Health and safety engineering is a critical discipline focused on designing systems and processes to protect people from illness and injury in the workplace and beyond. As industries strive to improve safety standards and reduce risks, 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, emerges as a powerful tool in this field. This technology offers innovative solutions for creating personalized protective equipment, ergonomic tools, and safety devices, significantly enhancing the effectiveness of health and safety measures in various environments.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Health and Safety Engineering
Initially used for prototyping in manufacturing and design industries, 3D printing has evolved to include the production of functional, durable safety equipment tailored to specific tasks and environments. Advances in 3D printing technologies and materials have expanded its application in health and safety engineering, allowing for the precise fabrication of items that meet rigorous safety standards and fit individual user specifications.
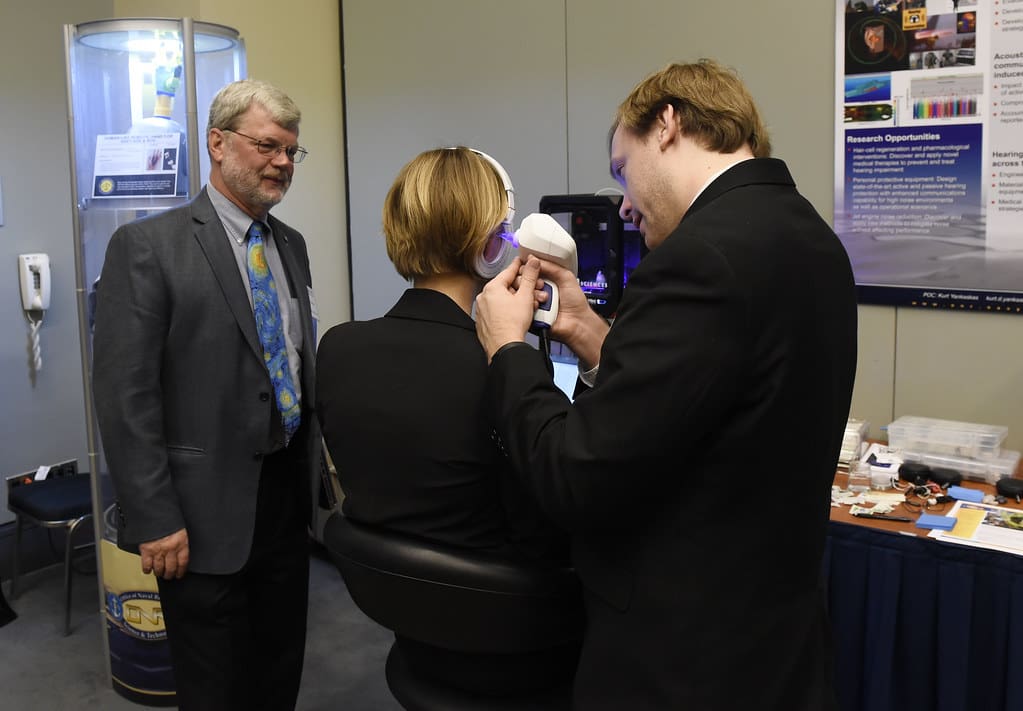

Advantages of 3D Printing in Health and Safety Engineering
Customization and Personalization: 3D printing excels at producing customized safety gear tailored to the individual’s body measurements and specific job requirements. This customization improves comfort, increases wearability, and enhances protection.
Rapid Prototyping and Iterative Design: The ability to quickly prototype safety devices allows for rapid testing and refinement, ensuring that products are both effective and user-friendly. This is crucial in developing solutions that address emerging risks and evolving workplace conditions.
Material Efficiency: Additive manufacturing reduces material waste by using only the necessary materials to build a part, aligning with sustainability goals and reducing the environmental impact of production processes.
Innovative Solutions for Complex Problems: 3D printing enables the creation of complex, multifunctional safety devices that combine various features and materials to address multiple safety concerns simultaneously.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Health and Safety Engineering
Protective Gear: Helmets, gloves, ear protection, and respirators can be 3D printed to match the contours of the user’s face, head, or hands, providing superior protection and comfort. This gear often incorporates advanced features such as improved airflow, lightweight materials, and enhanced durability.
Ergonomic Workplace Tools: Customized handles, grips, and other tools that conform to an individual’s hand reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders. 3D printing allows for ergonomic designs that are specifically tailored to reduce fatigue and increase productivity.
Safety Signage and Components: Quick production of safety signage, barrier systems, and emergency response components can be achieved with 3D printing, allowing for rapid deployment in dynamic work environments.
Simulated Safety Training Models: Detailed models of machinery, hazardous materials, and complex scenarios can be 3D printed to enhance safety training. These models help provide hands-on training experiences without the risks associated with real-life exposure.
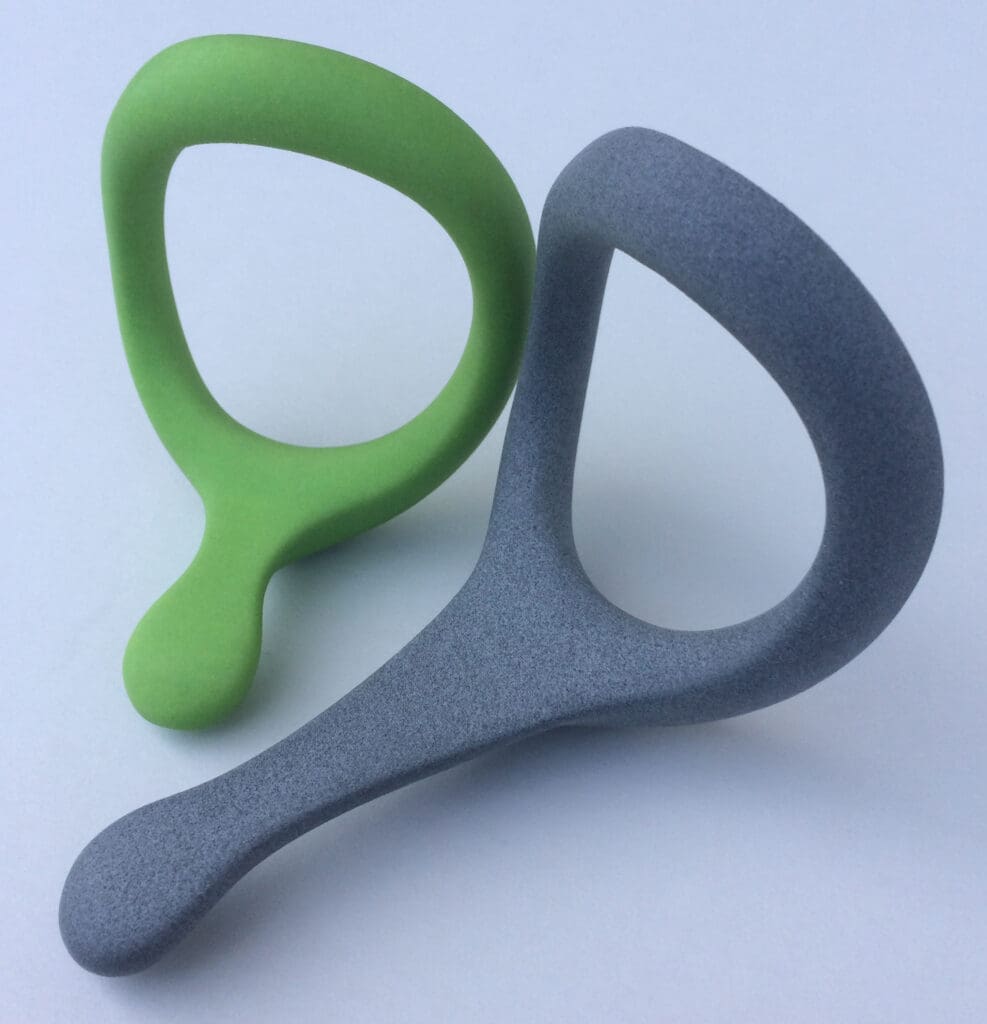

Challenges in 3D Printing for Health and Safety Engineering
Despite its benefits, several challenges remain in fully integrating 3D printing into health and safety engineering:
Material Performance: Ensuring that 3D-printed materials meet all safety standards and perform reliably under extreme conditions is crucial. Ongoing research is required to develop materials that are both durable and capable of providing the necessary protection.
Regulatory and Standard Compliance: Health and safety products must adhere to strict regulations and standards. Achieving certification for 3D-printed safety equipment can be complex and time-consuming, involving rigorous testing and quality control.
Cost and Accessibility: While the cost of 3D printing technology has decreased, the price barrier remains for widespread adoption, particularly in small and medium enterprises. Reducing the cost of 3D printers and materials is essential for broader utilization.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Health and Safety Engineering
The future of 3D printing in health and safety engineering looks promising, with ongoing advancements likely to address current limitations. Innovations in printer technology, materials science, and collaborative design platforms are expected to enhance the applications of 3D printing, making it a standard tool in safety engineering practices.
3D printing is poised to continue its transformative impact on health and safety engineering, offering innovative solutions that improve personal protection and workplace safety. As the technology evolves, it promises to redefine how safety equipment is designed and produced, leading to more effective and personalized solutions that better protect workers and the public.