In the world of 3D printing, especially in technologies like Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), and Digital Light Processing (DLP), the optical system plays a crucial role. This system, composed of a series of lenses, mirrors, and other optical components, directs and focuses light precisely to cure or sinter materials in fine detail. This article explores the importance, functionality, and maintenance of the optical system in 3D printing, highlighting its role in achieving high-resolution, accurate, and aesthetically superior printed products.
Importance of the Optical System in 3D Printing
High Precision and Resolution: The optical system enables printers to achieve extremely fine details and high accuracy by precisely focusing light or laser beams to the exact points where material needs to be cured or sintered.
Material Processing Efficiency: Properly configured optical systems optimize the delivery of energy to the material, whether for curing resin or sintering powder, which enhances the efficiency of the 3D printing process.
Quality and Consistency: The precision of the optical system ensures consistent quality across the build area, resulting in uniformly cured or sintered parts with fewer defects.
Adaptability: Advanced optical systems can adjust focus and intensity dynamically, accommodating different materials and complex geometries without the need for manual intervention.
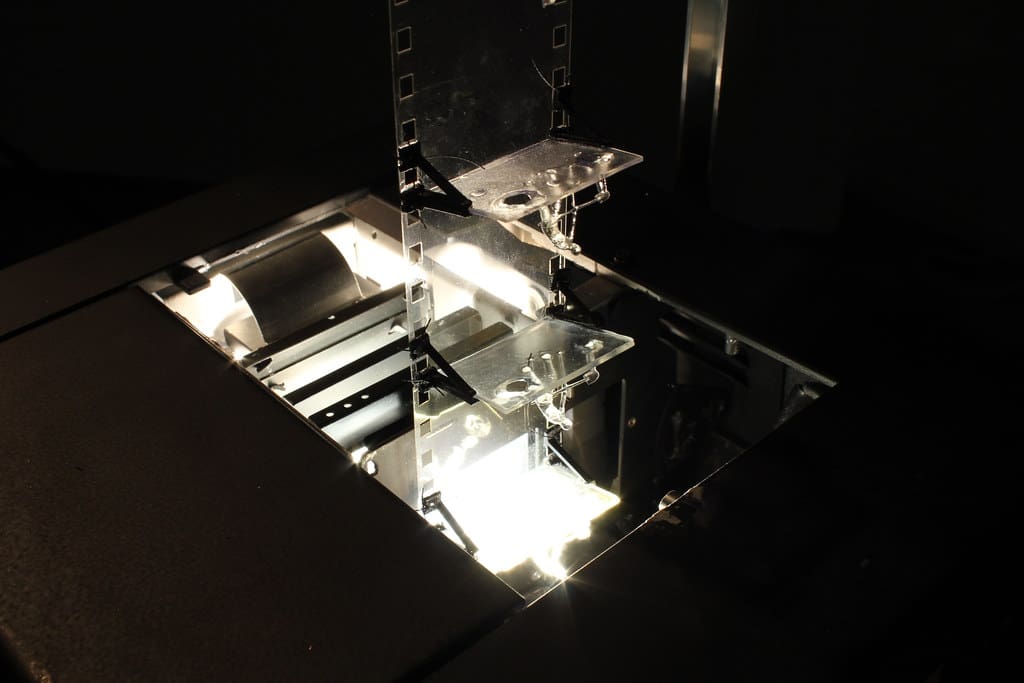
Components of the Optical System in 3D Printers
Laser or Light Source: The primary source of energy, which can be a UV laser, LED, or other light sources, depending on the printing technology.
Mirrors: Used to direct the beam path. In systems like SLA and SLS, mirrors, often galvanometer-mounted, allow for rapid and precise positioning of the laser beam across the print surface.
Lenses: Focus or spread the light to achieve the desired intensity and resolution at the material surface. Lenses must be chosen and aligned to match the specific wavelength and power output of the light source.
Beam Splitters and Modulators: These components control the intensity and distribution of light, crucial for managing how energy is applied during the printing process.
Optical Sensors: Monitor and adjust the light’s focus, intensity, and path in real-time, ensuring optimal interaction with the material and maintaining the precision of the print process.
Installation and Calibration of the Optical System
Proper Installation: Ensuring that all optical components are correctly installed and aligned is crucial. This includes checking that lenses and mirrors are clean, free from defects, and precisely positioned according to design specifications.
Calibration: The optical system must be calibrated to ensure that the focus and intensity of the light meet the requirements of the printing material and desired resolution. Calibration typically involves adjusting the lens positions and tuning the mirrors to achieve the optimal light path.
Testing: Initial and routine testing is essential to ensure that the optical system performs consistently under different operating conditions and over time. This may involve printing test patterns to verify that the light accurately reaches all intended areas of the build platform.
Maintenance and Optimization of the Optical System
Regular Cleaning: Optical components should be cleaned regularly to remove dust and residues that can scatter or block light, leading to inaccuracies in the printing process.
Component Inspections: Regular inspections of lenses, mirrors, and other optical parts are necessary to check for scratches, alignment issues, or other damage that could impair function.
Replacement of Worn Parts: Optical components can degrade over time, especially under intense light exposure. Replacing worn parts promptly ensures consistent printing performance.
Firmware and Software Updates: Keeping software updated can help in managing the optical system more effectively, potentially introducing new functionalities or improving existing calibration and control algorithms.
Challenges and Solutions
Thermal Effects: High-power lasers and light sources can generate significant heat, which might affect the alignment and focus of optical components. Integrating efficient cooling systems and using thermal-resistant materials can mitigate these effects.
Light Scattering: Unintended light scattering can reduce the precision of the print. Using high-quality optical components and ensuring proper sealing and cleanliness can reduce scattering.
System Complexity: The optical system’s complexity requires precise engineering and integration. Utilizing modular designs and automated calibration tools can simplify maintenance and adjustments.
The optical system is a critical component of many 3D printers, playing a key role in the accuracy, efficiency, and quality of the printing process. Proper management, regular maintenance, and careful calibration of the optical system are essential for maximizing the performance of 3D printers and ensuring the production of high-quality, reliable, and precise printed products. By thoroughly understanding and meticulously maintaining the optical system, manufacturers can achieve improved operational reliability and enhanced print quality, fully leveraging the capabilities of advanced 3D printing technology.