Machine Learning (ML) is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on enabling machines to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. Unlike traditional software that follows fixed instructions, machine learning systems analyze data, identify patterns, and make decisions or predictions. This adaptability has led to machine learning becoming essential in a variety of applications, from recommendation systems and fraud detection to self-driving cars and medical diagnostics.
Machine learning can be described as the science of enabling computers to solve problems by learning from examples. This means that the performance of an ML model improves as it is exposed to more data. Given the vast amounts of data available today, machine learning has become increasingly valuable in helping organizations and researchers unlock insights, automate processes, and improve decision-making.
This article provides an introduction to machine learning, covering its main types, essential algorithms, and the steps involved in building and evaluating models.
Types of Machine Learning
Machine learning is typically categorized into three main types, each suited to different types of tasks and data:
1. Supervised Learning
In supervised learning, the model is trained on labeled data, meaning each data point has an associated output. The goal is to learn the mapping between input variables and the output. This type of learning is commonly used for tasks where the outcome is known, such as predicting house prices or classifying emails as spam or not.
- Examples of Supervised Learning:
- Classification: Predicting categorical outcomes, like whether an email is spam or not. Common algorithms include Logistic Regression, Decision Trees, and Support Vector Machines.
- Regression: Predicting continuous outcomes, such as predicting the temperature or stock prices. Linear Regression and Ridge Regression are popular algorithms used for regression tasks.
2. Unsupervised Learning
In unsupervised learning, the model is trained on unlabeled data, meaning there are no predefined categories or outcomes. The model’s objective is to find hidden patterns or groupings within the data. Unsupervised learning is valuable for exploring data structures and finding relationships, especially when labels are not available.
- Examples of Unsupervised Learning:
- Clustering: Grouping data points with similar characteristics, used in applications like customer segmentation. K-Means and Hierarchical Clustering are widely used clustering algorithms.
- Dimensionality Reduction: Reducing the number of features in data while retaining essential information, making it easier to visualize or process. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and t-SNE are popular techniques in this area.
3. Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning is a more complex type of learning where an agent learns by interacting with its environment and receiving feedback in the form of rewards or penalties. The goal is to maximize cumulative rewards over time by learning the best sequence of actions. Reinforcement learning is commonly used in robotics, gaming, and autonomous driving, where the agent makes decisions in dynamic environments.
- Examples of Reinforcement Learning:
- Game Playing: Reinforcement learning algorithms like Deep Q-Learning have been used to train AI to play games like chess and Go.
- Robotics: Robots can use reinforcement learning to learn tasks such as navigation or object manipulation, making it highly useful in manufacturing and logistics.
Essential Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning includes a variety of algorithms, each suited to specific types of tasks. Here’s an introduction to some foundational algorithms across supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning:
1. Linear Regression
Linear Regression is a fundamental algorithm in supervised learning used for predicting continuous outcomes. It models the relationship between the input (independent variable) and output (dependent variable) by fitting a straight line through the data.
- Formula:
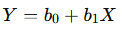
- Where Y is the predicted value, X is the input variable, b0 is the intercept, and b1 is the slope of the line.
- Application: Linear regression is commonly used in areas like finance (e.g., predicting stock prices) and economics (e.g., predicting market demand).
2. Decision Trees
Decision Trees are versatile algorithms used for both classification and regression tasks. A decision tree splits data into subsets based on feature values, creating branches until reaching a decision. Each branch represents a possible decision path based on the data’s features, and the end “leaves” represent outcomes.
- How It Works: Decision trees use criteria like Gini impurity or entropy to determine the best feature splits at each node.
- Application: Decision trees are used in credit scoring, where each node might represent a financial criterion, helping to determine if an applicant is creditworthy.
3. k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN)
The k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN) algorithm is a simple, instance-based learning algorithm used primarily for classification tasks. The algorithm classifies a data point based on the majority class of its closest neighbors.
- How It Works: The user specifies a value for kkk (the number of neighbors), and the algorithm assigns the new data point to the most common class among the kkk closest points.
- Application: k-NN is popular in recommendation systems and is often used to find similar products or users based on proximity in feature space.
4. Support Vector Machines (SVM)
Support Vector Machines (SVM) are powerful algorithms for both classification and regression. SVMs work by finding the optimal hyperplane that separates data points from different classes with the maximum margin.
- How It Works: SVMs maximize the margin between classes, providing a clear boundary between different groups of data points. They are particularly effective when there’s a clear separation between classes.
- Application: SVMs are commonly used in text classification, such as email filtering and sentiment analysis.
5. k-Means Clustering
k-Means Clustering is a widely used algorithm for unsupervised learning. It groups data points into kkk clusters based on similarity, minimizing the distance between each point and the centroid of its assigned cluster.
- How It Works: The algorithm iteratively assigns data points to the nearest cluster center and updates cluster centers based on the mean of points within each cluster.
- Application: k-Means is used in customer segmentation, where customers are grouped based on buying behavior or demographics.
6. Q-Learning (Reinforcement Learning)
Q-Learning is a popular reinforcement learning algorithm that uses a “Q-table” to store and update the expected rewards for actions taken in different states. The agent explores actions, receives rewards, and learns which actions yield the highest cumulative rewards over time.
- How It Works: The agent uses the Q-table to select the action with the highest reward value, progressively learning an optimal policy through trial and error.
- Application: Q-Learning is often used in gaming (e.g., training AI to play chess) and robotics for navigation tasks.
Steps in Building a Machine Learning Model
The process of developing a machine learning model is systematic, involving several key steps to ensure the model is effective and generalizes well to new data. Here’s an overview of the steps involved:
1. Define the Problem
The first step is to define the problem and identify the objective, which can vary from classification to regression or clustering. For instance, predicting whether a customer will churn is a classification problem, while forecasting sales is a regression problem.
2. Collect and Explore Data
Data is essential for building a machine learning model, and collecting high-quality, relevant data is crucial. Once collected, exploratory data analysis (EDA) helps you understand the structure, relationships, and potential issues in the data, such as missing values or outliers.
- Tools for EDA: Visualization tools like Matplotlib and Seaborn in Python can help visualize data distributions and relationships.
3. Preprocess the Data
Data preprocessing involves cleaning and transforming raw data into a suitable format for machine learning algorithms. This may include handling missing values, scaling numerical data, and encoding categorical variables.
- Example: In a dataset with categorical variables like “Gender” (Male/Female), label encoding or one-hot encoding converts these categories into numerical values for the model.
4. Split the Data
To evaluate the model’s performance, it’s necessary to split the data into training and testing sets. The training set is used to train the model, while the testing set assesses how well the model generalizes to unseen data.
- Typical Split: A common split is 70% for training and 30% for testing, but this can vary based on the dataset size and specific requirements.
5. Choose a Model
Selecting the right model depends on the problem type and data. For classification tasks, you might consider algorithms like decision trees or SVM, while for regression tasks, linear regression or ridge regression may be more appropriate.
6. Train the Model
Training the model involves feeding the training data into the algorithm so it can learn patterns. The algorithm adjusts its parameters during this process to minimize prediction errors.
7. Evaluate the Model
After training, evaluate the model on the test data. Evaluation metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score provide insights into how well the model performs. For regression, metrics like Mean Absolute Error (MAE) or Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) are commonly used.
Model Evaluation Techniques
After building and training a model, it’s crucial to evaluate its performance to ensure it meets the desired accuracy and generalization standards. Evaluation metrics provide insights into different aspects of a model’s accuracy and effectiveness, which vary depending on whether it’s a classification or regression problem.
1. Evaluation Metrics for Classification
Classification models aim to categorize data points into distinct classes. Here are some common metrics used to evaluate classification models:
Accuracy: Measures the percentage of correct predictions over the total predictions. Although accuracy is straightforward, it can be misleading if the data is imbalanced (e.g., when one class significantly outweighs others).
- Formula:

from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print("Accuracy:", accuracy)Precision: Indicates the proportion of positive predictions that were correct, making it valuable when minimizing false positives is crucial.
- Formula:

from sklearn.metrics import precision_score
precision = precision_score(y_test, y_pred, average='binary')
print("Precision:", precision)Recall: Shows the proportion of actual positives that the model correctly identified, useful when it’s essential to catch all positive cases, such as in medical diagnoses.
- Formula:

from sklearn.metrics import recall_score
recall = recall_score(y_test, y_pred, average='binary')
print("Recall:", recall)F1-Score: The harmonic mean of precision and recall, balancing the two metrics. F1-Score is particularly valuable for datasets where you need to manage both false positives and false negatives.
- Formula:

from sklearn.metrics import f1_score
f1 = f1_score(y_test, y_pred, average='binary')
print("F1-Score:", f1)ROC-AUC Score: The ROC (Receiver Operating Characteristic) curve illustrates the trade-off between true positive rate and false positive rate at various thresholds. The AUC (Area Under Curve) score measures the area under the ROC curve, where a higher AUC indicates better discrimination between classes.
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
roc_auc = roc_auc_score(y_test, model.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1])
print("ROC-AUC Score:", roc_auc)2. Evaluation Metrics for Regression
Regression models predict continuous outcomes, and the following metrics help assess their performance:
Mean Absolute Error (MAE): Measures the average magnitude of prediction errors, providing a straightforward view of accuracy. Lower values indicate better performance.
- Formula:
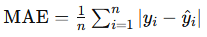
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error
mae = mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred)
print("Mean Absolute Error:", mae)Mean Squared Error (MSE): Similar to MAE, but squares the errors before averaging. MSE penalizes larger errors more heavily, making it valuable when large deviations are particularly costly.
- Formula:

from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
print("Mean Squared Error:", mse)Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE): The square root of MSE, which brings the metric back to the original units of the target variable.
rmse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred, squared=False)
print("Root Mean Squared Error:", rmse)R² Score: Also known as the coefficient of determination, R² measures the proportion of variance in the target variable that is predictable from the features. An R² score closer to 1 indicates a better fit.
- Formula:
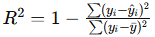
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
r2 = r2_score(y_test, y_pred)
print("R² Score:", r2)These metrics allow data scientists to assess different aspects of model performance, which is essential for determining a model’s effectiveness.
Overfitting and Underfitting
Two common challenges in machine learning are overfitting and underfitting, which occur when a model’s complexity doesn’t align well with the data.
- Overfitting: This happens when a model learns the training data too well, capturing noise and details that don’t generalize to new data. Overfitted models perform well on training data but poorly on test data, as they fail to generalize.
- Solution: Reducing the model’s complexity (e.g., reducing tree depth in decision trees), using regularization techniques, or adding more training data can mitigate overfitting.
- Underfitting: This occurs when a model is too simple to capture the underlying patterns in the data, resulting in poor performance on both training and test data.
- Solution: Increase model complexity (e.g., adding more layers in neural networks) or select a more sophisticated algorithm to address underfitting.
Hyperparameter Tuning
Hyperparameters are settings that control the behavior of machine learning algorithms but are not learned from the data. Tuning these hyperparameters can significantly improve model performance, and it typically involves testing different combinations to find the optimal configuration.
1. Grid Search
Grid search is a systematic approach to hyperparameter tuning, where all possible combinations of specified hyperparameters are tested. Although it can be computationally intensive, grid search ensures that the best hyperparameter configuration is found.
- Example: Using Grid Search with cross-validation to optimize hyperparameters for a Support Vector Machine (SVM):
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.svm import SVC
# Define parameter grid
param_grid = {'C': [0.1, 1, 10], 'kernel': ['linear', 'rbf']}
grid_search = GridSearchCV(SVC(), param_grid, cv=5)
grid_search.fit(X_train, y_train)
print("Best Parameters:", grid_search.best_params_)
print("Best Score:", grid_search.best_score_)2. Random Search
Random search is a faster alternative to grid search, where random combinations of hyperparameters are tested rather than all possibilities. This method can yield good results in a fraction of the time, especially for models with large parameter spaces.
- Example: Using Random Search with cross-validation:
from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV
from scipy.stats import uniform
# Define parameter distribution
param_dist = {'C': uniform(0.1, 10)}
random_search = RandomizedSearchCV(SVC(), param_distributions=param_dist, n_iter=10, cv=5)
random_search.fit(X_train, y_train)
print("Best Parameters:", random_search.best_params_)
print("Best Score:", random_search.best_score_)Hyperparameter tuning helps improve model accuracy and can make a significant difference in predictive performance, particularly in complex models.
Cross-Validation for Reliable Model Evaluation
Cross-validation is a technique to evaluate the performance of a model across different data splits. It reduces the risk of overfitting and ensures the model generalizes well to unseen data. One common method is k-fold cross-validation, where the dataset is split into kkk folds, with each fold used as a test set once while the others are used for training.
- Example: Using 5-fold cross-validation with Scikit-Learn:
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
scores = cross_val_score(model, X, y, cv=5)
print("Cross-Validation Scores:", scores)
print("Mean Cross-Validation Score:", scores.mean())Cross-validation helps estimate model performance more accurately, especially on smaller datasets where a single train-test split may not be representative.
Advanced Concepts in Machine Learning
As machine learning models become more sophisticated, techniques like ensemble methods and regularization play an increasingly important role in improving performance and preventing overfitting. Let’s explore these advanced concepts in detail.
1. Ensemble Methods
Ensemble methods combine multiple models to create a more accurate and robust model than any single model alone. By aggregating predictions, ensemble methods help reduce variance, minimize bias, and improve generalization.
Bagging (Bootstrap Aggregating): In bagging, multiple instances of the same model are trained on different subsets of the data, created through sampling with replacement. The predictions are then averaged (for regression) or voted on (for classification).
- Example: Random Forest, an ensemble of decision trees, is a popular bagging method that aggregates the predictions of multiple decision trees for more accurate results.
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
# Initialize and train the model
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)Boosting: Boosting involves sequentially training models, where each new model attempts to correct the errors of the previous models. Boosting models, such as AdaBoost, Gradient Boosting, and XGBoost, are known for their high accuracy and are often used in competitive machine learning.
- Example: Using Gradient Boosting for classification tasks.
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier
# Initialize and train the model
model = GradientBoostingClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)Stacking: Stacking combines different types of models (e.g., decision trees, logistic regression, SVMs) and uses another model, known as a meta-model, to learn from their outputs. Stacking can capture diverse patterns by leveraging the strengths of different algorithms.
- Example: Using Scikit-Learn’s
StackingClassifierto combine multiple models.
from sklearn.ensemble import StackingClassifier
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.svm import SVC
# Define base models
base_models = [
('svc', SVC(probability=True)),
('rf', RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100))
]
# Define stacking model
model = StackingClassifier(estimators=base_models, final_estimator=LogisticRegression())
model.fit(X_train, y_train)Ensemble methods are powerful for increasing model accuracy and robustness, especially when individual models have high variance.
Regularization Techniques
Regularization is a method to prevent overfitting by penalizing large coefficients in machine learning models, thereby simplifying the model. Regularization improves generalization and performance on new data.
1. L1 Regularization (Lasso Regression)
L1 regularization adds a penalty equal to the absolute value of the magnitude of coefficients. This results in sparse models where some coefficients become zero, effectively performing feature selection by eliminating less relevant features.
- Example: Applying L1 regularization with Lasso in Scikit-Learn.
from sklearn.linear_model import Lasso
# Initialize and train Lasso regression
model = Lasso(alpha=0.1)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)2. L2 Regularization (Ridge Regression)
L2 regularization penalizes the square of the coefficient values, shrinking them but keeping all features in the model. Ridge regression is widely used when you want to reduce overfitting without eliminating features.
- Example: Applying L2 regularization with Ridge in Scikit-Learn.
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge
# Initialize and train Ridge regression
model = Ridge(alpha=0.1)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)3. Elastic Net
Elastic Net combines both L1 and L2 regularization, offering a balance between feature selection and regularization. It’s useful when dealing with datasets that contain highly correlated variables.
- Example: Applying Elastic Net in Scikit-Learn.
from sklearn.linear_model import ElasticNet
# Initialize and train Elastic Net regression
model = ElasticNet(alpha=0.1, l1_ratio=0.5)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)Regularization is essential for high-dimensional datasets, where too many features can lead to overfitting and poor generalization. By penalizing larger coefficients, regularization techniques help create simpler, more interpretable models.
Practical Tips for Improving Machine Learning Workflows
To build successful machine learning models, optimizing workflows and incorporating best practices are key. Here are some practical tips to enhance your ML development process:
1. Use Pipelines for Consistency
Creating a pipeline automates data preprocessing, feature engineering, and model training, ensuring consistent transformations are applied to both training and test data. Pipelines make it easier to replicate workflows, reducing errors and saving time.
- Example: Using Scikit-Learn’s
Pipelineto streamline data preprocessing and modeling.
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.svm import SVC
# Define pipeline
pipeline = Pipeline([
('scaler', StandardScaler()),
('svc', SVC(kernel='rbf'))
])
# Train the pipeline
pipeline.fit(X_train, y_train)2. Experiment with Different Algorithms
Testing multiple algorithms helps identify the best-performing model for your dataset. Libraries like Scikit-Learn make it easy to experiment with different models, and automated machine learning tools (e.g., AutoML) can streamline this process further.
3. Leverage Feature Engineering
Feature engineering is crucial for improving model accuracy. Experimenting with different transformations, interactions, and feature selection techniques can significantly impact the final model’s performance. Some commonly used methods include:
- Polynomial Features: Adding polynomial terms to capture non-linear relationships.
- Interaction Terms: Combining features to capture interactions between variables.
4. Monitor Model Performance Over Time
When deploying models in production, performance can change over time due to evolving data, also known as data drift. Monitoring performance regularly and setting up alerts for declining metrics help ensure the model continues to perform well.
- Tools for Monitoring: Tools like Prometheus for metrics tracking or MLflow for model management can automate monitoring, enabling quicker responses to issues.
5. Document and Version Your Models
Versioning models and keeping records of configurations, parameters, and evaluation metrics is essential for reproducibility. Documenting each experiment allows you to track changes and revert to previous versions if needed. Tools like DVC (Data Version Control) and MLflow make versioning easier.
- Example: Using MLflow to log experiments and version models.
import mlflow
# Log model parameters and metrics
mlflow.log_param("model", "RandomForest")
mlflow.log_metric("accuracy", accuracy)
mlflow.sklearn.log_model(model, "random_forest_model")Challenges and Future Trends in Machine Learning
As machine learning continues to evolve, new challenges and trends shape its applications and impact on various industries.
1. Ethical and Responsible AI
With the growing use of machine learning in sensitive applications, ethical concerns like bias, transparency, and fairness are at the forefront. Ensuring responsible AI requires addressing these issues and adopting guidelines for transparent, unbiased models.
- Bias Mitigation: Implementing fairness-aware machine learning techniques and conducting regular audits can help reduce bias in ML models.
2. Interpretability and Explainability
As models become more complex, understanding their inner workings becomes challenging, especially in high-stakes areas like healthcare and finance. Techniques like SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) and LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) make models more interpretable, increasing trust among stakeholders.
3. Federated Learning
Federated learning enables models to train on decentralized data (e.g., data stored on individual devices) without moving it to a central server. This approach enhances privacy and security, making it ideal for applications in healthcare and finance.
4. AutoML (Automated Machine Learning)
AutoML automates the process of selecting, training, and tuning machine learning models, enabling non-experts to build high-quality models. As AutoML tools continue to develop, they are expected to simplify machine learning workflows further, saving time and resources.
Conclusion
Machine learning is transforming industries by enabling systems to learn from data, uncover patterns, and make data-driven decisions. This introduction has covered the essentials, from supervised and unsupervised learning to evaluation metrics, model optimization, and practical workflow tips.
By mastering these fundamentals, you are well-equipped to build and deploy machine learning models that can solve complex problems, enhance efficiency, and drive innovation. As you delve deeper, exploring advanced techniques and staying updated with industry trends will allow you to create robust and impactful machine learning solutions that adapt to changing needs and challenges.