The boat manufacturing industry is witnessing a significant transformation, driven by the adoption of 3D printing technology. This innovative approach to manufacturing, also known as additive manufacturing, is revolutionizing how boats are designed, produced, and customized. With the ability to create complex, lightweight structures and customize designs to individual specifications, 3D printing is paving the way for more efficient, sustainable, and innovative nautical craft.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Boat Manufacturing
3D printing began as a tool for prototyping across various industries but has rapidly evolved into a viable method for producing end-use products, including boat components and even entire boats. This expansion is facilitated by advancements in 3D printing technologies and materials that can withstand the aquatic environment and meet the specific demands of marine applications. As 3D printing technology matures, it is increasingly embraced by boat builders for its ability to enhance performance, reduce waste, and streamline production processes.

Advantages of 3D Printing in Boat Manufacturing
Design Flexibility and Complexity: 3D printing excels at creating intricate and complex designs that are difficult to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. This capability allows for the optimization of hydrodynamic shapes and the integration of unique aesthetic features, enhancing both the performance and appearance of boats.
Weight Reduction: One of the primary benefits of 3D printing is the ability to produce lightweight structures. By optimizing material placement and reducing unnecessary bulk, 3D printing can significantly decrease the weight of boat components, leading to better fuel efficiency and higher speeds.
Customization and Personalization: 3D printing offers unparalleled customization opportunities, enabling boat manufacturers to tailor products to the specific needs and preferences of customers. This includes custom fittings, personalized aesthetics, and adapted designs that cater to particular sailing conditions or accessibility requirements.
Reduced Material Waste: Additive manufacturing contributes to sustainability efforts by minimizing waste. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing processes, 3D printing uses only the material necessary to build a part, reducing the environmental impact associated with production.
Cost-Effective Prototyping and Production: The technology allows for rapid prototyping and efficient small-scale production runs without the need for expensive molds or tooling. This reduces the overhead costs associated with developing new boat models and custom projects.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Boats
Hulls and Structural Components: Advanced composites used in 3D printing can produce hulls and structural components that are both strong and lightweight. These components can be optimized for specific performance characteristics, such as durability, flexibility, and impact resistance.
Interior Fixtures and Custom Decor: 3D printing enables the creation of intricate interior fixtures and bespoke decor elements that meet the luxurious standards expected in yacht design. Custom seating, dashboard elements, and storage solutions are just a few examples where 3D printing can enhance functionality and aesthetic appeal.
Functional Parts and Mechanisms: From hinges and latches to mounts and holders, 3D printing can produce various functional parts required in boat construction. These parts can be designed to integrate seamlessly with other boat systems, improving overall functionality and user experience.
Repair and Replacement Parts: 3D printing offers a practical solution for producing replacement parts on demand, particularly for older boats where original parts may no longer be available. This capability is invaluable for maintaining the longevity and functionality of maritime vessels.
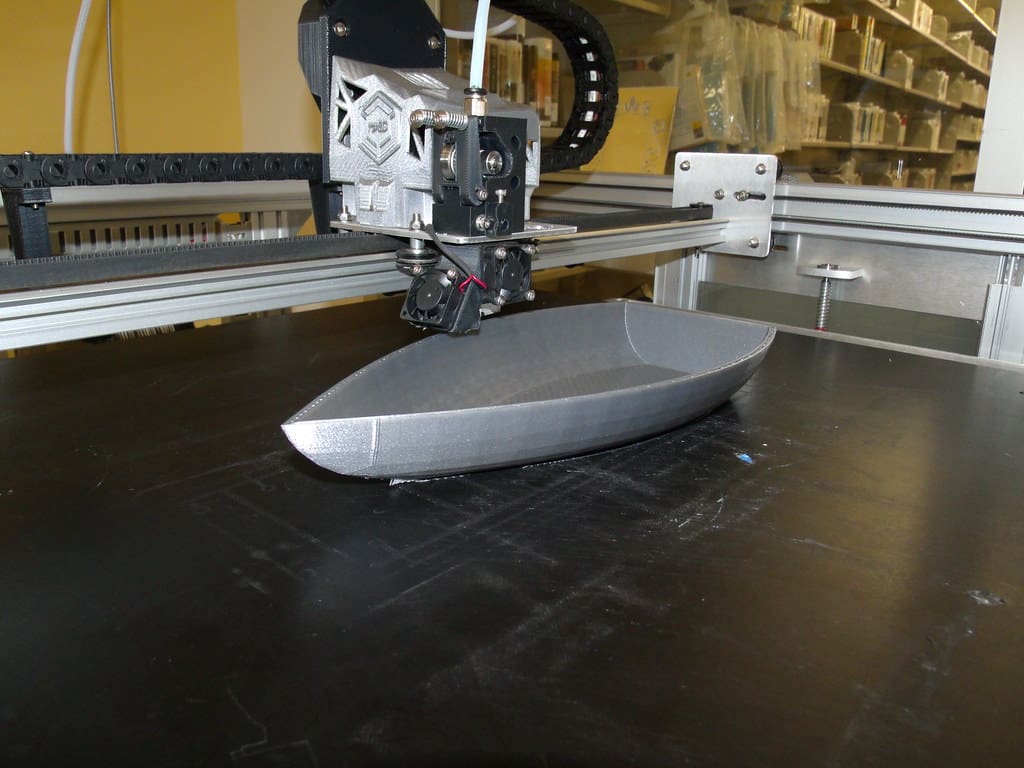

Challenges in 3D Printing for Boats
Despite its growing popularity, several challenges hinder the widespread adoption of 3D printing in boat manufacturing:
Material Durability: Ensuring that 3D-printed materials can endure the harsh marine environment, including exposure to UV rays, saltwater, and extreme weather conditions, is crucial. The development of more robust, corrosion-resistant materials is ongoing.
Scale and Efficiency: While 3D printing is effective for small components and custom pieces, scaling up to large structures like entire boat hulls requires significant advancements in printing technology and materials.
Regulatory Compliance: Boats must meet strict safety and regulatory standards. Obtaining certification for 3D-printed boats and components can be complex, involving rigorous testing to ensure they meet these standards.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Boats
The future of 3D printing in boat manufacturing looks promising, with ongoing advancements likely to address current limitations. Innovations in large-scale printing technologies, stronger and more durable materials, and more efficient production methods are expected to further integrate 3D printing into mainstream boat manufacturing. As these technologies develop, they will open new possibilities for more sustainable, efficient, and customized boat production.
3D printing is set to continue transforming the boat manufacturing industry by providing new ways to enhance design, reduce costs, and increase sustainability. As the technology advances, it promises to redefine traditional boat building, making it possible to produce boats that are not only more environmentally friendly and cost-effective but also tailored to the specific needs and desires of boaters around the world.