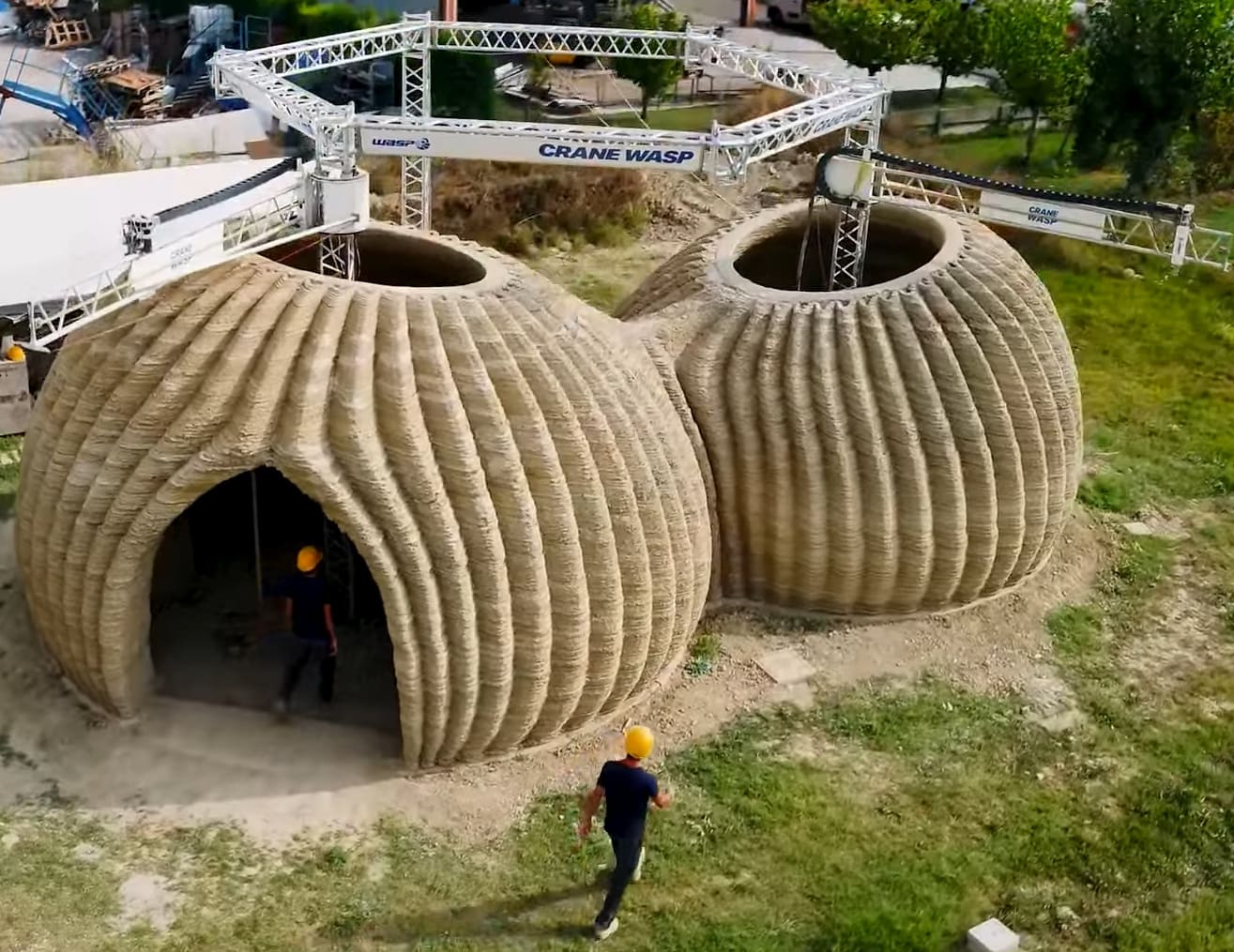
3D printing is making significant inroads into the construction industry, heralding a new era in how structures are designed, built, and maintained. This technology, also known as additive manufacturing, allows for the layer-by-layer construction of buildings, offering a paradigm shift in construction efficiency, design flexibility, and waste reduction. As the industry faces increasing pressure to find more sustainable and cost-effective building solutions, 3D printing emerges as a pivotal technology.
Advantages of 3D Printing in Construction
The adoption of 3D printing in construction brings numerous advantages:
Efficiency and Speed: 3D printing significantly speeds up the construction process. Structures that traditionally took months to build can now be completed in a fraction of the time. This rapid construction capability is particularly advantageous in urgent housing needs and disaster recovery scenarios.
Cost Reduction: By automating parts of the construction process, 3D printing reduces the need for manual labor, which can significantly cut down labor costs. Additionally, the precision of 3D printing minimizes waste during the building process, further reducing overall project costs.
Design Flexibility: 3D printing allows architects and designers to experiment with complex, innovative designs that would be difficult or impossible to execute with traditional construction methods. This flexibility opens up new possibilities in architectural aesthetics and functionality.
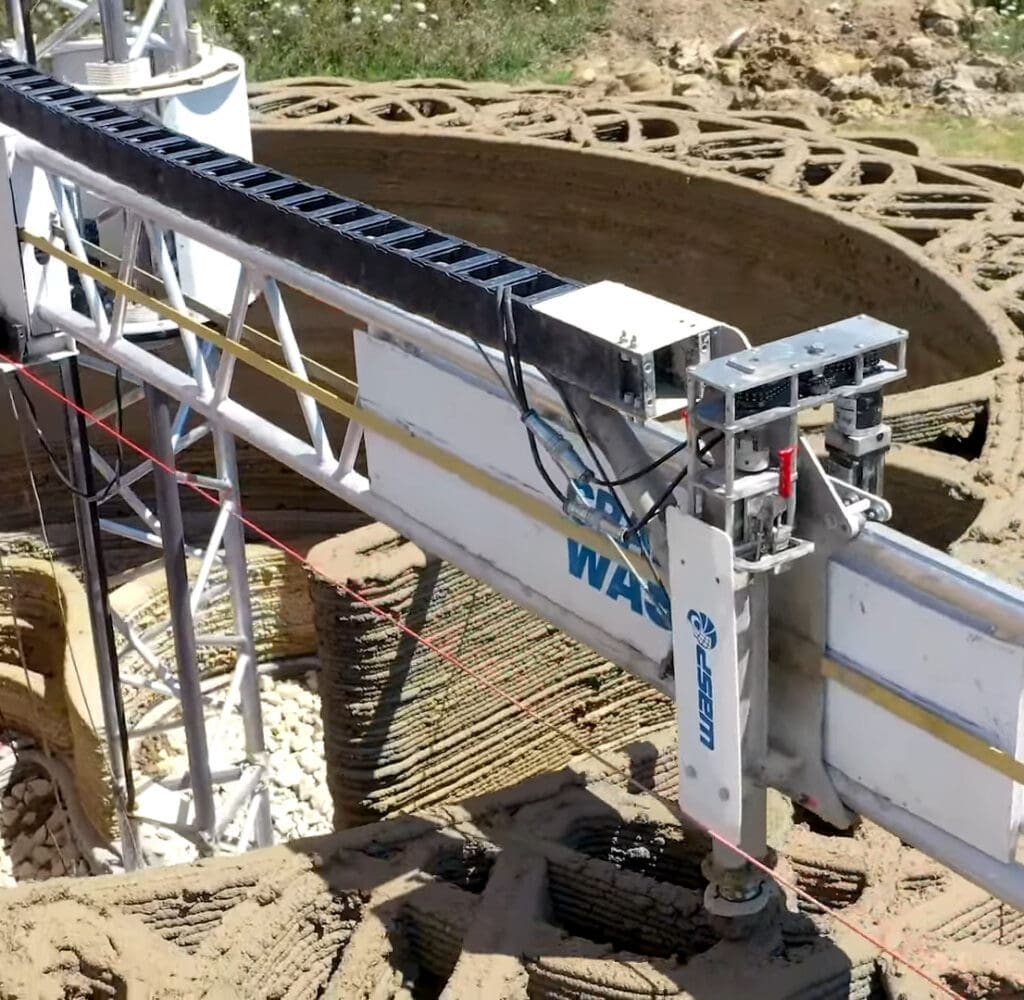

Key Applications of 3D Printing in Construction
3D printing is applied in various facets of the construction industry:
Building Structures: Around the world, there are increasing instances of residential and commercial buildings being constructed with 3D printing. These buildings often feature designs that maximize the technology’s ability to create intricate, durable structures quickly.
Infrastructure Projects: Significant infrastructure projects, such as bridges and overpasses, have utilized 3D printing for key components. These applications demonstrate not only the feasibility but also the durability and strength of 3D-printed construction elements.
Custom Components and Ornamentation: 3D printing excels in producing bespoke architectural details and building components. This capability allows for personalized and unique design elements that can be tailored to specific projects without substantial cost increases.
Emergency and Low-Cost Housing: In response to natural disasters or housing crises, 3D printing can provide quick, affordable, and durable housing solutions. This rapid deployment capability is crucial in alleviating immediate shelter needs in affected regions.
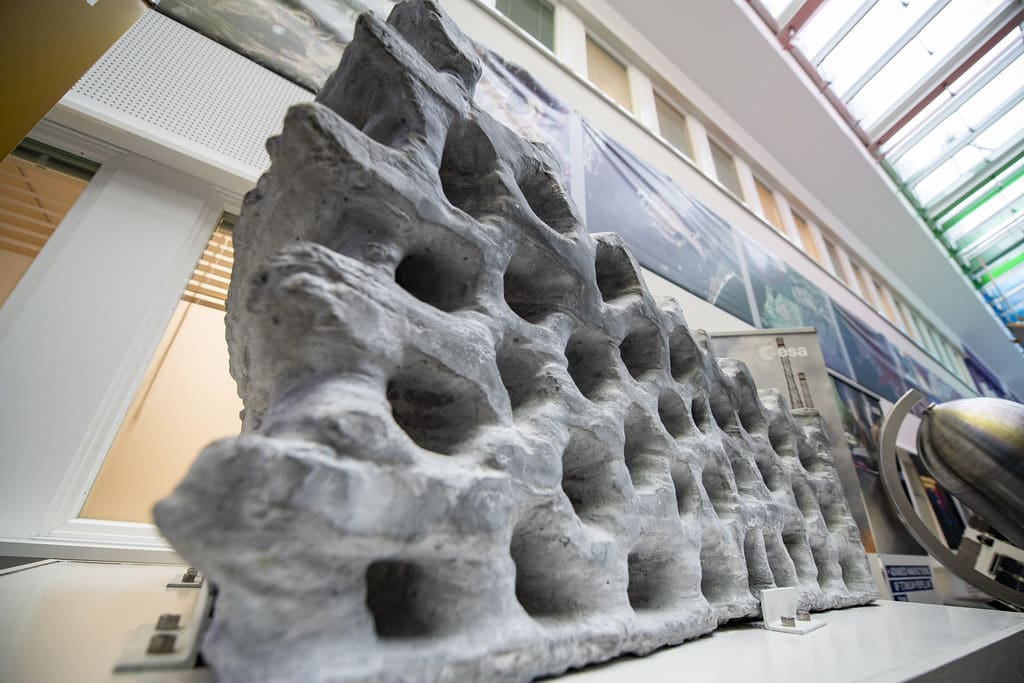

Challenges and Considerations
Despite its potential, 3D printing in construction faces several challenges:
Material Limitations: The range of materials suitable for 3D printing is currently somewhat limited, primarily to certain types of concrete and polymers, which may not meet all construction requirements or preferences.
Regulatory Hurdles: Building codes and regulations are often not adapted to new technologies like 3D printing, creating hurdles in widespread adoption and integration.
Technological Barriers: Scaling 3D printing for larger, more complex projects remains a technological challenge. The size of 3D printers and the integration of the technology into traditional construction processes require ongoing development and investment.
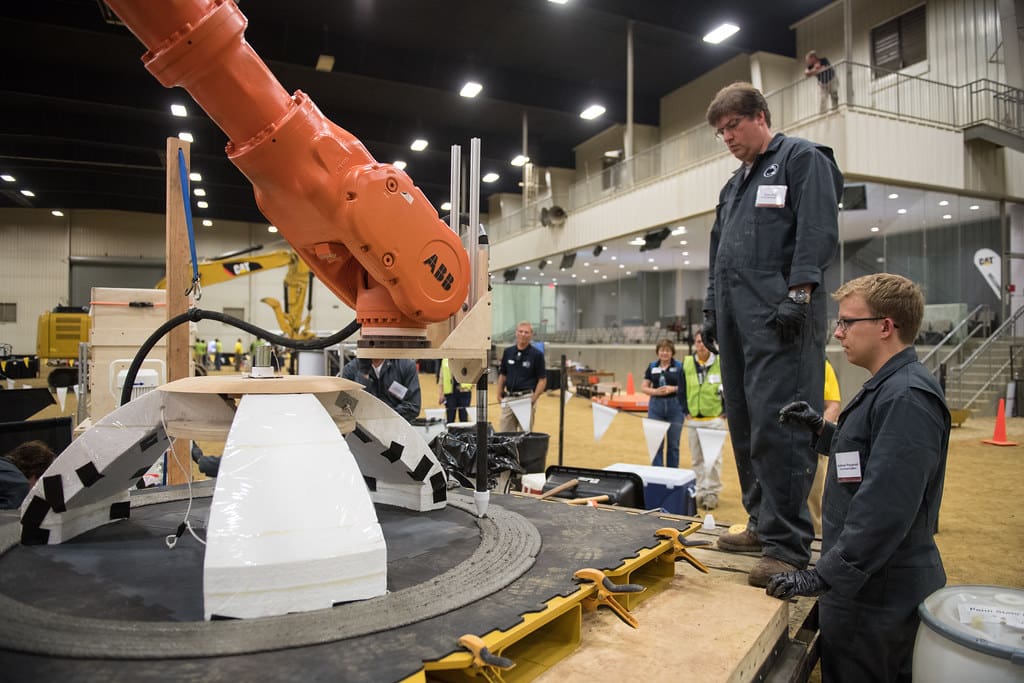

Future Trends in 3D Printing for Construction
Looking ahead, the future of 3D printing in construction is promising, with several key trends on the horizon:
Material Innovations: Advances in materials science are expected to broaden the range of substances available for 3D printing, including enhanced concrete formulations and composite materials that offer greater durability and environmental benefits.
Integration with Building Information Modeling (BIM): Combining 3D printing with BIM technology promises to enhance the precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of construction projects, from initial design through to completion.
Sustainability Impact: As the construction industry seeks more sustainable practices, 3D printing offers a compelling path forward by minimizing waste and potentially using recycled materials.
3D printing is poised to revolutionize the construction industry by offering faster, cost-effective, and more flexible building solutions. As the technology continues to evolve, it will likely become an integral part of the construction landscape, driving innovation and sustainability. Stakeholders in the construction sector are encouraged to explore and integrate 3D printing technologies to remain competitive and address the changing needs of the market.