Sustainable environment design focuses on creating spaces and structures that minimize environmental impact while promoting efficiency and well-being. As global awareness of sustainability grows, the need for innovative approaches in design and construction becomes increasingly urgent. 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, has emerged as a powerful tool in this endeavor, offering significant advantages in terms of material usage, energy efficiency, and waste reduction. By integrating 3D printing into sustainable design practices, architects and engineers can not only enhance the environmental friendliness of their projects but also push the boundaries of architectural creativity.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Sustainable Environment Design
Initially used for prototyping in various industries, 3D printing has rapidly evolved to include applications in large-scale construction and design. Its ability to precisely deposit materials layer by layer allows for minimal waste production—a key advantage in sustainable construction. Furthermore, the flexibility of 3D printing enables the use of a variety of eco-friendly materials, including recycled plastics and composites, which are essential for reducing the carbon footprint of building projects.
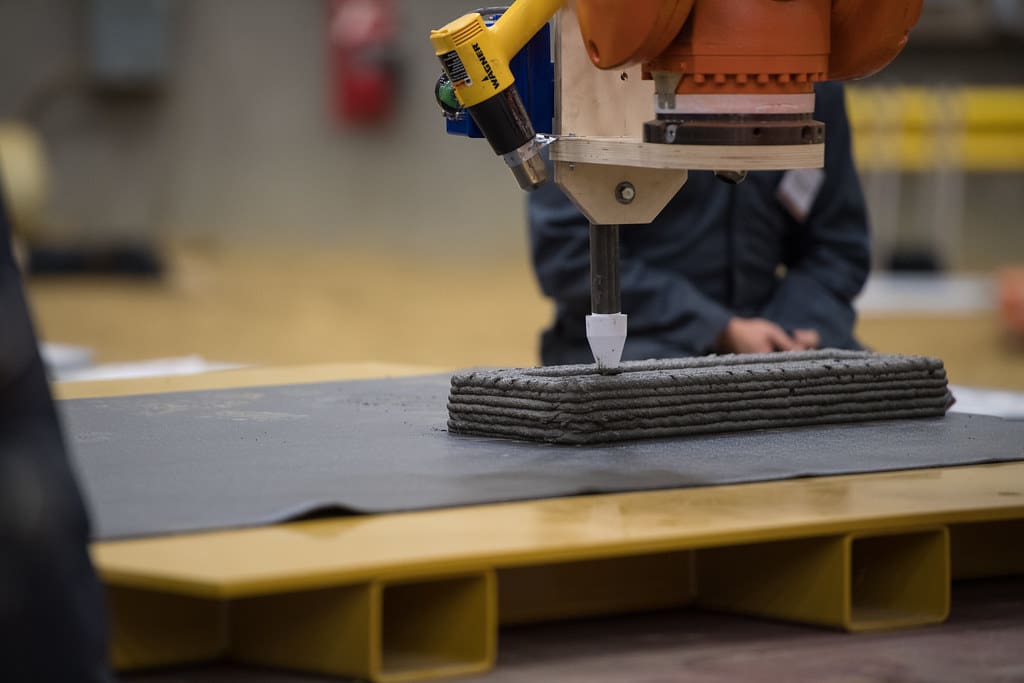

Advantages of 3D Printing in Sustainable Environment Design
Efficient Use of Materials: 3D printing dramatically reduces waste by using only the amount of material necessary to create a structure. This precise material usage is crucial for sustainability, as it minimizes the environmental impact associated with resource extraction and processing.
Enhanced Design Flexibility: Additive manufacturing allows for the creation of complex, organic shapes that can optimize natural light and air flow, reducing the need for artificial lighting and climate control. This not only enhances the energy efficiency of buildings but also contributes to more aesthetically pleasing and functional designs.
Reduction in Construction Waste: Traditional construction methods often result in significant waste due to cut-offs, overruns, and materials damaged on-site. 3D printing minimizes this waste, contributing to more sustainable construction practices.
Use of Renewable and Recycled Materials: 3D printers can utilize a range of sustainable materials, including recycled plastics, biodegradable composites, and even organic materials like wood cellulose. This capability supports the recycling economy and reduces the reliance on non-renewable resources.
Energy Efficiency: The production and transportation of building materials are major sources of energy consumption in the construction industry. 3D printing often allows for local production of materials and parts, significantly reducing the energy spent on transportation and manufacturing.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Sustainable Environment Design
Eco-Friendly Housing: 3D printing is used to construct homes that are specifically designed to minimize environmental impact. These houses often feature sustainable materials and designs that optimize energy use, such as strategic window placement for natural lighting and insulation techniques to reduce heating and cooling needs.
Green Infrastructure: Additive manufacturing facilitates the creation of green roofs, walls, and other sustainable infrastructure elements. These features not only enhance the energy efficiency of buildings but also contribute to urban biodiversity and air quality improvement.
Customized Water Management Solutions: 3D printing allows for the design of customized solutions for rainwater harvesting and efficient water management systems. These systems can be seamlessly integrated into the architecture of a building, enhancing its sustainability.
Innovative Public Spaces: Urban furniture, park elements, and public installations designed with 3D printing can include integrated solar panels, LED lighting, and other sustainable technologies. This promotes energy self-sufficiency and reduces the carbon footprint of public areas.
Disaster-Resilient Structures: In regions prone to natural disasters, 3D printing can be used to quickly construct resilient and sustainable shelters. These structures are designed to be both eco-friendly and capable of withstanding extreme weather conditions, providing safe housing solutions in emergency situations.

Challenges in 3D Printing for Sustainable Environment Design
Material Durability and Performance: Ensuring that 3D printed materials can meet the long-term durability and performance standards required for sustainable construction is essential. Ongoing research and development are needed to address these concerns.
Scale and Accessibility: Scaling 3D printing for large projects and making the technology accessible to all regions, including developing countries, remain significant challenges.
Regulatory and Standards Compliance: As 3D printing in construction is still relatively new, regulatory frameworks and building standards are evolving. Ensuring compliance with these standards is crucial for the widespread adoption of 3D printing in sustainable environment design.
Technical Expertise: Proficient use of 3D printing technology requires specialized knowledge and skills, which can be a barrier to its integration into traditional construction and design practices.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Sustainable Environment Design
The future of 3D printing in sustainable environment design is promising, with potential advancements in technology, materials, and methods expected to further enhance its applications. Innovations could include more robust and versatile printers, development of new sustainable materials, and improved integration techniques that combine traditional building methods with additive manufacturing.
3D printing is poised to play a transformative role in sustainable environment design, offering a more efficient, flexible, and environmentally friendly approach to construction. As the technology continues to evolve, it promises to further empower architects and designers to innovate while adhering to the principles of sustainability. This alignment of technology and environmental stewardship heralds a new era in building design, where ecological responsibility and architectural creativity go hand in hand.