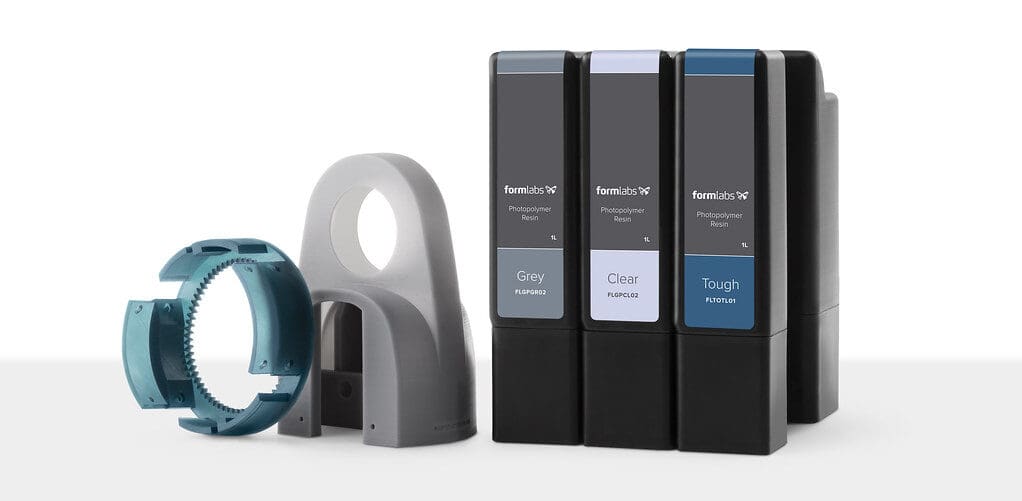
In the world of 3D printing, particularly within technologies like Stereolithography (SLA) and Digital Light Processing (DLP), photopolymer resin cartridges play a pivotal role in the efficient and effective delivery of materials needed for the printing process. These cartridges are designed to store, protect, and dispense photopolymer resins that are cured by ultraviolet (UV) light to form solid 3D objects. This article explores the importance, functionality, and maintenance of photopolymer resin cartridges, emphasizing their role in enhancing print quality, simplifying material handling, and ensuring consistency in 3D printing operations.
Importance of Photopolymer Resin Cartridges in 3D Printing
Material Quality Preservation: Resin cartridges are specifically designed to shield photopolymer resins from environmental factors such as light exposure and air, which can degrade the resin’s quality and affect its curing properties.
Precision in Dispensing: Cartridges allow for precise and controlled dispensing of resin, reducing waste and ensuring that the right amount of material is used for each print, enhancing both economic efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Ease of Use: Designed for user convenience, resin cartridges can be easily installed, replaced, and maintained without direct contact with the resin, minimizing the risk of contamination and exposure to potentially hazardous materials.
Consistency and Reliability: Using cartridges helps maintain consistency in the printing process, as each cartridge is pre-filled with a measured quantity of resin formulated to achieve optimal results, ensuring reliability and repeatability in print quality.
Components of Photopolymer Resin Cartridges in 3D Printers
Resin Container: The primary component where the resin is stored, typically made from a material that is compatible with the resin and resistant to UV light to prevent premature curing.
Dispensing Mechanism: Includes valves or nozzles that control the flow of resin out of the cartridge, designed to prevent leaks and ensure a smooth, consistent flow during the printing process.
Integrated Chips or Sensors: Many cartridges are equipped with chips or sensors that communicate with the printer, providing information about the type of resin, the quantity remaining, and other data to optimize print settings automatically.
Sealing Elements: Ensures that the resin remains free from contamination and prevents exposure to air, which can introduce impurities or cause unwanted polymerization.
Installation and Calibration of Photopolymer Resin Cartridges
Proper Installation: Ensuring that resin cartridges are correctly installed is crucial for their effective operation. This includes making sure that they are securely connected to the printer’s dispensing system and that there are no leaks.
Calibration: Depending on the printer model, calibrating the amount of resin dispensed for specific print jobs may be necessary. This helps in maintaining precision in resin usage and reducing material wastage.
Testing: Initial tests after installing a new cartridge or switching resin types are essential to ensure that the printer adjusts correctly for the resin’s properties, verifying that the flow rate and polymerization are as expected.
Maintenance and Optimization of Photopolymer Resin Cartridges
Regular Cleaning: Keeping the dispensing nozzles and mechanisms clean is crucial to prevent clogging and ensure smooth operation. This might involve running cleaning cycles with specialized solutions recommended by the manufacturer.
Storage Conditions: Store resin cartridges in a cool, dark place to prevent accidental exposure to light or heat, which could compromise the resin’s quality.
Regular Inspections: Check cartridges regularly for any signs of damage or leaks, as these can lead to resin wastage and potentially messy cleanup operations.
Firmware Updates: For cartridges equipped with chips or sensors, keeping the printer’s firmware updated ensures compatibility and optimal functionality.
Challenges and Solutions
Resin Viscosity Management: Handling different viscosities can be challenging, as thicker resins may require different dispensing pressures or temperatures. Adjusting printer settings and regularly cleaning the dispensing mechanisms can help manage this issue.
Cartridge Compatibility: Not all resins are compatible with every type of printer or cartridge system. Using only recommended or approved resin types can avoid issues with print quality or hardware compatibility.
Environmental Responsibility: Disposal of resin cartridges should be handled with care to minimize environmental impact. Recycling programs or returning used cartridges to the manufacturer for refilling can be effective strategies.
Photopolymer resin cartridges are indispensable components in the SLA and DLP 3D printing ecosystem, offering significant advantages in terms of material quality management, user safety, and operational efficiency. Effective management and meticulous maintenance of these cartridges are essential for maximizing the capabilities of 3D printers and ensuring the production of high-quality, consistent, and reliable printed products. Understanding and optimizing the function and maintenance of photopolymer resin cartridges will enable users to achieve improved operational reliability and enhanced print quality, leveraging the full potential of advanced 3D printing technology.