Binder Jetting is a unique 3D printing technology that stands out for its ability to print with a wide variety of materials, including metals, sand, and ceramics. Unlike methods that rely on heat to fuse materials, such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) or Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), Binder Jetting uses a liquid binding agent to join powder particles, enabling it to produce parts quickly and with great material flexibility.
How Binder Jetting Works
The process of Binder Jetting begins with spreading a thin layer of powder material over the build platform. An inkjet print head then moves across the powder layer, selectively depositing a liquid binding agent in the specific locations where the part is to be formed. After each layer, a new layer of powder is spread, and the process repeats until the entire part is built up. The unbound powder supports the part during printing and can be removed and reused, enhancing material efficiency.
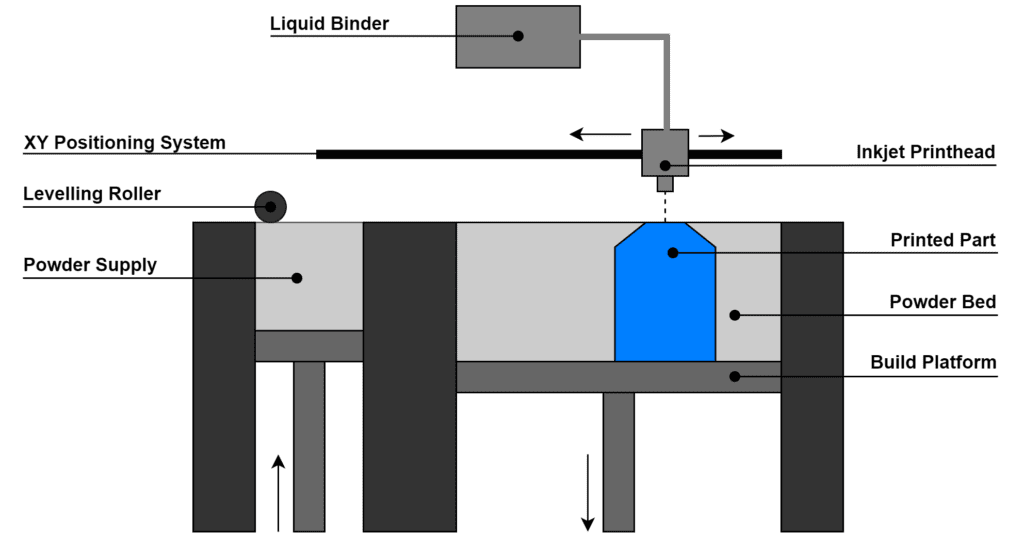
Once the printing is complete, the build box is removed from the printer, and the parts contained within the unbound powder need to be carefully extracted. These “green parts” are then subjected to post-processing, which typically involves curing, sintering, or infiltration to reach the final mechanical strength and resolution.
Advantages of Binder Jetting
Binder Jetting offers several significant advantages:
Speed: It is one of the fastest 3D printing technologies available, capable of producing multiple parts in a single build thanks to the simultaneous application of the binder across the powder bed.
Material Diversity: This method can process a vast array of materials, allowing for applications ranging from metal parts to ceramic objects and sand molds.
Cost Efficiency: For large-scale productions, Binder Jetting is cost-effective, particularly when using materials like metals and ceramics that are otherwise expensive to process.
Applications of Binder Jetting
Binder Jetting has found applications in several fields:
Industrial Tooling: It is extensively used for creating sand molds and cores for metal casting. These molds can be produced directly from digital data, bypassing traditional mold-making processes.
Manufacturing: The technology is ideal for manufacturing complex or customized metal parts that would be challenging or costly to produce with conventional manufacturing methods.
Art and Architecture: Artists and architects use Binder Jetting to fabricate large-scale sculptures and detailed architectural models directly from CAD data.
Considerations and Limitations
Despite its advantages, Binder Jetting comes with challenges:
Post-Processing: The parts require significant post-processing, which can include curing, sintering, and infiltration to achieve functional strength and desired properties.
Precision and Strength: While Binder Jetting is versatile, the dimensional accuracy and mechanical strength of the final parts can be less than those produced by methods like SLS or Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), especially if proper post-processing is not conducted.
The Future of Binder Jetting
Advancements in Binder Jetting technology are continually being made to enhance its resolution, strength, and the range of compatible materials. These developments are expected to broaden its application scope further, potentially making it a more dominant force in the fields of specialized manufacturing and mass production.
Binder Jetting occupies a unique position in the 3D printing landscape, offering remarkable flexibility and speed. As the technology continues to evolve, it holds the potential to transform manufacturing processes in numerous industries, providing a cost-effective solution for producing complex, customized parts. For businesses looking to innovate and streamline their production capabilities, Binder Jetting presents a compelling option.