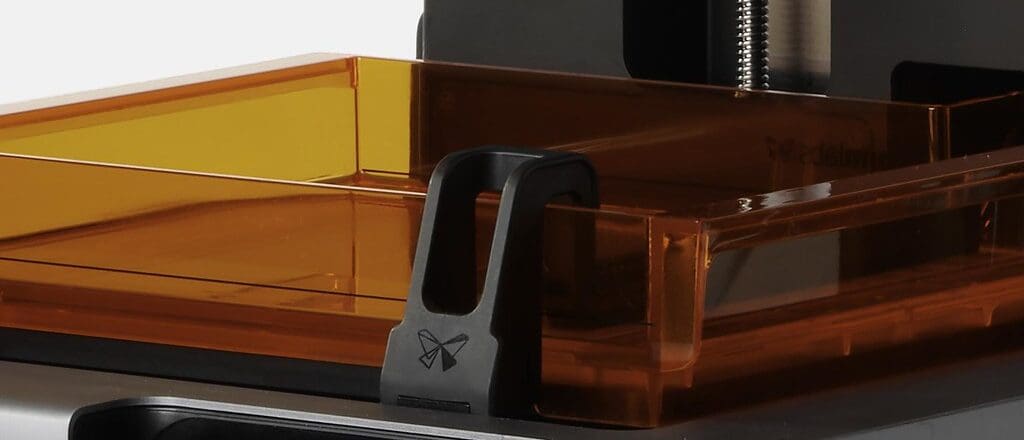
In the world of 3D printing, particularly in processes that involve resin or powder, such as Stereolithography (SLA) and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), the wiper plays a crucial role. This component is responsible for maintaining the cleanliness and evenness of the build platform or vat, which is essential for achieving high-quality prints. This article explores the importance, functionality, and maintenance of the wiper in 3D printing, highlighting its role in enhancing the precision, efficiency, and overall success of the printing process.
Importance of the Wiper in 3D Printing
Maintaining Surface Quality: The wiper ensures that each layer of resin or powder is smooth and uniform before the next layer is applied or cured, which is crucial for the dimensional accuracy and surface finish of the final product.
Preventing Defects: By removing excess material and debris from the build area, the wiper helps prevent defects that can arise from contaminated or uneven layers, such as warping, incomplete curing, or layer misalignment.
Increasing Print Consistency: Consistent application of new material layers is key to reliable print quality. The wiper aids in this consistency by regularly conditioning the build surface throughout the printing process.
Enhancing Material Economy: Efficient use of materials is a significant advantage in 3D printing. The wiper contributes to material economy by recycling excess material and minimizing waste, especially in powder-based printing techniques.
Components of the Wiper System in 3D Printers
Blade or Squeegee: The primary component that comes into direct contact with the print surface. It is usually made from materials that are durable yet gentle enough to not damage the build area or vat.
Actuation Mechanism: This includes the motor and linkage system that controls the movement of the wiper blade across the build platform or vat. The mechanism must offer precise control over speed and pressure to effectively spread materials without causing disruption to already solidified parts.
Mounting System: Provides stable and adjustable support for the wiper, allowing it to be positioned accurately relative to the build surface. This system often includes mechanisms for adjusting the blade angle and pressure.
Control Electronics: Manage the operation of the wiper, synchronizing its movements with the printing process to optimize cleaning and material spreading without interrupting the build cycle.
Installation and Calibration of the Wiper
Proper Installation: Ensuring that the wiper is correctly installed is crucial for its effective operation. This includes securing the blade at the right angle and ensuring that the actuation mechanism is properly aligned and functional.
Calibration: The wiper system needs to be calibrated to ensure that it contacts the build surface appropriately. This involves setting the correct pressure and angle to effectively clear the surface without damaging it.
Testing: Conduct operational tests to ensure that the wiper performs consistently across the entire build area. This helps in identifying any issues with uneven wiping or insufficient material removal.
Maintenance and Optimization of the Wiper
Regular Cleaning: The wiper blade and its surrounding components should be cleaned regularly to prevent material build-up, which can impair its function and potentially contaminate the print.
Blade Replacement: Wiper blades wear out over time and need to be replaced periodically to maintain effectiveness. Keeping spare blades and scheduling regular inspections can help avoid unexpected failures.
System Checks: Routine checks of the actuation mechanism and mounting system are necessary to ensure that they remain in good working condition and properly adjusted.
Lubrication and Adjustments: Proper lubrication of moving parts and regular adjustments to the blade pressure and alignment are essential for smooth operation and longevity of the wiper system.
Challenges and Solutions
Material Compatibility: Different printing materials may require different types of wiper blades or pressures. Using modular or adjustable wiper systems that can be easily adapted to various materials is beneficial.
Mechanical Wear: The continuous movement and exposure to materials can cause mechanical wear in the wiper system. Implementing a preventive maintenance schedule can help manage wear and prolong the life of the system.
Integration with Printing Process: Synchronizing the wiper’s operation with the printing cycle is critical to avoid disruptions. Advanced control systems that can be finely tuned to the printer’s operations are crucial for seamless integration.
The wiper is a vital component in many 3D printing systems, playing a key role in maintaining the quality and consistency of prints. Proper management, regular maintenance, and careful calibration of the wiper are essential for maximizing the performance of 3D printers and ensuring the production of high-quality, precise, and reliable printed products. By understanding and optimizing the function and maintenance of the wiper, manufacturers can achieve improved operational reliability and enhanced print quality, fully leveraging the capabilities of advanced 3D printing technology.