3D environments and visualizations are crucial in fields ranging from architecture and engineering to entertainment and education, offering immersive experiences that enhance understanding and engagement. The integration of 3D printing into these domains is revolutionizing the way professionals and consumers interact with digital models, providing a tangible aspect to what was once solely virtual. This synergy between digital visualization and physical modeling facilitates better communication, more detailed analysis, and a greater appreciation of the complexities involved in various projects or studies.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in 3D Environments and Visualizations
Initially utilized for prototyping in industrial design, 3D printing has found extensive applications in creating detailed models that represent digital 3D environments. By transforming digital files into physical objects, 3D printing bridges the gap between virtual visualization and real-world tangibility. This capability is particularly valuable in industries where spatial understanding and the physical context of designs are crucial.
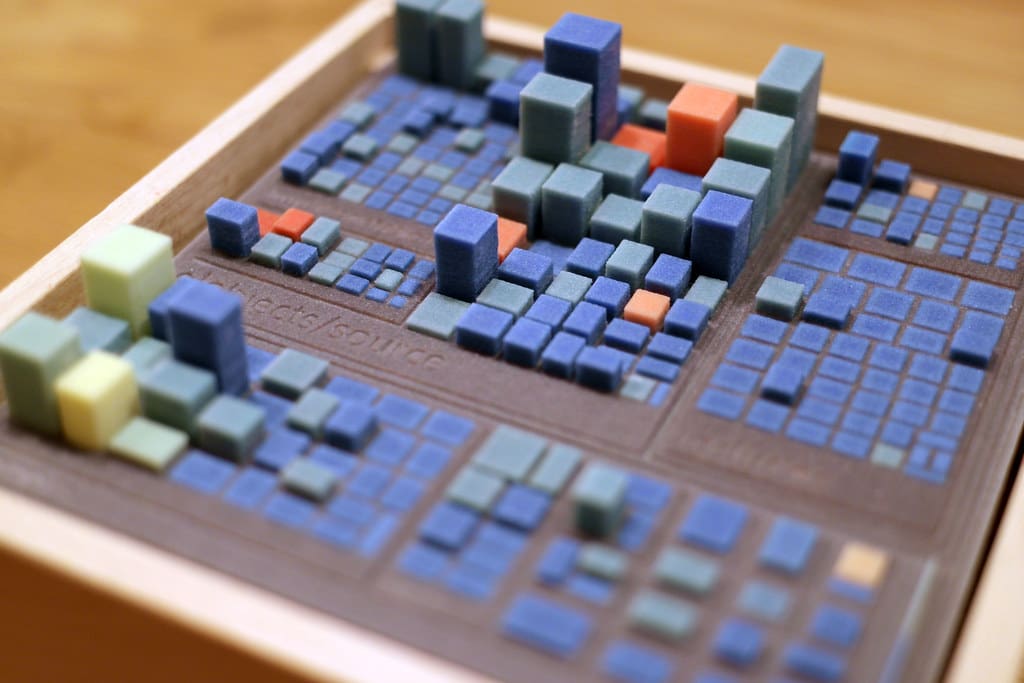

Advantages of 3D Printing in 3D Environments and Visualizations
Enhanced Communication: Physical models produced through 3D printing help convey complex ideas and designs more clearly than digital images alone. This is especially important in client presentations, educational settings, and collaborative projects.
Detailed Analysis and Testing: 3D printed models allow for hands-on testing and analysis of architectural, engineering, and scientific concepts. These models can be used to conduct airflow, structural integrity, and ergonomic studies, providing valuable insights that are difficult to achieve through digital simulations alone.
Increased Engagement: Interactive models captivate attention more effectively than 2D drawings or computer screens. In educational and public outreach contexts, 3D printed models engage users, making learning and exploration more compelling.
Customization and Flexibility: 3D printing allows for rapid customization of models based on evolving designs or requirements. Changes can be quickly implemented in the digital design and reprinted, providing flexibility throughout the development process.
Cost-Effectiveness: While traditional model-making can be labor-intensive and costly, 3D printing reduces these costs significantly. Once the digital model is created, it can be printed multiple times with relatively minimal additional cost.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in 3D Environments and Visualizations
Architectural Development: Architects use 3D printed models to visualize new projects and renovations, allowing clients and stakeholders to understand the spatial dynamics and aesthetic elements of a building before construction begins.
Urban Planning: City planners and developers utilize 3D printed models to visualize urban development projects, including infrastructure, landscaping, and large-scale developments, facilitating public consultations and decision-making processes.
Education and Training: In educational settings, 3D printed models of anatomical parts, historical artifacts, and scientific phenomena aid in teaching complex subjects in a more interactive and comprehensible manner.
Entertainment and Film: The entertainment industry uses 3D printing to create detailed props and set models, helping directors and designers visualize scenes and settings with a high degree of accuracy.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): 3D printing enhances VR and AR experiences by creating physical props or models that users can interact with, blending the virtual and real worlds for more immersive experiences.

Challenges in 3D Printing for 3D Environments and Visualizations
Material Limitations: The choice of materials in 3D printing can affect the detail, durability, and aesthetics of printed models. Finding the right materials that accurately mimic the desired properties can be challenging.
Scale and Detail: Achieving the correct scale and maintaining high levels of detail, especially for very complex or large models, can be difficult with current 3D printing technologies.
Technical Expertise: Effective use of 3D printing for visualization requires a combination of skills in 3D modeling, printing technology, and material science, necessitating specialized training and experience.
Integration with Digital Tools: Seamlessly integrating 3D printed models with digital visualization tools requires compatible software and hardware, which can involve significant setup and coordination.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for 3D Environments and Visualizations
As 3D printing technology continues to advance, its integration with 3D visualization tools is expected to become more sophisticated and widespread. Future developments may include enhanced printing resolution, faster production times, and the use of multi-material printing capabilities that can mimic a variety of textures and colors more accurately.
3D printing is transforming the landscape of 3D environments and visualizations, offering tools that enhance realism, interaction, and understanding across multiple disciplines. By providing a tangible connection to digital models, 3D printing not only improves communication and analysis but also enriches the user experience, making it an invaluable component in modern visualization strategies. As technology evolves, the possibilities for innovation and integration in 3D printing will continue to expand, further bridging the gap between virtual and physical worlds.