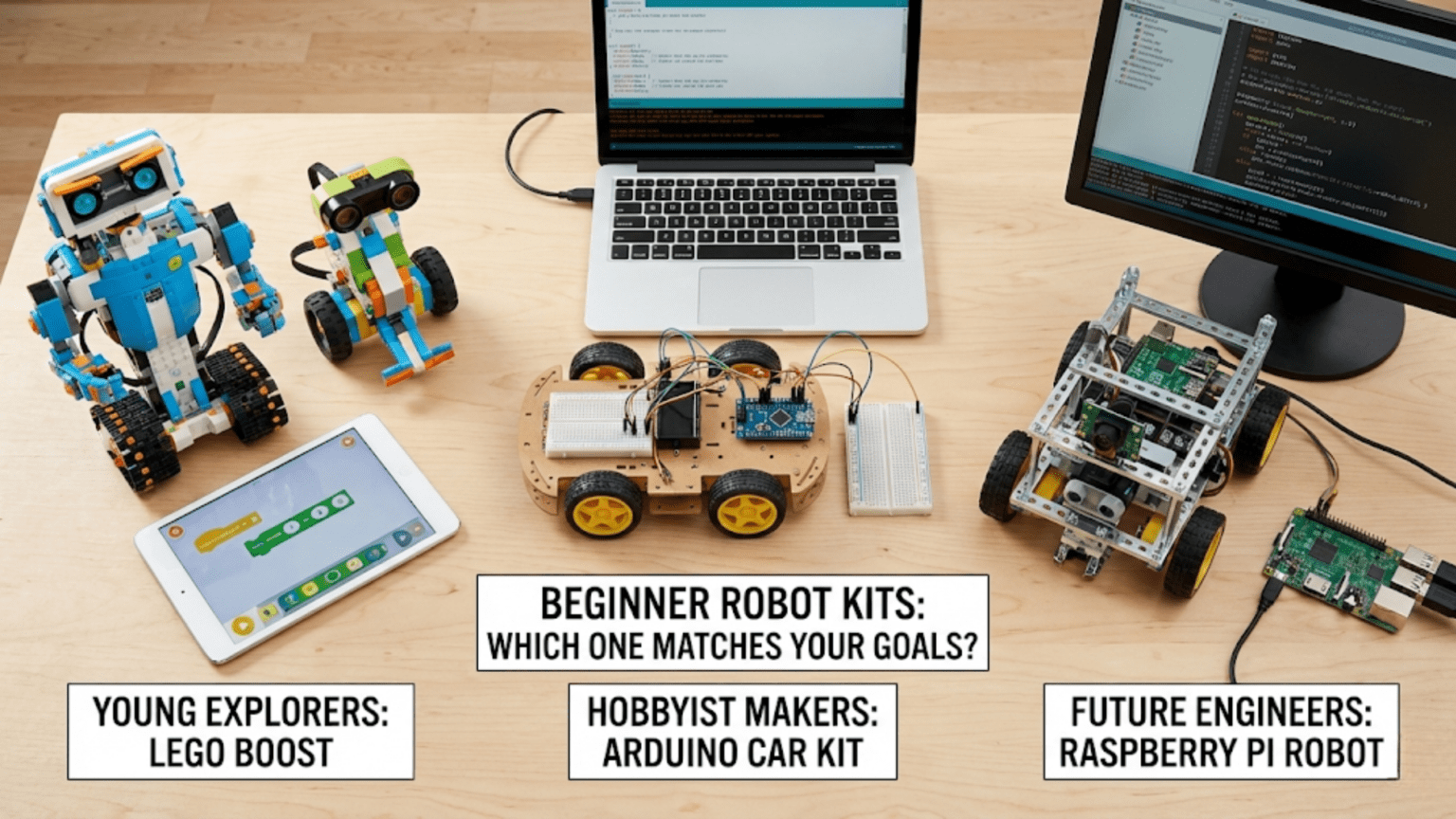
Walking into the world of robotics kit selection feels overwhelming when faced with dozens of options, each claiming to be perfect for beginners. Manufacturer websites showcase impressive capabilities, customer reviews praise various kits, and price points range from forty dollars to several hundred. Without clear criteria for evaluation, choosing your first robot kit becomes paralyzing decision-making where you might delay indefinitely or purchase something that frustrates rather than educates because it mismatches your actual needs and learning style.
The fundamental challenge in selecting beginner robot kits lies not in finding good options—many excellent kits exist—but rather in matching kit characteristics to your specific goals, background, constraints, and preferences. A kit perfect for a ten-year-old learning basic programming differs dramatically from one ideal for an adult with software experience wanting to explore hardware. A classroom teacher seeking kits for thirty students has different requirements than an individual hobbyist building at home. Budget constraints, available time, interest in specific robotics domains, and tolerance for technical complexity all influence which kit serves you best.
This article provides framework for evaluating beginner robot kits systematically rather than listing “the best kit” that might not suit your circumstances. You will learn what characteristics distinguish different kit categories, which factors matter most for various use cases, how to identify your own priorities, and finally examine specific popular kits through this analytical lens. This structured approach empowers you to make informed selection matching your unique situation rather than following generic recommendations that might serve others better than you.
Understanding Kit Categories and Approaches
Robot kits span a spectrum from highly integrated, beginner-friendly systems to component collections requiring significant assembly and programming. Recognizing where kits fall on this spectrum helps you match complexity to your readiness and goals.
Complete integrated kits provide everything needed including chassis, motors, sensors, controller, and software in single package. These kits typically include detailed instructions taking you from unboxing through completed robot capable of performing specific tasks. LEGO Mindstorms exemplifies this category, as do complete rover kits like mBot or various Arduino-based all-in-one systems. Integrated kits minimize decisions and sourcing challenges, letting you focus on learning rather than shopping for compatible parts. The tradeoff involves less flexibility and higher cost compared to modular approaches.
Platform-specific kits center on particular controllers like Arduino or Raspberry Pi, including that controller plus compatible sensors, motors, and accessories. These kits teach specific platform ecosystems while providing hardware to explore platform capabilities. Examples include Arduino starter kits bundled with sensors and motors, or Raspberry Pi kits with robot chassis and GPIO accessories. Platform-specific kits balance guidance with flexibility—you follow provided projects initially but can expand beyond kit contents using the same platform.
Component collections provide diverse sensors, motors, and parts without dictating specific robot designs. Rather than building particular robots, you experiment with components, learning their characteristics and combining them in ways you design. Elegoo and Freenove offer such collections, typically Arduino-compatible but emphasizing breadth of components over complete robot designs. These kits suit learners wanting to explore widely and design custom projects rather than following predefined paths.
Educational curriculum kits package robotics hardware with structured lesson plans, challenges, and learning materials aligned with educational standards. VEX IQ, LEGO Education sets, and various classroom-oriented packages emphasize pedagogical design as much as hardware quality. These kits cost more than hobby-focused alternatives but provide teaching resources reducing instructor burden and ensuring learning outcome alignment with educational goals.
Competition-focused kits prepare for specific robotics competitions like FIRST LEGO League, VEX competitions, or similar events. These kits include regulation-compliant hardware and design tools optimized for competition requirements. While usable for general learning, competition kits emphasize features mattering for competitive success—rugged construction, rapid reconfiguration, powerful motors—over features purely educational learners might prioritize.
Hybrid and advanced kits combine multiple technologies or target more experienced beginners. Kits incorporating both Arduino and Raspberry Pi, robots with computer vision, or platforms supporting multiple programming languages offer advanced capabilities for learners ready to tackle complexity. These kits require more prerequisite knowledge or learning effort but enable more sophisticated projects than pure beginner kits.
Critical Evaluation Criteria
Systematically evaluating kits across consistent criteria reveals which options best match your priorities. Different criteria matter more or less depending on your specific situation.
Learning objectives determine which kit capabilities align with what you want to learn. Want to understand electronics deeply? Kits requiring breadboard circuits and component selection teach electronics better than preassembled systems. Interested primarily in programming? Platform with rich software ecosystem and minimal hardware complexity focuses attention on code. Curious about mechanical design? Kits emphasizing construction and modification teach mechanical principles better than fixed-chassis systems. Clearly defining learning goals prevents choosing kits that teach topics you care little about while neglecting subjects you want to master.
Technical prerequisites affect which kits you can successfully use. Some kits assume no prior knowledge, providing complete instructions from absolute basics. Others expect familiarity with electronics concepts, programming fundamentals, or mechanical assembly. Honestly assessing your current knowledge prevents frustration from selecting kits assuming expertise you lack. However, slight stretch beyond current abilities promotes learning, so don’t restrict yourself only to kits well below your level.
Assembly complexity ranges from pre-built plug-and-play systems to extensive construction projects. Consider whether you enjoy building as part of learning or prefer focusing on programming and operation. Some learners find assembly deeply satisfying, others view it as frustrating barrier before interesting work begins. Match kit assembly requirements to your preferences and patience. Kits requiring soldering or permanent assembly commit you to specific configurations, while tool-free snap-together systems enable easy modification and experimentation.
Programming approach—visual blocks, simplified languages, or full programming environments—dramatically affects user experience. Young learners and programming novices benefit from visual programming removing syntax barriers. Experienced programmers often find visual programming frustratingly limited compared to text languages offering full expressiveness. Some kits support multiple programming approaches, providing growth path from visual blocks through text-based languages. Consider both current comfort level and desire to learn text programming when evaluating kit software.
Expandability determines whether you can grow beyond initial kit contents without replacing entire platform. Open ecosystems accepting diverse sensors, motors, and accessories allow continuous expansion matching skill development. Proprietary closed systems limit expansion to manufacturer’s offerings, potentially requiring complete platform changes when you outgrow included capabilities. For longer-term learning, expandable platforms provide better value despite potentially higher initial complexity.
Documentation quality separates frustrating experiences from successful learning. Well-documented kits include clear instructions, troubleshooting guides, example projects, and active community forums. Poor documentation leaves you struggling unnecessarily even with capable hardware. Research documentation thoroughly—read reviews mentioning instruction quality, browse manufacturers’ tutorial websites, and search for community content supporting the kit. Good documentation multiplies kit value enormously.
Community size affects available help, project examples, and shared knowledge. Popular platforms with large communities provide abundant tutorials, forums answering questions, and inspiration from others’ projects. Niche platforms might offer less community support, requiring more self-sufficiency. For beginners particularly, strong community support prevents getting stuck permanently on solvable problems.
Cost extends beyond initial purchase to include expansion components, replacement parts, and software. Some platforms require expensive proprietary parts for expansion while others use commodity components costing far less. Consider total cost of ownership across your expected usage period, not just initial kit price. Sometimes more expensive kits with open ecosystems cost less long-term than cheaper proprietary systems requiring expensive expansion parts.
Age appropriateness matters for young learners. Kits designed for children include safety considerations, appropriate complexity, and engaging themes. Adult learners might find kid-oriented kits patronizing or limiting. Conversely, kits targeting adults might overwhelm or bore children. Match kit design intent to actual user age and maturity.
Matching Kits to Common Learning Profiles
Rather than recommending single “best” kit, examining which kits suit common learner profiles helps you identify where you fit and what works for similar situations.
Young children (ages 6-10) learning basic concepts benefit from highly integrated, visual systems emphasizing creativity over technical depth. LEGO WeDo, Dash & Dot, or simple programmable toys teach sequencing, problem-solving, and basic robotics without overwhelming complexity. These kits use tablet or computer interfaces with visual programming, provide immediate feedback through robot behaviors, and emphasize playful exploration over formal learning. Durability matters as young children handle equipment roughly. Success at this level builds confidence and interest supporting later technical depth.
Tweens and early teens (ages 10-14) ready for more challenge but still benefiting from structure find sweet spot in platforms like LEGO Mindstorms, VEX IQ, or Arduino-based kits with comprehensive tutorials. Visual programming with text option supports gradual sophistication. Construction elements engage hands-on learning preferences. Competition frameworks through FIRST LEGO League or VEX competitions provide motivation and social learning. Kits in this category balance accessibility with genuine capability, avoiding both oversimplification and overwhelming complexity.
High school students with technical interest and adequate frustration tolerance can tackle Arduino or Raspberry Pi platforms with appropriate support. Pure Arduino starter kits teach electronics and embedded programming. Raspberry Pi kits emphasize computing and software with some hardware interaction. Combined kits bridge both worlds. Students at this level benefit from platforms exposing technical reality rather than abstracting it away. Text-based programming becomes essential rather than optional. Projects can tackle real applications beyond purely educational demonstrations.
Adult beginners without technical background appreciate complete kits with exceptional documentation and supportive communities. Arduino-based integrated rovers, comprehensive Raspberry Pi robot kits, or educational platforms designed for self-teaching work well. Adults bring discipline and motivation children sometimes lack but may carry anxiety about technical subjects from negative school experiences. Kits removing frustration barriers through clear instructions and reliable hardware help adults overcome confidence issues while building genuine skills.
Software developers entering hardware need platforms emphasizing electronics and mechanical systems rather than software complexity. Arduino platforms teaching circuit basics, sensor interfacing, and motor control fill knowledge gaps. These learners tolerate software complexity easily but struggle with hardware concerns. Kits bundling necessary electronic components with clear hardware tutorials help software experts develop hardware competence without fighting software also.
Hobbyist makers with general technical competence but no specific robotics background benefit from flexible platforms offering both guidance and freedom. Component collections like Elegoo or Freenove kits provide diverse parts for exploration. Platform documentation offers starting projects while component variety enables custom designs. These learners want enough structure to get started but freedom to pursue evolving interests without platform limitations.
Educators purchasing for classrooms need robust, well-documented systems with curriculum integration and professional development. Educational editions of LEGO Mindstorms, VEX systems, or specialized educational robotics platforms justify higher costs through teacher resources, classroom-tested lessons, and alignment with standards. Classroom purchasing decisions weigh factors beyond individual learning—equipment durability, simultaneous student capacity, and teaching preparation time matter enormously.
Specific Kit Recommendations by Category
With evaluation framework established, examining specific popular kits through this analytical lens helps you understand what various options offer and which might suit your goals.
Arduino Starter Kit represents comprehensive introduction to Arduino ecosystem. Includes Arduino Uno board, breadboard, sensors, LEDs, motors, and components for fifteen guided projects. Excellent documentation through official Arduino project book provides gentle introduction to electronics and programming. Cost around eighty dollars balances affordability with quality. Best for learners wanting electronics understanding, comfortable with breadboard circuits, and interested in Arduino’s rich ecosystem. Less suitable for those preferring pre-assembled systems or focusing primarily on robot mobility over electronics principles.
Elegoo Arduino robotics kits combine Arduino Uno compatible boards with chassis, motors, sensors, and remote control. Various models range from forty to one hundred dollars offering different sensor packages. Reasonable documentation with online tutorials. Component quality acceptable for learning though not premium. Excellent value for budget-conscious learners wanting complete robots. Trade-offs include lower-quality printed instructions and less community support than pure Arduino kits. Works well for hands-on learners comfortable following diagrams to assemble electronics.
mBot educational robot presents fully integrated system with Scratch-based visual programming and Arduino-compatible processor. Tool-free assembly, included sensors, and pre-built chassis simplify physical construction. Extensive online lessons and community content support learning. Costs around one hundred dollars. Excellent for elementary and middle school students or beginners preferring construction simplicity. Extension packs add capabilities as skills grow. Limitations include proprietary components for expansion and eventual outgrowing visual programming environment.
Raspberry Pi robot kits vary widely as multiple manufacturers create Pi-based robots. GoPiGo, AlphaBot, and various chassis kits package Pi with motors, sensors, and robot-specific hardware. Prices range from seventy-five to two hundred fifty dollars depending on included capabilities. Best for learners interested in computer vision, networking, or AI who need Pi’s computational power. Requires more software configuration than Arduino alternatives. Documentation quality varies by manufacturer—research carefully before purchase.
LEGO Mindstorms EV3 or newer Robot Inventor provides premium integrated experience with sophisticated capabilities. Tool-free LEGO construction, robust hardware, visual and Python programming, comprehensive curriculum materials. Costs three hundred to four hundred dollars representing significant investment. Exceptional for classroom use, young learners, families, and hands-on learners. Strong competition framework through FIRST LEGO League. Limitations include cost, proprietary ecosystem, and eventual platform limitations for advanced users. Best considered multi-year investment rather than quick learning platform.
VEX IQ robotics systems target classroom and competition use with robust construction, capable hardware, and educational resources. Costs three hundred plus dollars for complete kits. Excellent durability and support for collaborative learning. Strong competition pathway through VEX Robotics Competition. Programming options from visual blocks through text-based languages. Better suited to educational institutions than individual hobbyists due to cost and educational focus. Exceptional for structured learning environments with long-term educational goals.
Raspberry Pi AI Kit bundles Pi with camera and AI accessories for machine learning exploration. Costs approximately one hundred fifty to two hundred dollars. Specifically targets computer vision and AI learning rather than general robotics. Best for learners with programming background interested in perception and learning algorithms. Requires substantial software knowledge and interest in data science aspects of robotics. Less suitable for those wanting immediate robot mobility and basic mechanical understanding.
Makeblock Ultimate 2.0 offers ten-in-one platform supporting diverse robot configurations. Premium components and construction quality, comprehensive documentation. Costs approximately three hundred fifty dollars. Metal construction provides durability and authentic mechanical experience. Arduino and Raspberry Pi compatible enabling platform growth. Best for serious hobbyists willing to invest in long-term platform. Cost and complexity inappropriate for casual interest or young children.
Red Flags and What to Avoid
Understanding problematic kit characteristics helps you avoid disappointing purchases that waste money and discourage learning.
Poor documentation represents fatal flaw that ruins otherwise capable kits. Vague instructions, missing steps, errors in diagrams, and lack of troubleshooting guidance leave you struggling unnecessarily. Before purchasing, research documentation quality through reviews specifically mentioning instructions. Well-documented kits clearly state what they teach, provide sequential learning, and help you recover from mistakes. No amount of hardware quality compensates for unusable documentation.
Proprietary ecosystems that lock you into single manufacturer’s expensive expansion parts reduce long-term value. While proprietary systems might offer integration advantages, the inability to use standard components limits growth and increases costs. Prefer kits compatible with common standards—Arduino-compatible processors, standard motors and sensors, and open software. This compatibility provides freedom to expand economically beyond initial kit.
Unrealistic capability claims suggesting kits teach “advanced AI” or “professional robotics” through simple projects indicate marketing over substance. Quality kits honestly describe learning outcomes and required skill levels. Exaggerated claims often disguise inadequate kits with borrowed authority. Trust kits with specific, realistic learning objectives over those promising everything.
Low-quality components that break easily, provide inconsistent results, or fail quickly frustrate learning and waste money. While budget constraints necessitate accepting component quality tradeoffs, some kits cut costs through unusably poor components. Reviews mentioning broken parts, unreliable sensors, or stripped gears signal problematic quality. Balance cost savings against frustration from replacing failed parts repeatedly.
Insufficient content where kits provide hardware without adequate projects, tutorials, or learning pathway leave you uncertain how to proceed. Opening a box of components without guidance about what to build or how to learn wastes purchase. Kits should include either comprehensive printed materials or clear directions to online resources providing learning structure. Hardware alone, however capable, provides limited educational value without teaching materials.
Abandoned platforms where manufacturers have discontinued support, stopped updating software, or ceased producing compatible parts threaten kit longevity. While deals on discontinued kits might seem attractive, ensure adequate documentation and community support continue even without manufacturer involvement. Active platforms receive bug fixes, compatibility updates, and new content. Abandoned platforms eventually become unusable as software platforms evolve incompatibly.
Age mismatches where kits designed for different age groups frustrate users. Kits oversimplified for your level bore and waste money on capabilities you immediately outgrow. Conversely, kits too advanced frustrate and discourage. Carefully assess kit design intent and match to actual user maturity and technical readiness.
Making Your Decision
With evaluation framework, learner profiles, and specific kit knowledge, you can now make informed kit selection matching your unique circumstances.
List your priorities explicitly—learning goals, budget limits, time available, space constraints, and interest areas. Rank these priorities recognizing you likely cannot optimize everything simultaneously. Clear priorities guide tradeoff decisions. Someone prioritizing minimum cost accepts limitations that budget permits. Someone prioritizing depth of learning invests more in comprehensive systems.
Research thoroughly before purchasing. Read multiple reviews from different sources. Watch unboxing and tutorial videos. Browse manufacturer support sites assessing documentation quality. Search for troubleshooting discussions revealing common problems. Visit robotics forums asking current users about experiences. This research prevents impulsive purchases you regret.
Start conservative rather than overcommitting immediately. Unless certain about requirements and commitment, favor less expensive options initially. Success with modest kits justifies investing in premium systems. Discovering robotics does not engage you as expected costs less when initial investment was minimal. Many roboticists progress through multiple platforms as skills and interests evolve rather than finding perfect permanent platform immediately.
Consider buying used for expensive kits if budget constrains. LEGO Mindstorms, VEX, and similar premium systems maintain resale value, creating used market. Purchasing used reduces entry cost significantly while accessing capable systems. Verify completeness and functionality before buying used, but recognize used equipment teaches identically to new while costing less.
Plan your growth path before purchasing. Will this kit serve your learning for months or years? What comes next when you outgrow it? Does the platform enable gradual expansion or require complete platform change? Anticipating progression prevents prematurely investing in platforms you will quickly outgrow or avoid platforms that never provide needed capabilities.
Trust your instincts about what excites you. Analytical framework guides decisions but genuine interest determines success. If particular kit fascinates you despite analytical concerns, that enthusiasm might outweigh limitations. Conversely, analytically perfect kits that do not excite probably will not maintain motivation. Excitement and curiosity drive learning more than optimal specifications.
Getting Started After Kit Arrival
Selecting appropriate kit represents only first step. Maximizing kit value requires deliberate approach to initial projects and learning progression.
Follow provided tutorials completely before attempting custom projects. Tutorials teach platform capabilities, common patterns, and proper techniques. Skipping tutorials to immediately attempt custom designs often results in frustration from lacking foundation. Complete tutorials build competence and confidence supporting successful custom work later.
Work systematically through complexity progression rather than jumping to advanced projects. Each project typically introduces new concepts building on previous work. Racing ahead creates gaps in understanding that undermine later projects. Methodical progression might feel slow initially but prevents confusion and provides solid foundation.
Document your work through photos, notes, and saved programs. Documentation helps you return to projects later, provides reference when similar challenges arise, and creates portfolio demonstrating progress. Regular documentation develops professional habits valuable beyond robotics learning.
Join community forums and engage with other learners. Communities provide help when stuck, inspiration for next projects, and social motivation maintaining engagement. Lurking initially to understand community norms, then gradually participating through asking questions and eventually helping newer users creates valuable learning network.
Plan expansion strategically based on emerging interests and skills. As you complete kit projects, interests specific to certain robotics domains develop. Use these interests to guide expansion purchases—additional sensors exploring particular perception capabilities, different motors enabling new robot types, or accessories supporting identified next challenges. Strategic expansion avoids accumulating random components while building capabilities matching evolving goals.
Your beginner robot kit journey begins with careful selection matching kit characteristics to your unique goals, constraints, and learning style. By understanding kit categories, evaluating options systematically, recognizing your learner profile, and making informed choices, you select platforms that educate effectively rather than disappoint through mismatched expectations. The right kit for you might differ dramatically from what suits others, and that individuality makes careful selection worth the analytical effort. Your thoughtfully chosen kit becomes gateway into robotics, launching learning journey extending far beyond that initial platform into increasingly sophisticated and exciting robotic explorations.