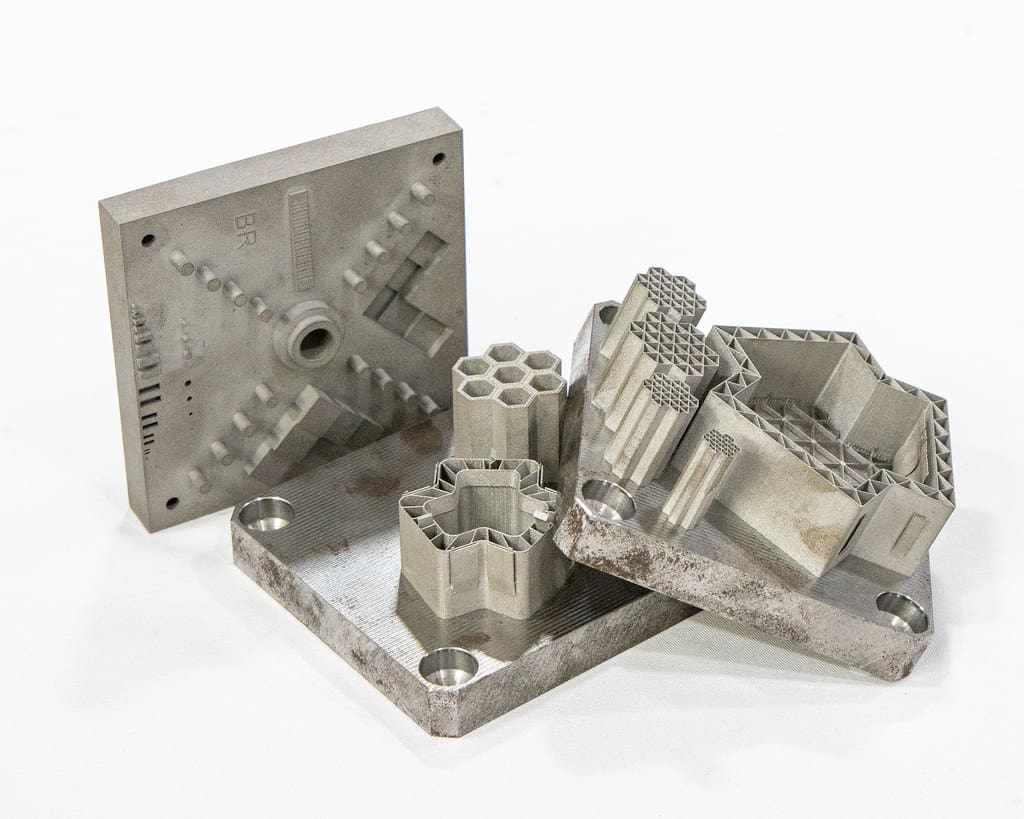
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is increasingly becoming a cornerstone in the production of industrial goods, offering transformative benefits across various sectors, including heavy machinery, aerospace, and automotive industries. This technology enables manufacturers to create parts that are both complex and customized, revolutionizing traditional manufacturing processes with its flexibility and efficiency.
Advantages of 3D Printing in Industrial Manufacturing
3D printing introduces several significant advantages in the production of industrial goods:
Customization: This technology excels in producing custom-designed parts tailored to specific functional requirements, allowing for more efficient machinery and systems. Each component can be optimized for its particular application, leading to improved overall performance.
Reduced Waste and Cost: Unlike subtractive manufacturing methods that cut away significant amounts of material, 3D printing adds material layer by layer to create a part. This process significantly reduces waste, which not only lowers material costs but also minimizes the environmental impact associated with production.
Speed to Market: 3D printing speeds up the prototyping phase dramatically, allowing companies to test and refine designs quickly. This rapid prototyping capability enables faster development and iteration, reducing the time it takes to bring a product to market.
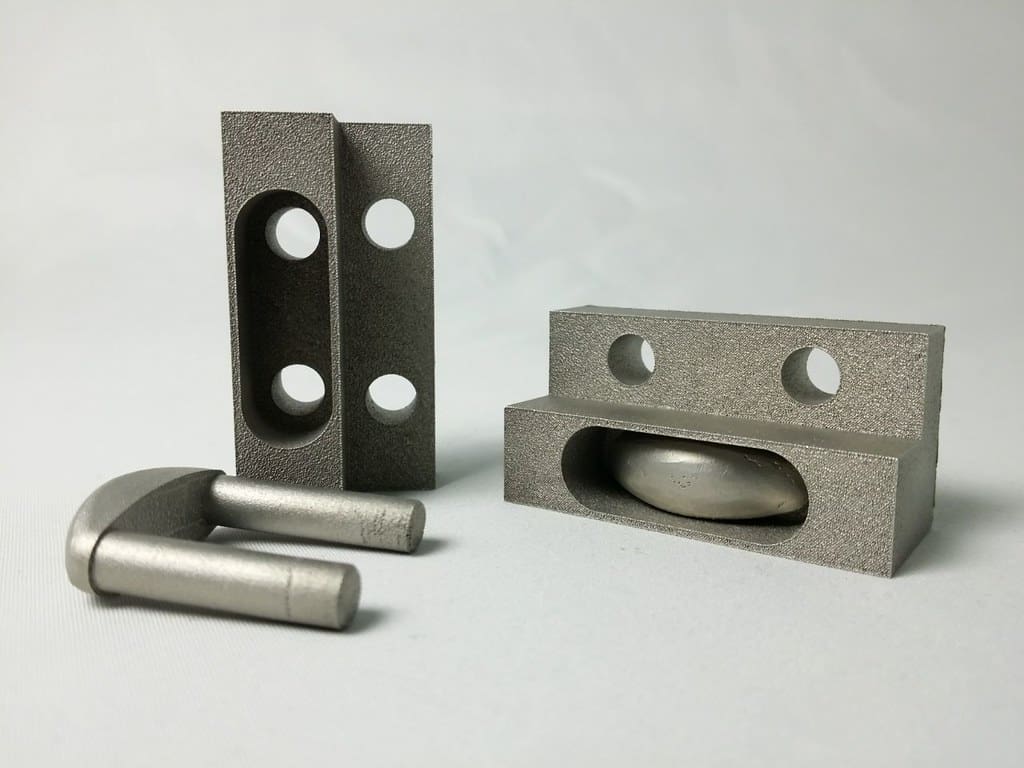

Key Applications of 3D Printing in Industrial Goods
The applications of 3D printing in industrial manufacturing are both broad and impactful:
Tooling and Fixtures: Manufacturing custom tools, jigs, and fixtures with 3D printing is not only faster but also cheaper. These tools are often lighter and more ergonomically designed, which can improve the assembly line efficiency and worker safety.
Functional Parts: Many industries are now relying on 3D printing for production-ready components. For example, the aerospace industry uses 3D printing to create lightweight, high-strength parts that withstand the rigors of flight. Similarly, in robotics, 3D printing is used to produce complex parts that require precise dimensions and geometries.
Complex Components: The ability to produce complex geometries that are impossible to achieve with traditional methods is one of the most significant advantages of 3D printing. This capability is particularly useful for creating intricate components for machinery and engines, where complexity often equates to improved functionality.
Repair and Maintenance: 3D printing allows for the on-demand production of replacement parts. This is especially valuable for older machinery, where parts may no longer be in production. The ability to 3D print spare parts as needed can significantly reduce downtime and extend the machinery’s operational life.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its advantages, 3D printing in industrial applications comes with challenges:
Material Strength and Durability: Some 3D printed materials may not yet match the strength and durability of those used in traditional manufacturing, which can be a concern for structural components in high-stress environments.
Scale of Production: While 3D printing is excellent for low-volume production, scaling it for high-volume manufacturing remains economically challenging compared to traditional methods like injection molding.
Integration with Existing Systems: Incorporating 3D printing into traditional manufacturing processes can require significant workflow adjustments and investments in new equipment and training.
Future Trends in 3D Printing for Industrial Goods
Looking forward, the future of 3D printing in industrial manufacturing is bright:
Advancements in Materials and Technology: Ongoing developments in new 3D printing materials and more advanced printers promise to overcome current limitations regarding speed, cost, and material properties.
Sustainability Impact: As global emphasis on sustainability grows, 3D printing is well-positioned to become a more dominant technology due to its efficiency and waste reduction capabilities.
3D printing is set to continue its expansion in the industrial goods sector, reshaping how products are designed, manufactured, and distributed. By embracing 3D printing, industries can not only boost efficiency and customization but also gain significant competitive advantages in a rapidly evolving marketplace. The continued integration of 3D printing will undoubtedly unlock new potentials and pave the way for future innovations in industrial manufacturing.