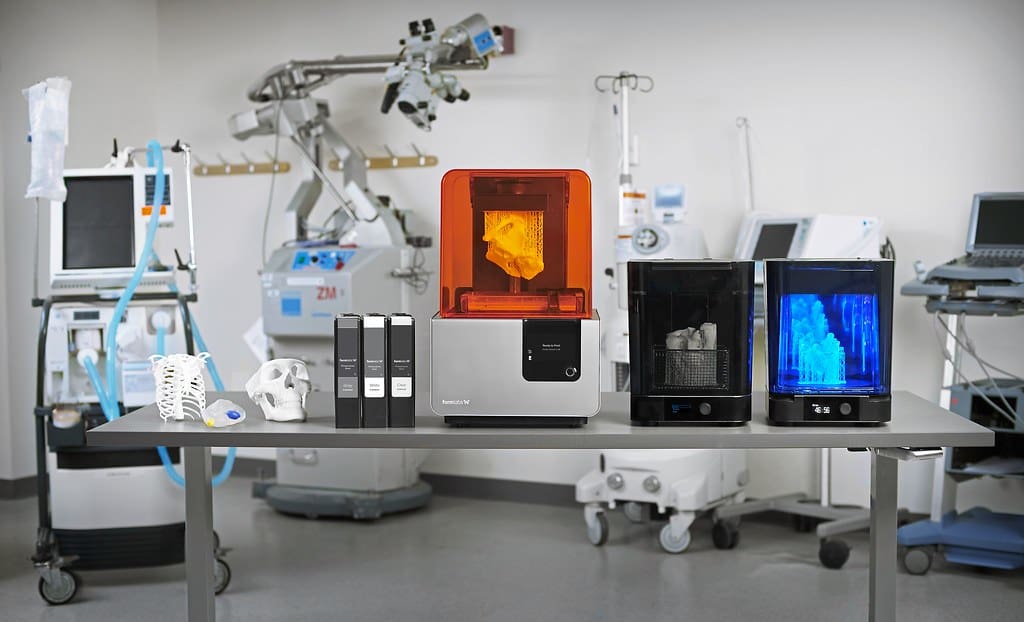
3D printing is revolutionizing the medical industry by enabling the customization of healthcare solutions, accelerating medical device development, and pushing the boundaries of regenerative medicine. From personalized prosthetics to complex bioprinted tissues, 3D printing offers promising solutions that enhance patient care and treatment outcomes. The technology’s versatility in creating patient-specific items on-demand is transforming traditional medical practices and opening new avenues for medical research and application.
Customized Prosthetics and Implants
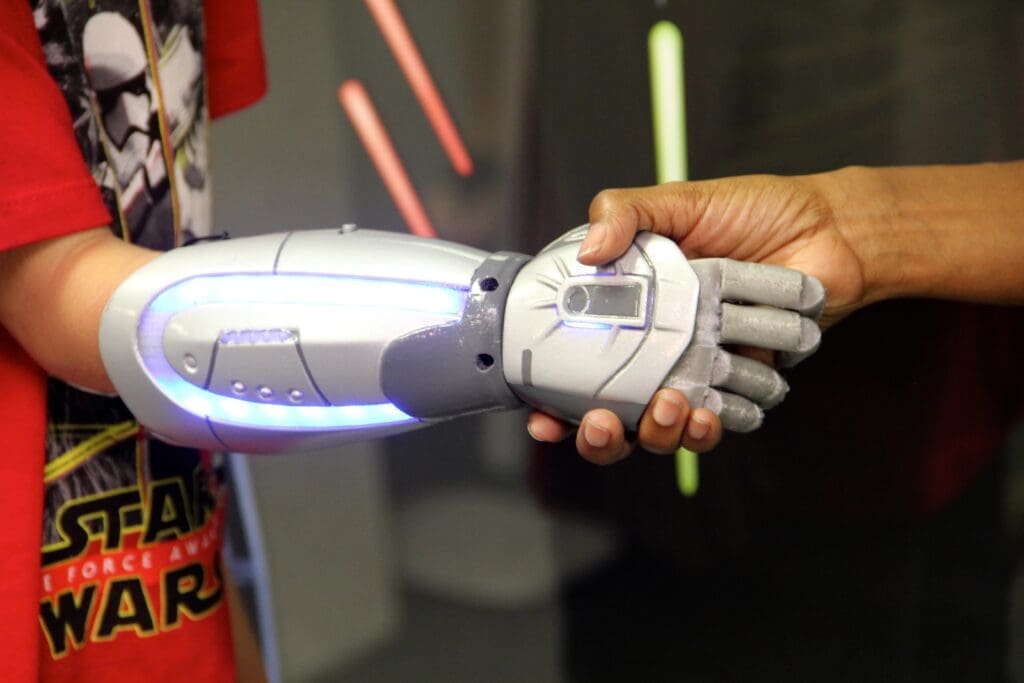
One of the most impactful applications of 3D printing in medicine is the creation of customized prosthetic limbs and surgical implants. These devices are tailored to fit the unique anatomy of each patient, which improves comfort and integration. For instance, 3D printing allows for the rapid production of dental implants and cranial plates that precisely match the patient’s dimensions, leading to better outcomes and shorter recovery times. Orthopedic implants, such as knee and hip joints, are also customized using 3D printing, providing patients with improved mobility and a higher quality of life post-surgery.

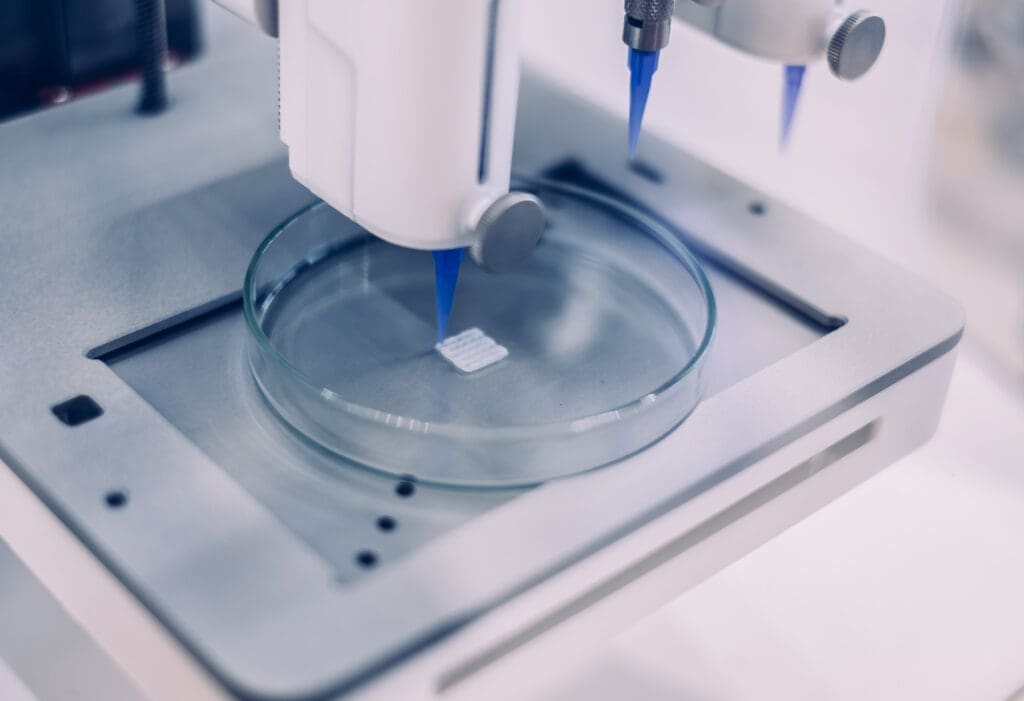
Bioprinting and Tissue Engineering
Bioprinting is a groundbreaking application of 3D printing in the medical field, involving the layer-by-layer creation of tissue structures that mimic natural biological systems. Researchers are currently developing methods to print organs such as kidneys and hearts, which could one day alleviate the shortage of organ donations. In the shorter term, bioprinted skin for burn victims and other complex tissue structures for medical testing are becoming more feasible. This aspect of 3D printing holds the potential to revolutionize transplant medicine and facilitate advanced drug testing, reducing the reliance on animal testing.

Surgical Preparation and Training Tools
3D printing is instrumental in enhancing surgical precision through the creation of patient-specific anatomical models based on CT or MRI scans. Surgeons use these models to prepare for and practice complex operations, reducing surgery times and improving outcomes. These models are also invaluable educational tools in medical training, providing students and new surgeons with tactile, realistic practice materials that help them learn surgical techniques and understand human anatomy in a hands-on setting.
Medical Devices and Equipment
The flexibility of 3D printing extends to the production of custom medical devices and equipment. From tailored surgical tools designed for specific procedures to innovative devices that meet unique clinical needs, 3D printing enables rapid prototyping and production. For example, tools like forceps, retractors, and even surgical guides can be produced quickly and cost-effectively, allowing for rapid iteration and customization for individual surgeries.
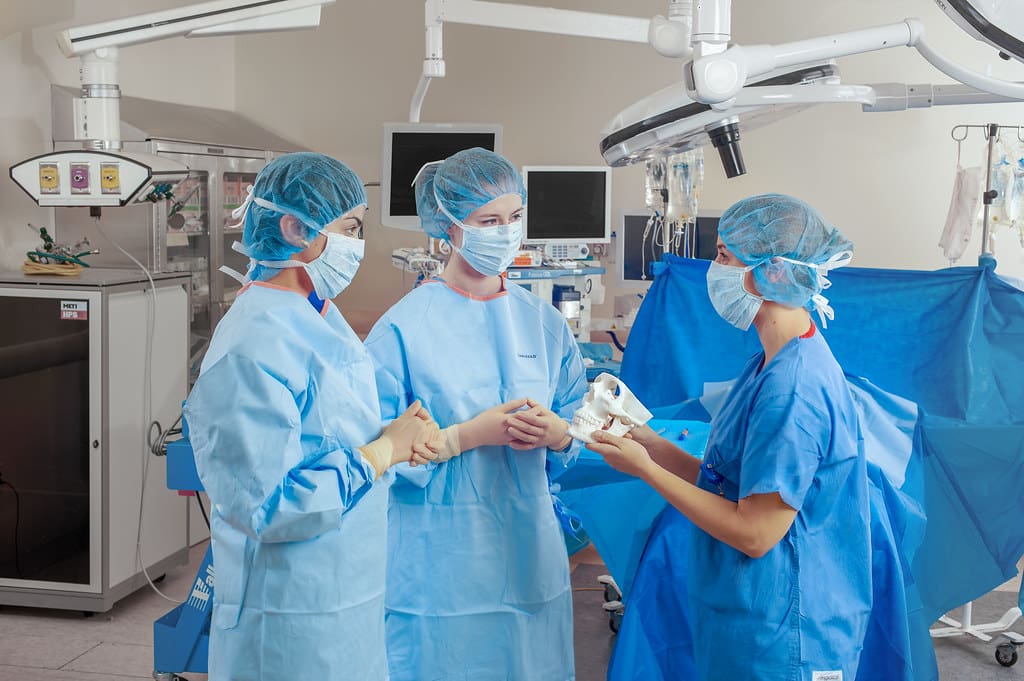
Challenges and Regulatory Considerations
Despite its advantages, 3D printing in medicine faces several challenges. The requirement for biocompatible materials that meet rigorous health and safety standards is paramount. Additionally, the regulatory landscape for 3D printed medical products is complex and still evolving. Bodies like the FDA are actively working to establish guidelines that ensure the safety and efficacy of 3D printed items, but the pace of technological development sometimes outstrips regulatory processes.
Future Prospects
Looking ahead, the potential of 3D printing in medicine continues to expand. Innovations in bioprinting could eventually lead to routine production of functional human organs. Meanwhile, the adoption of 3D printing by hospitals and clinics is set to increase, driven by the technology’s ability to reduce costs and improve patient care. As 3D printing becomes more integrated into medical practice, it will likely become a standard part of the medical toolkit, transforming the landscape of healthcare and patient treatment.
3D printing presents a transformative shift in the medical industry, offering personalized healthcare solutions that were unthinkable a few decades ago. By fostering closer collaboration between engineers, healthcare professionals, and regulatory bodies, the full potential of 3D printing can be harnessed to improve patient outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and lead the way in medical innovation.