Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) is a powerhouse in the realm of additive manufacturing, enabling the creation of metal parts that often surpass the capabilities of traditional fabrication methods. DMLS is particularly noted for its precision and flexibility, allowing for the production of complex geometries that are otherwise challenging to achieve. This technology is essential in fields requiring high-performance, durable parts with intricate designs.
How DMLS Printing Works
DMLS operates by fusing metal powder into a solid part using a high-power laser beam. The process starts with a layer of metal powder spread onto a build platform. A laser selectively sinters the powder particles according to the 3D model’s cross-sectional design, binding them together to form a solid structure. The build platform then lowers slightly, and a new layer of powder is applied. This process repeats until the part is fully formed.
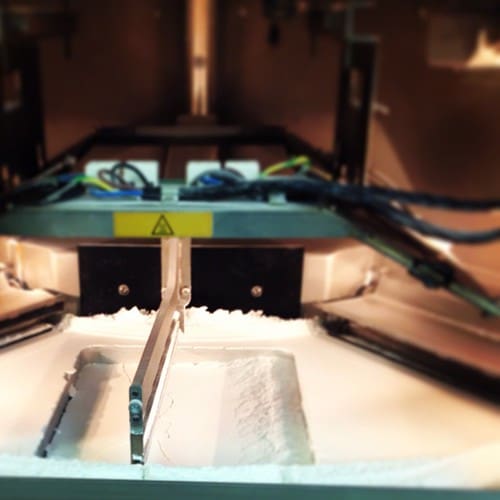
As each layer is added, the parts are encapsulated within the unsintered powder, which supports them without the need for dedicated support structures. This capability enables DMLS to create parts with complex internal features and intricate channels that are impossible with other manufacturing processes.
Advantages of DMLS 3D Printing
Strength and Durability: DMLS produces parts that are extremely dense and can possess mechanical properties similar to those found in wrought metals, making them suitable for functional applications in demanding environments.
Design Freedom: This technology allows for the construction of complex assemblies as a single piece, reducing the necessity for assembly and welding, and thereby enhancing the structural integrity of the part.
Efficiency and Speed: Compared to traditional metalworking, DMLS can significantly shorten production cycles by eliminating the need for tooling and reducing material waste, as only the amount of powder sintered forms part of the final product.
Applications of DMLS 3D Printing
DMLS is widely used in several high-tech industries:
Aerospace: For components that must withstand extreme pressures and temperatures while maintaining a low weight, such as turbine blades and fuel nozzles.
Medical: In the production of custom implants and prosthetics that benefit from the material biocompatibility and capability to match exact anatomical features.
Automotive: Particularly in the performance and motorsports sectors, where tailored parts like gears and brackets can be designed for optimal performance without the constraints of traditional manufacturing methods.
Considerations and Limitations
Despite its advantages, DMLS presents certain challenges:
Cost and Accessibility: The high cost of DMLS machines and the price of metal powders can be prohibitive for small-scale productions or less financially robust companies.
Post-Processing: Most DMLS parts require some level of post-processing, including heat treatment to relieve internal stresses, surface smoothing to achieve desired finishes, and machining to meet precise tolerances.
Material Limitations: DMLS is typically limited to metals like steel, titanium, aluminum, and nickel alloys, and each type requires specific processing parameters for optimal results.
The Future of DMLS Printing
The future of DMLS looks promising with ongoing advancements aimed at increasing the speed of production, expanding the range of compatible materials, and reducing costs. As these technological improvements mature, DMLS is poised to become even more integral in manufacturing, potentially expanding into more mainstream applications across various industries.
Direct Metal Laser Sintering is revolutionizing how high-strength, complex metal parts are made. With its unmatched precision and efficiency, DMLS offers significant advantages over traditional metal fabrication techniques. For industries that rely on the utmost in part performance and complexity, DMLS represents a formidable manufacturing tool, driving innovation and providing solutions that were once deemed impractical or impossible.