The electronics industry, always at the forefront of innovation, is undergoing a significant transformation with the adoption of 3D printing technology. Known for enabling rapid prototyping and flexibility in manufacturing, 3D printing is now paving the way for revolutionary changes in how electronic devices are designed, developed, and produced. This technology not only enhances the creation of intricate and miniaturized electronic components but also fosters advancements in wearable technology and customized electronics.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Electronics
Initially embraced for rapid prototyping, 3D printing has expanded its capabilities to include the production of functional electronic components such as sensors, antennas, and circuit boards. Advances in 3D printing technologies now allow for the integration of conductive, dielectric, and substrate materials into a single manufacturing process, thereby enabling the creation of complex multi-material electronic devices in shapes and configurations that were previously impossible.
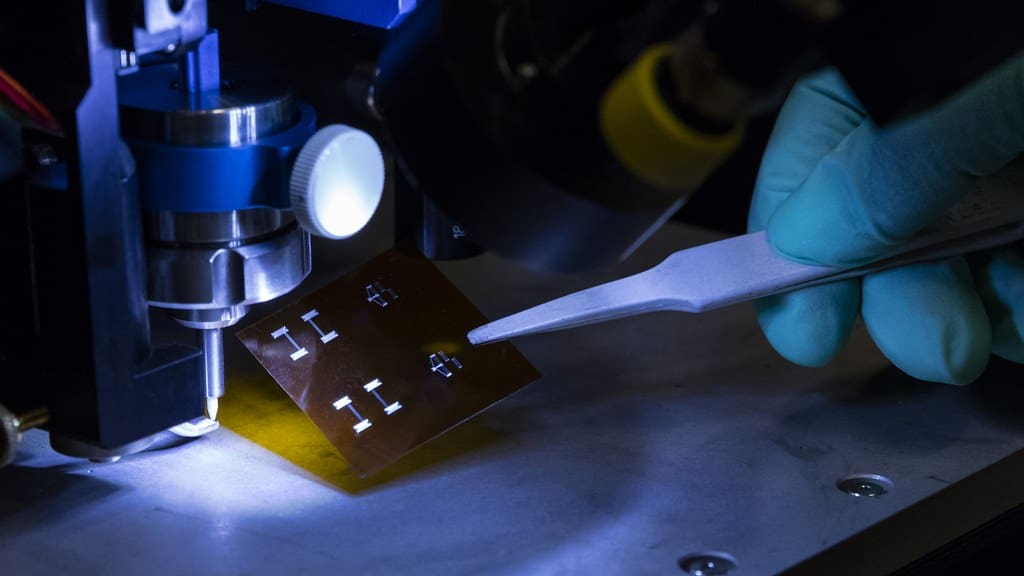

Advantages of 3D Printing in Electronics
Design Flexibility: 3D printing allows for the creation of complex geometries that traditional manufacturing methods cannot achieve. This flexibility is crucial for developing more compact and efficient electronic devices.
Speed of Innovation: 3D printing accelerates the design process by allowing rapid iteration of ideas. Engineers can quickly prototype and refine designs, significantly reducing the development cycle and leading to faster product launches.
Reduction in Material Waste: Traditional electronic manufacturing can be wasteful, with substantial material loss during the etching and milling processes. 3D printing minimizes this waste by adding material layer by layer to form a part.
Cost-Effective Small Batch Production: For low-volume manufacturing, 3D printing offers a cost-effective solution without the need for expensive molds and setup costs, making it ideal for custom or niche market products.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Electronics
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs): 3D printing is transforming PCB production by enabling the direct printing of conductive tracks on various substrates. This method not only reduces the complexity and size of the boards but also integrates them more seamlessly into electronic devices.
Antennas and RF Components: Custom antennas and RF components are crucial for the wireless communication capabilities of modern devices. 3D printing facilitates the design of antennas that are specifically optimized for their application, improving performance and device integration.
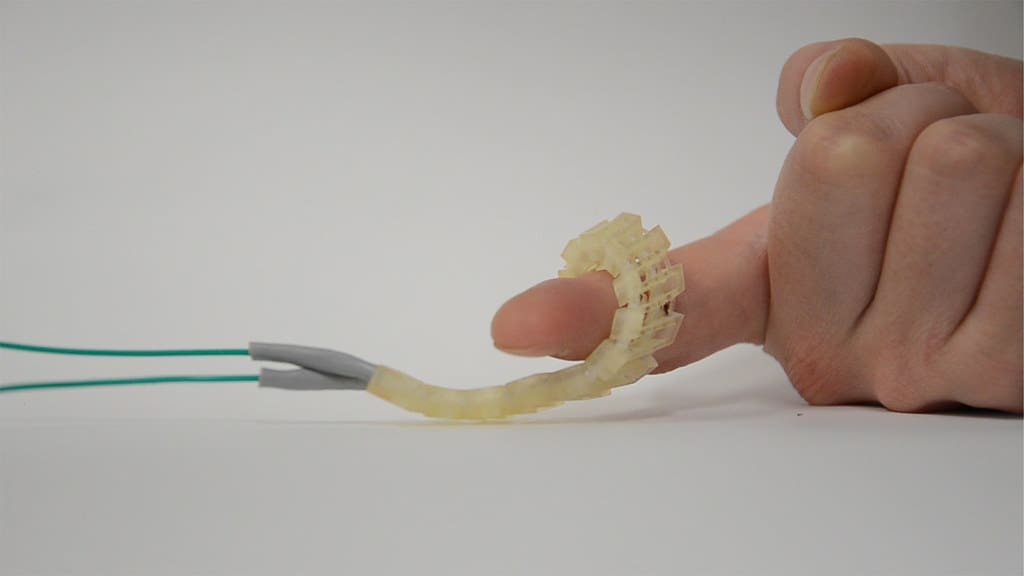
Sensors and Interfaces: With 3D printing, sensors can be designed to fit specific applications perfectly, enhancing their performance and integration into devices. This is particularly important in fields like wearable technology and medical devices, where sensors must conform to ergonomic and biological factors.
Wearable Electronics: 3D printing is ideal for developing wearable electronics, as it can produce lightweight, flexible, and body-conforming structures. These devices can integrate sensors, connectivity, and other electronic functionalities directly into user-friendly formats.
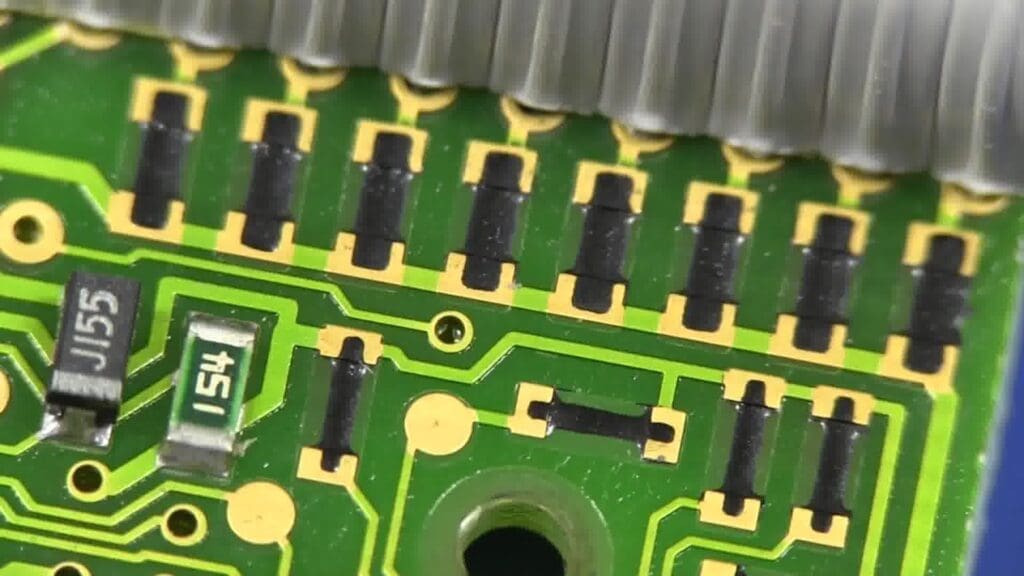

Challenges in 3D Printing for Electronics
Despite the promising advancements, several challenges remain in the widespread adoption of 3D printing in electronics:
Material Limitations: The range of materials suitable for 3D printing is currently limited, especially when it comes to conductive materials that match the performance of traditional materials used in electronics.
Resolution and Precision: Achieving the high precision required for electronic components is a challenge for 3D printing technologies. Improvements in resolution and accuracy are necessary to meet the stringent demands of electronic device fabrication.
Durability and Reliability: Ensuring that 3D printed electronic components can withstand operational stresses over time is crucial. Long-term reliability remains a concern, particularly for critical applications in aerospace, automotive, and medical devices.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Electronics
The future of 3D printing in electronics looks bright, with ongoing research and development focusing on overcoming current material and technological limitations. Innovations are likely to yield better conductive materials and improved printing processes that could open up new applications in electronics manufacturing.
Additionally, the integration of 3D printing with other cutting-edge technologies, such as AI and IoT, offers exciting possibilities for smart manufacturing processes that could further streamline production and increase functionality in electronic devices.
3D printing is poised to revolutionize the electronics industry by providing greater design flexibility, reducing production costs, and accelerating the innovation process. As this technology continues to evolve, it is expected to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of electronic design and manufacturing, leading to more sophisticated, efficient, and personalized electronic products.