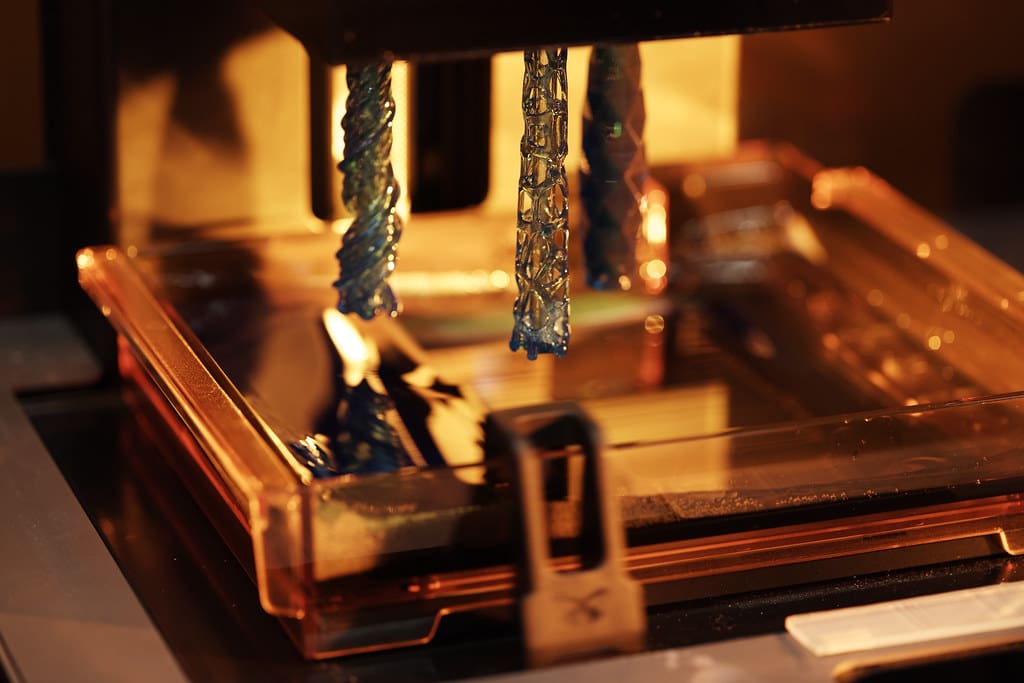
Curing lamps play an indispensable role in various 3D printing technologies, particularly those that use photopolymers, such as Stereolithography (SLA) and Digital Light Processing (DLP). These specialized lamps emit ultraviolet (UV) light or other wavelengths necessary to induce the photochemical reaction that turns liquid resin into solid plastic. This article delves into the importance, functionality, and maintenance of curing lamps in 3D printing, highlighting their crucial role in enhancing the efficiency, precision, and quality of the printing process.
Importance of Curing Lamps in 3D Printing
Efficient Curing Process: Curing lamps are essential for quickly and effectively solidifying photopolymer resins. The speed and uniformity of curing significantly affect the throughput and cycle times of 3D printing operations.
Precision and Detail: The quality of the curing light, including its intensity and wavelength, influences the resolution and accuracy of the final print. Precise control over the curing process allows for the creation of parts with intricate details and complex geometries.
Material Properties: Proper curing is crucial for achieving the desired mechanical and thermal properties in the finished parts. Curing lamps help ensure that the materials exhibit optimal strength, flexibility, and durability.
Energy Efficiency: Modern curing lamps are designed to maximize energy use, reducing operational costs and enhancing the sustainability of the printing process.
Components of Curing Lamps in 3D Printers
Light Source: The primary component, typically consisting of UV LEDs or laser diodes, provides the necessary wavelengths to cure photopolymer resins. LEDs are favored for their longevity and energy efficiency.
Optical System: Includes lenses and reflectors that focus and direct the light precisely onto the resin surface, ensuring even distribution and minimizing light wastage.
Cooling System: High-intensity lamps generate significant heat, which must be managed to maintain performance and extend the lifespan of the light source. Cooling systems can be passive (heat sinks) or active (fans or liquid cooling).
Control Electronics: Govern the intensity, duration, and pattern of light exposure. These controls must be finely tuned to the specific type of resin and printing process to optimize curing conditions.
Housing and Safety Features: The lamp housing is designed to protect the light source and electronics while ensuring user safety. It often includes UV-blocking materials and safety interlocks to prevent exposure to harmful radiation.
Installation and Calibration of Curing Lamps
Proper Installation: Ensuring that curing lamps are correctly positioned and securely mounted is crucial for their effective operation. This includes aligning them precisely with the build platform and integrating them properly within the printer’s enclosure.
Calibration: Regular calibration is necessary to maintain the accuracy and effectiveness of the curing lamps. This involves adjusting the light intensity, focus, and uniformity across the build area.
Testing: Before initiating regular manufacturing cycles, it is essential to test the curing lamps under various operating conditions to validate their performance and make necessary adjustments.
Maintenance and Optimization of Curing Lamps
Regular Cleaning: Keeping the lamp lenses and reflectors clean is crucial for maintaining optimal light transmission and preventing overheating due to dust accumulation.
Bulb or LED Replacement: Light sources in curing lamps have a finite lifespan. Regularly checking their output and replacing them as needed ensures consistent curing performance.
System Checks: Routine inspections should be conducted to assess the cooling system, electrical connections, and the structural integrity of the housing to prevent failures during operation.
Firmware and Software Updates: Keeping the control software updated can improve the functionality of the curing lamps, potentially introducing more efficient light management protocols and new features.
Challenges and Solutions
Light Intensity and Distribution: Achieving uniform light distribution can be challenging, especially over large build areas. Using advanced optical designs and regularly calibrating the light output can help mitigate these issues.
Heat Management: Managing the heat produced by high-intensity curing lamps is crucial to prevent damage to the printer and resin. Enhancing cooling strategies and incorporating thermal sensors can aid in effective heat management.
Lamp Lifespan and Reliability: The high-intensity and frequent use of curing lamps can lead to rapid degradation. Implementing a preventive maintenance schedule and opting for high-quality, durable lamp components can extend their usable life.
Curing lamps are critical components of 3D printers that significantly influence the speed, efficiency, and quality of the printing process, particularly in resin-based technologies. Proper management, regular maintenance, and careful calibration of these lamps are essential for maximizing the capabilities of 3D printers and ensuring the production of high-quality, precise, and durable printed products. By thoroughly understanding and meticulously maintaining curing lamps, manufacturers can achieve improved operational reliability and enhanced print quality, fully leveraging the advanced capabilities of 3D printing technology.