Food engineering is an innovative discipline where science and technology intersect to enhance food production, processing, and consumption. Recently, 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has emerged as a transformative force in this field, enabling new levels of customization, efficiency, and creativity in food design. This technology allows for the precise construction of complex food items, tailored nutritional content, and even the development of new textures and forms that were previously unimaginable.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Food Engineering
Initially popular in industries such as manufacturing and healthcare, 3D printing has found a novel application in food engineering. The ability to layer ingredients precisely offers a unique opportunity to create complex geometries and personalized food items on demand. As food safety and nutritional customization become more prominent, 3D printing is being recognized for its potential to tailor food products to individual dietary needs, enhance aesthetic appeal, and even reduce food waste.
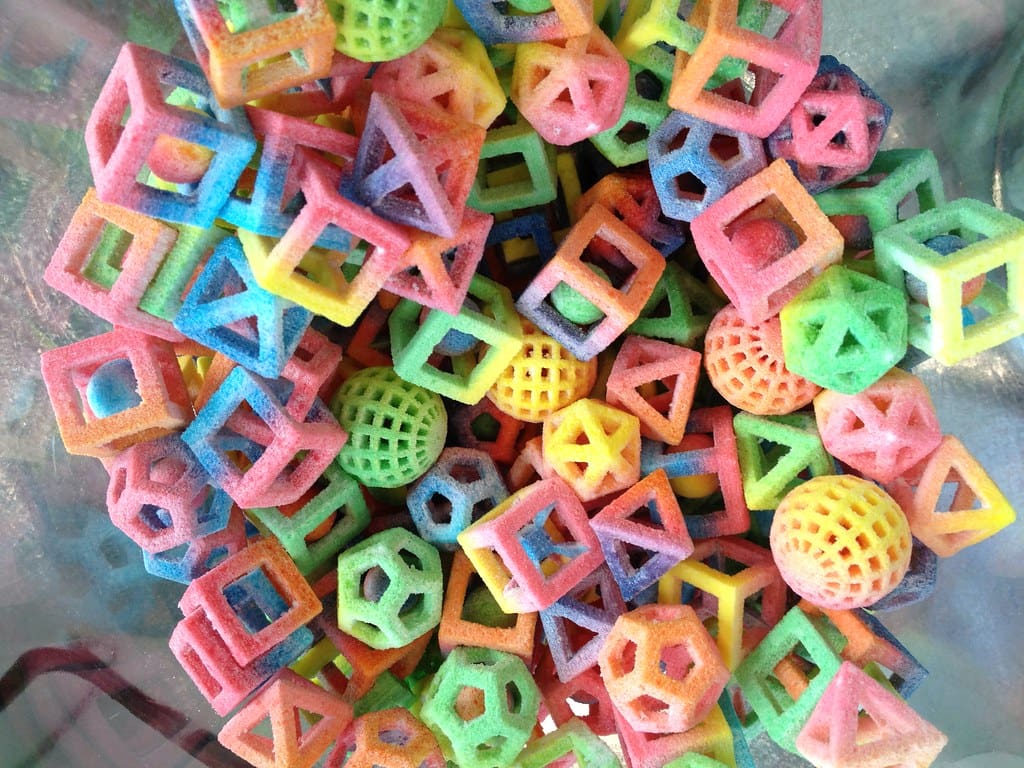

Advantages of 3D Printing in Food Engineering
Customization of Nutritional Content: 3D printing enables the customization of food products based on nutritional requirements. Ingredients can be modified and portioned to cater to specific dietary needs, such as altering macronutrient profiles or incorporating micronutrients to address deficiencies.
Complex Geometric Designs: This technology allows for the creation of intricate and precise shapes that are not achievable with traditional food processing methods. It opens up new avenues for food presentation and innovation, particularly in gourmet and high-end culinary applications.
Reduction in Food Waste: 3D printing contributes to sustainability efforts by precisely using ingredients needed for each item, significantly reducing food waste during production.
Efficiency and Speed: In commercial settings, 3D printers can streamline food preparation processes, enhance consistency, and reduce labor costs. This is particularly advantageous in environments where speed and precision are critical, such as large-scale catering and personalized meal production.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Food Engineering
Custom-Designed Confections: From intricate chocolate figures to personalized candies and cakes, 3D printing is ideal for creating detailed and customized confections that cater to specific consumer preferences.
Textured Food Products for Special Diets: For individuals with swallowing difficulties, 3D printing can produce food that is safe to eat yet enjoyable. Foods can be designed to dissolve quickly in the mouth while still offering nutritional value and flavor.
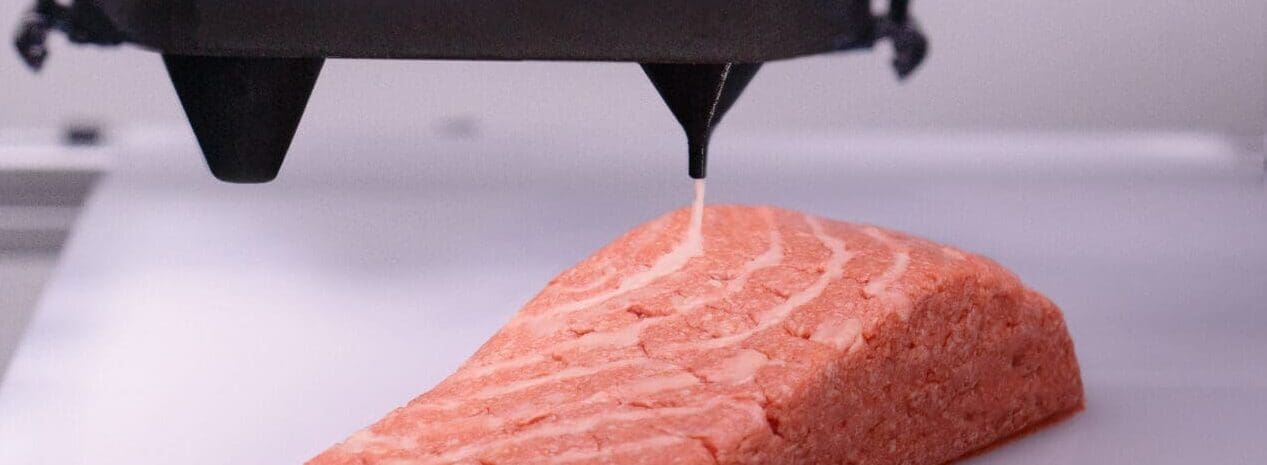
Plant-Based Meat Alternatives: 3D printing is at the forefront of developing plant-based meat, where it mimics the texture and appearance of animal meat, providing a sustainable and ethical alternative without compromising taste or aesthetics.
Experimental Cuisine and Gastronomy: Chefs and food innovators are using 3D printing to push the boundaries of traditional cuisine, creating unique dining experiences that combine unusual forms and flavors.
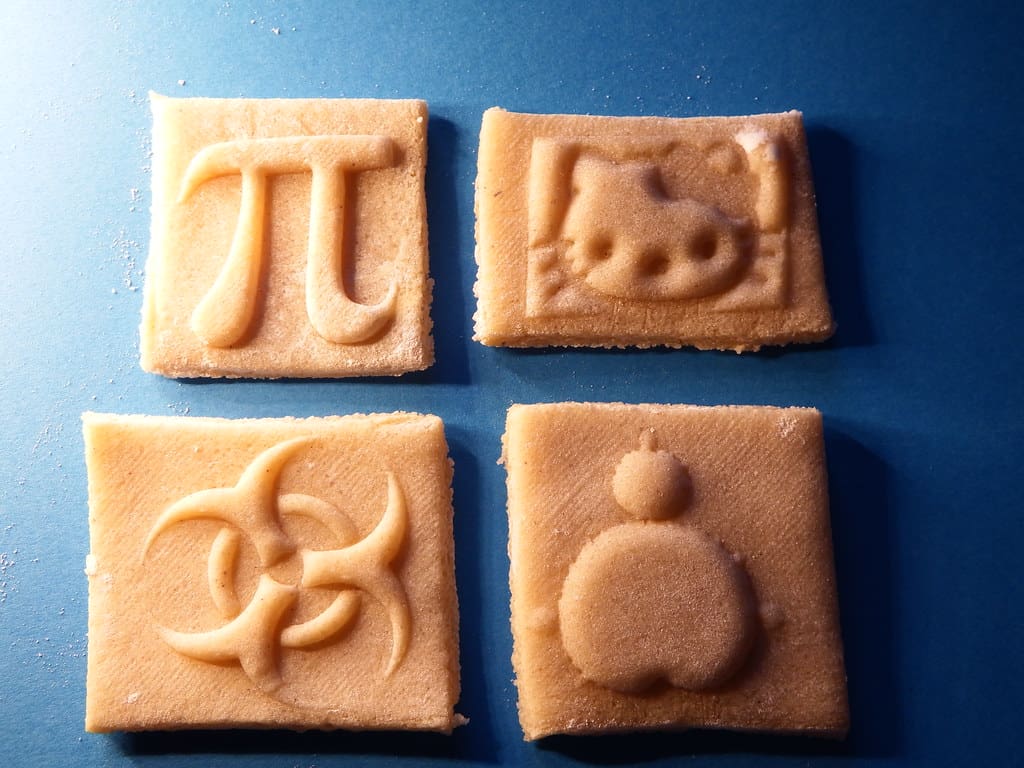

Challenges in 3D Printing for Food Engineering
Despite its potential, the adoption of 3D printing in food engineering faces several challenges:
Food Safety and Hygiene: Ensuring that 3D printers and associated materials meet stringent food safety and hygiene standards is crucial. The risk of contamination must be carefully managed, and machines must be designed to be easily cleaned and maintained.
Material Limitations: The range of ingredients that can be effectively printed is currently limited. Expanding the variety of printable food materials while maintaining quality and stability during the printing process is an ongoing area of research.
Consumer Acceptance: While 3D printed food offers many benefits, consumer acceptance varies. Some may be hesitant to embrace foods produced via additive manufacturing due to perceptions of artificiality or concerns about taste and texture.
Scalability and Cost: Scaling 3D food printing from small prototypes to large-scale production is challenging and can be cost-prohibitive. Reducing the cost of 3D food printers and associated materials is essential for broader adoption.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Food Engineering
The future of 3D printing in food engineering is promising, with continuous advancements in technology, materials, and design software expected to enhance its applications and accessibility. Innovations in multi-material printing, flavor and texture simulation, and integration with artificial intelligence for automated nutritional customization are likely to drive further growth in this field.
3D printing is set to continue its transformative impact on food engineering, offering innovative solutions that enhance food design, customization, and production. As the technology evolves, it promises to enable more personalized, sustainable, and efficient food production methods, redefining our relationship with what and how we eat.