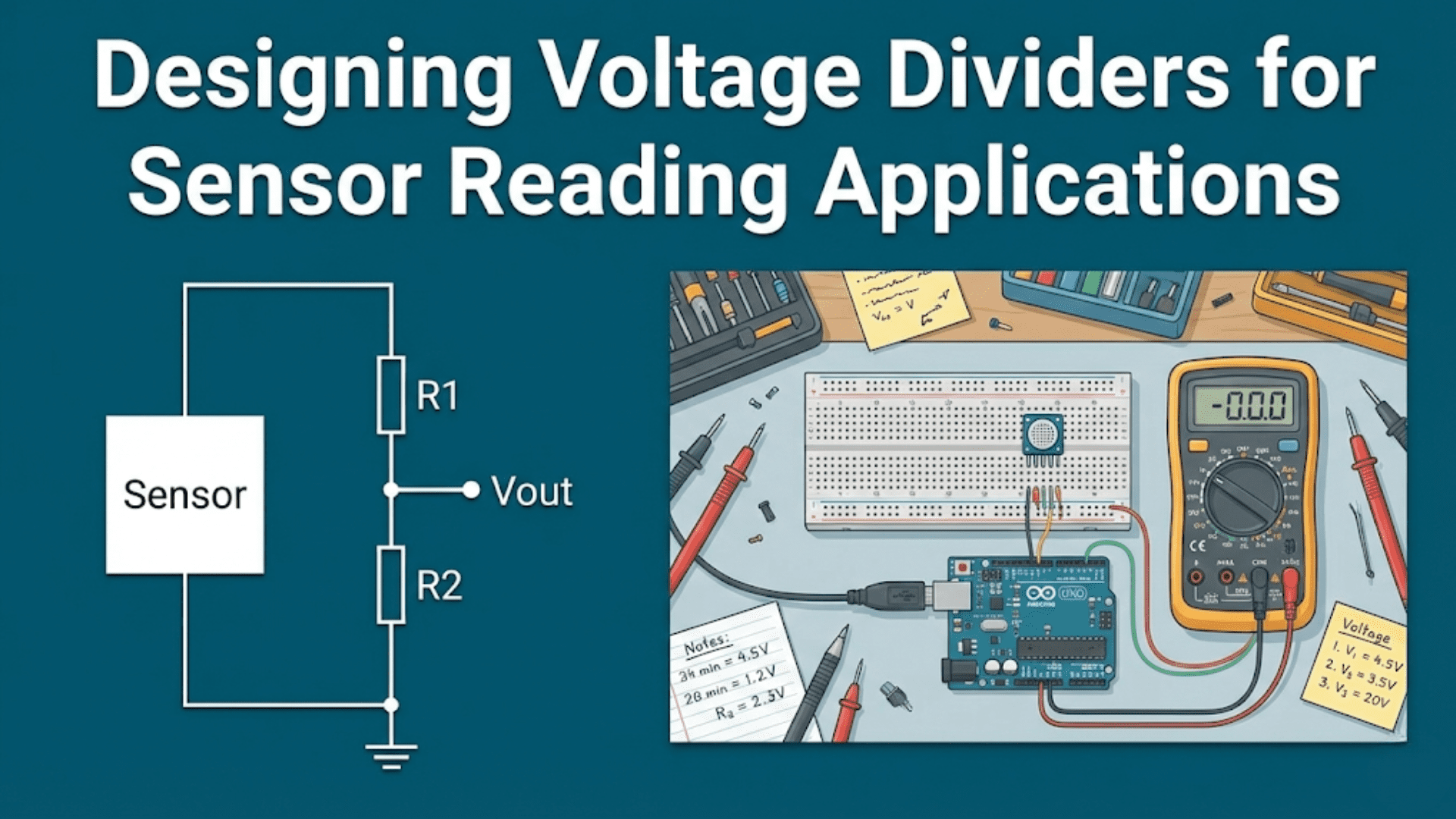
Complex Geometries and Customization: 3D printing excels in producing intricate designs that traditional manufacturing methods struggle to achieve. Designers can create unique, complex shapes that enhance light diffusion and aesthetic appeal, tailored to the specific needs of a space.
Rapid Prototyping and Iteration: Designers can quickly produce prototypes to test and refine their ideas, significantly accelerating the design process. This rapid prototyping allows for immediate feedback and continuous improvement, ensuring that the final product perfectly aligns with client expectations.
Cost-Effectiveness: 3D printing reduces the need for expensive molds and tooling, lowering the barrier to entry for creating custom designs. It enables cost-effective small production runs and even single-piece manufacturing, making it ideal for bespoke projects or limited edition pieces.
Material Innovation: With a wide range of printable materials available, including plastics that diffuse light in desirable ways and metals for durable fixtures, designers can select properties specific to their lighting needs. Advances in materials also include the integration of conductive materials for seamless electrical setups.
Sustainability: 3D printing promotes sustainability by minimizing waste through additive processes and enabling the use of recycled or biodegradable materials. This aspect is particularly appealing in the context of growing environmental concerns within the design and manufacturing industries.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Lighting Design
Residential Lighting: In home decor, 3D printed lamps and fixtures can be customized to fit the style and lighting needs of any room, from intricate bedside lamps to large, sculptural ceiling fixtures that serve as the focal point of a living space.
Commercial Lighting: For commercial spaces like hotels, restaurants, and offices, 3D printing allows for the creation of uniform lighting solutions that are both functional and thematic. Customizable options help reinforce brand identity through unique designs that cannot be found elsewhere.
Outdoor Lighting: Durable materials developed for 3D printing can withstand environmental factors, making them suitable for outdoor lighting applications. Customizable designs can blend seamlessly with architectural elements or landscape features.
Art Installations and Sculptural Lighting: Artists and designers use 3D printing to merge lighting with art, creating sculptural pieces that illuminate spaces while providing visual interest. These installations often become centerpieces in galleries, lobbies, and public spaces.
Medical and Specialty Lighting: In fields requiring specialized lighting solutions, such as medical facilities or industrial settings, 3D printing can produce fixtures designed to meet precise specifications for light intensity, direction, and color.
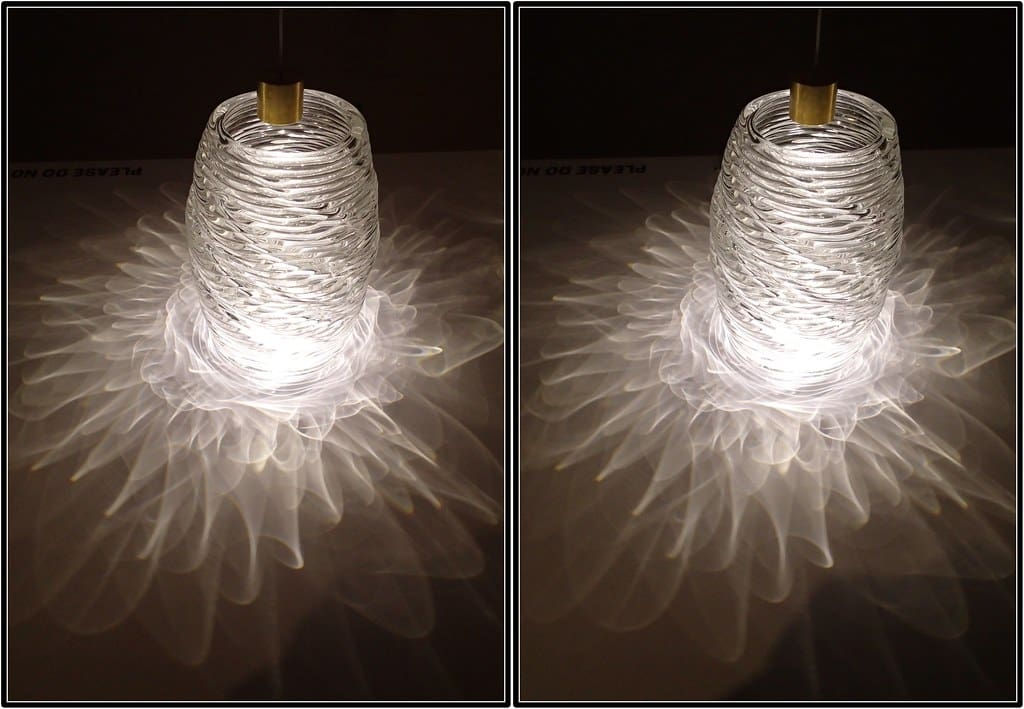

Challenges in 3D Printing for Lighting Design
Technical Limitations: While 3D printing offers remarkable design flexibility, there are limitations regarding size and material properties, which can affect the feasibility of certain designs.
Quality and Consistency: Ensuring consistency and high quality in finished products can be challenging, particularly when scaling up production from prototypes to full production runs.
Light Performance Optimization: Balancing aesthetic design with optimal light performance requires careful planning and testing. The material and structure of the print must effectively support light diffusion and emission without compromising design integrity.
Regulatory and Safety Standards: Adhering to electrical safety and building codes is crucial when designing lighting fixtures. Ensuring that 3D printed products meet these standards can sometimes be complex due to the novel materials and techniques involved.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Lighting Design
As 3D printing technology continues to advance, its applications in lighting design are expected to broaden. Future developments may include enhanced material properties, greater printing precision, and more sustainable practices. Additionally, the integration of smart lighting technology into 3D printed fixtures could open up new possibilities for interactive and adaptive lighting systems.
3D printing is reshaping the landscape of lighting design, providing designers with the tools to create innovative and personalized lighting solutions. This technology not only enhances the aesthetic and functional aspects of lighting but also aligns with the sustainability goals of modern design practices. As 3D printing continues to evolve, it promises to further illuminate the possibilities within the lighting industry, driving forward a new era of design excellence and innovation.