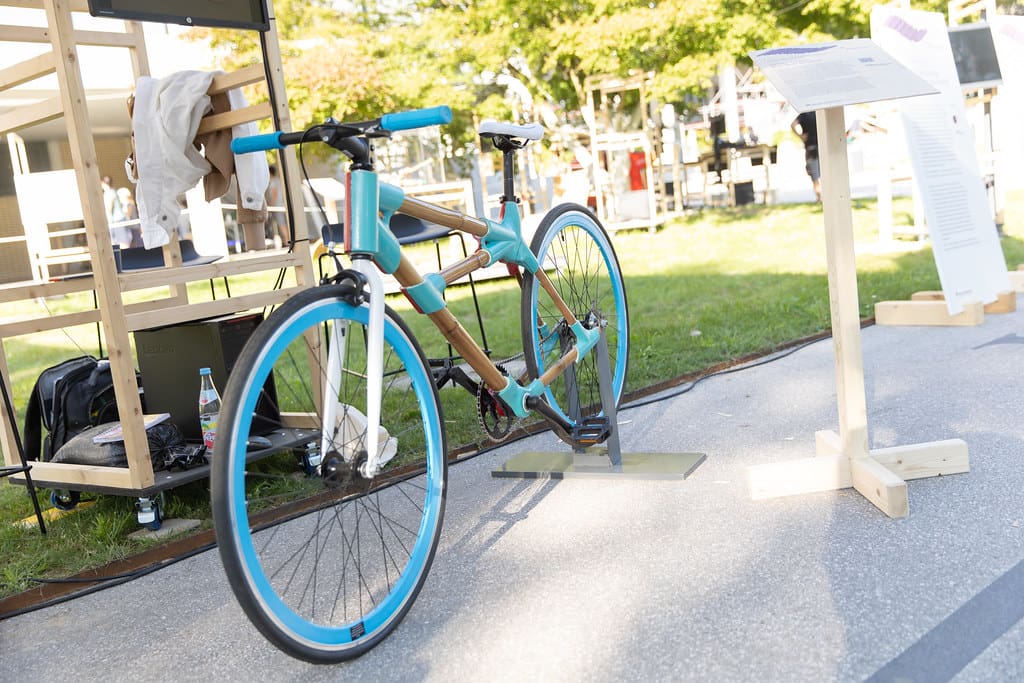
The cycling industry is experiencing a technological transformation, driven in part by the integration of 3D printing technology. This innovative approach to manufacturing is redefining the possibilities in bicycle design, production, and customization, allowing for lighter, stronger, and more efficient bicycles. Whether for competitive racing, urban commuting, or recreational use, 3D printing is empowering manufacturers and cyclists alike to push the boundaries of what a bicycle can be.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Bicycle Manufacturing
Initially utilized primarily for prototyping across various industries, 3D printing has evolved into a method for producing end-use products, including bicycle components. Advances in 3D printing technologies and materials have made it possible to manufacture parts that are both lightweight and durable enough to meet the demands of cycling, from casual riding to professional racing. Today, 3D printing is not just reshaping how bicycles are designed but also how they are produced and personalized.
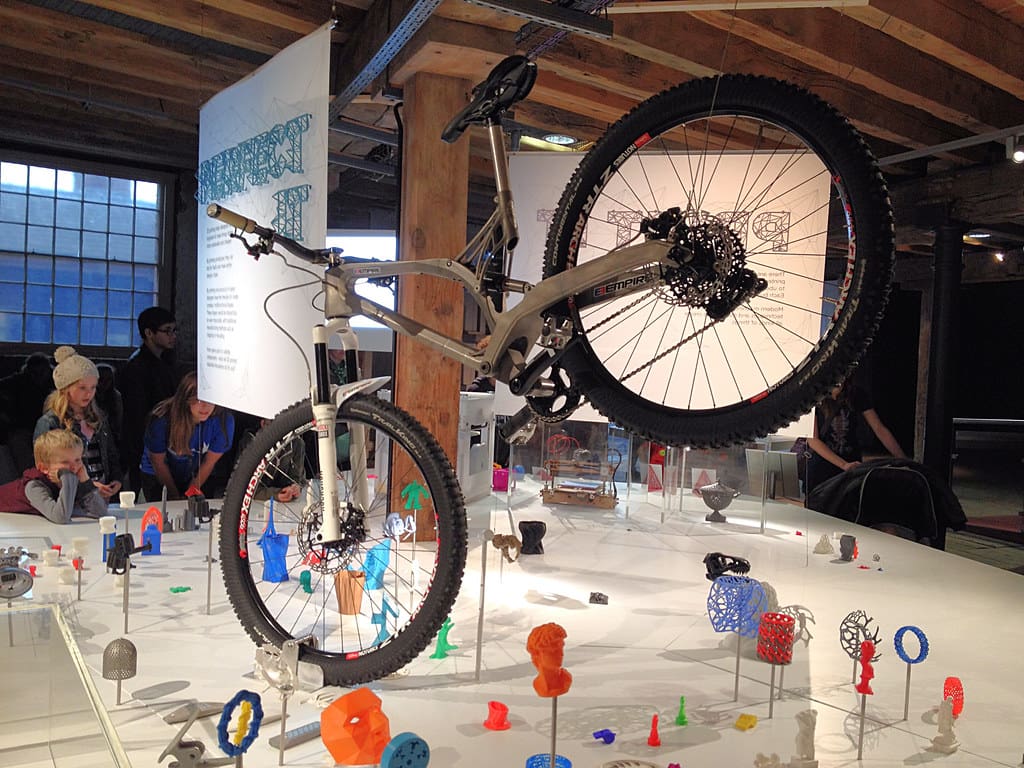

Advantages of 3D Printing in Bicycles
Customization and Personalization: 3D printing offers unparalleled customization capabilities, allowing both manufacturers and cyclists to tailor components to specific needs and preferences. This includes geometry, size, and even the stiffness of the frame and components to suit different riding styles and body ergonomics.
Innovative Designs: The technology enables the creation of complex geometries that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. This capability is particularly beneficial for developing integrated components, such as combining the seat post, saddle, and frame into a single, cohesive unit.
Weight Reduction: 3D printing allows for the use of lattice structures and hollow yet strong geometrical forms that significantly reduce the weight of bicycle parts without compromising strength or durability. This is crucial for performance bicycles where every gram counts.
Rapid Prototyping: 3D printing accelerates the design process, enabling rapid prototyping and testing of new ideas. This speed allows for quicker innovation cycles and the ability to bring new bicycle designs to market faster than ever before.
Sustainability: By minimizing material waste and enabling the use of recyclable materials, 3D printing aligns with the cycling industry’s goals of sustainability and environmental responsibility.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Bicycles
Frames and Forks: Manufacturers are using 3D printing to produce bike frames and forks that offer improved strength-to-weight ratios. These components can be optimized for specific performance characteristics, such as stiffness and shock absorption.
Custom Fittings and Components: Items like handlebars, grips, and even pedals can be customized to fit an individual rider’s anatomy, improving comfort and efficiency. Personalized components also allow for a more ergonomic riding position, which can enhance overall performance and reduce the risk of injury.
Prototyping New Technologies: 3D printing is ideal for developing and testing new bicycle technologies, including advanced suspension systems or innovative drivetrains. This flexibility is vital for pushing the envelope in bicycle design and functionality.
Aesthetic and Functional Customization: Beyond structural components, 3D printing allows for aesthetic customization, including unique colorways, patterns, and integrated features that reflect a rider’s personal style or branding.
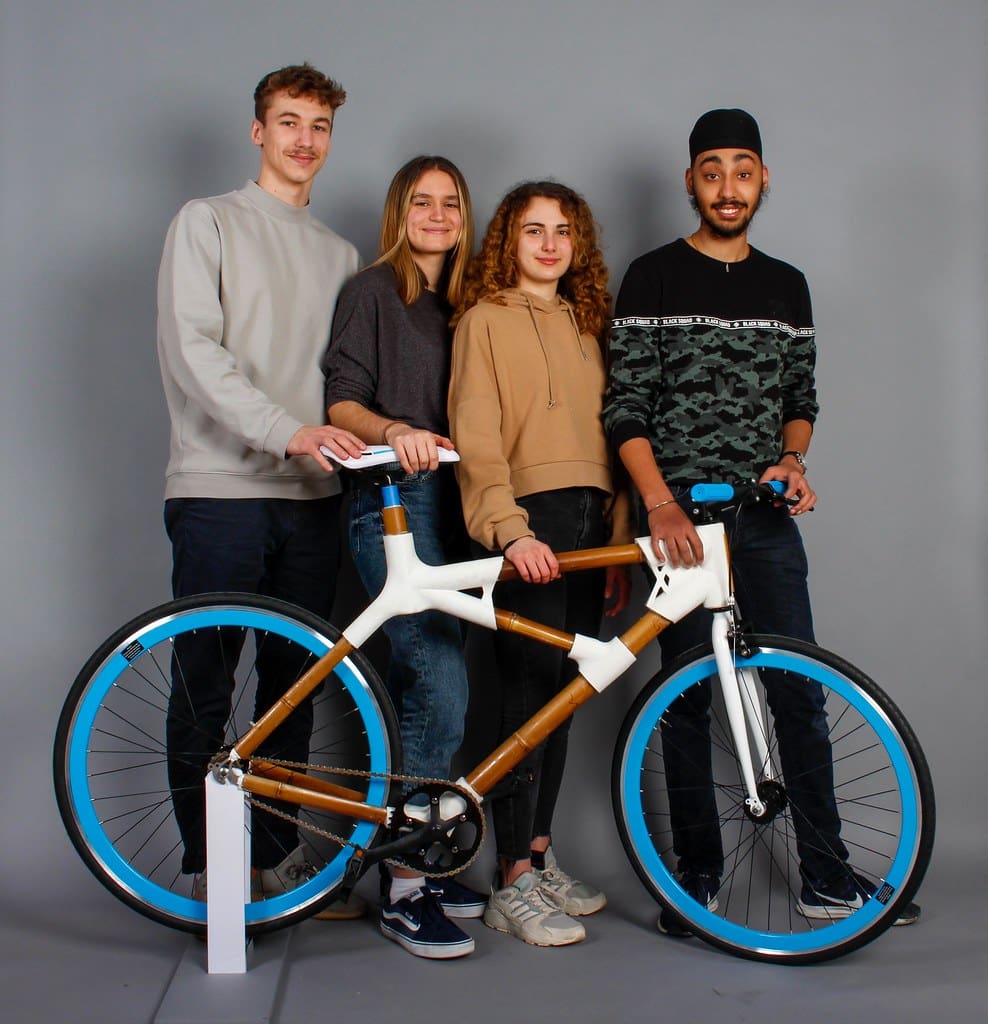

Challenges in 3D Printing for Bicycles
Despite its many advantages, the application of 3D printing in the bicycle industry faces several challenges:
Material Limitations: While there are significant innovations in printable materials, finding substances that can endure the stress and strain of regular or competitive cycling while maintaining lightness and durability is ongoing.
Cost Efficiency: Initially, the cost of 3D printing, particularly at a quality that meets cycling standards, can be higher than traditional manufacturing methods, especially for large-scale production.
Technical Expertise: Designing and producing 3D printed bicycles requires specialized knowledge, including expertise in computer-aided design (CAD), material science, and 3D printing technology, which can be a barrier to entry for some manufacturers.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Bicycles
The future of 3D printing in bicycle manufacturing looks promising, with ongoing advancements in printer technologies, materials, and design software expected to overcome current challenges. As these innovations continue, 3D printing is likely to become more integrated into mainstream bicycle production, offering more sophisticated, efficient, and personalized cycling experiences.
3D printing is poised to continue its transformative impact on the bicycle industry, providing exciting opportunities for innovation in bike design, customization, and production. As the technology progresses, it promises to redefine the standards of what is possible in cycling, making bikes lighter, stronger, and more tailored to individual riders than ever before.