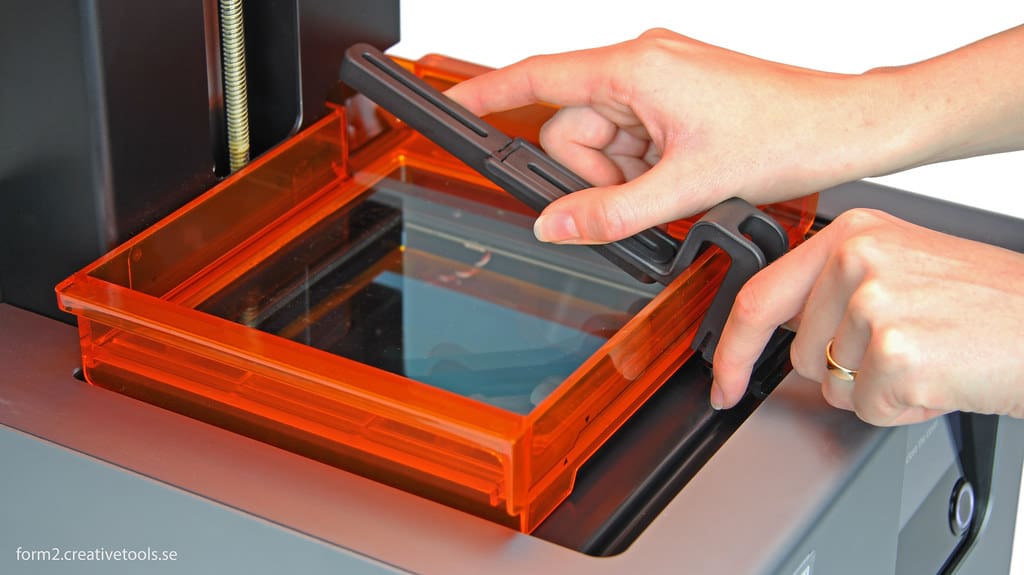
Optical components are integral to the accuracy and efficiency of several types of 3D printers, particularly those that rely on laser or light-based technology, such as Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), and Digital Light Processing (DLP). These components, which include lenses, mirrors, and optical sensors, play a critical role in directing, focusing, and monitoring the light used to cure resin or sinter powder. This article explores the functionalities, importance, and maintenance of optical components in 3D printers, highlighting how they impact the overall quality and reliability of the printing process.
Importance of Optical Components in 3D Printing
Precision in Light Delivery: Optical components control the path and focus of the light or laser beams, ensuring that they accurately target the areas needed to create detailed and dimensionally accurate prints.
Quality of the Final Print: The clarity and adjustment of optical systems directly affect the surface finish and structural integrity of printed objects by ensuring consistent energy distribution across the print area.
Efficiency and Speed: Well-maintained and correctly calibrated optics contribute to faster printing processes by minimizing errors and rework, thus speeding up production cycles.
Versatility in Material Processing: Advanced optical systems allow printers to effectively process a variety of materials by adjusting the light intensity and focus to suit different resins or powders.
Components of the Optical System in 3D Printers
Lenses: Lenses focus or diffuse the laser or light beams to the precise requirements of the print job. They must be high-quality to withstand the intense energy throughput without degrading.
Mirrors: Used to steer the laser beam in laser-based printers, mirrors must be positioned with high precision and have coatings that reflect the specific wavelengths of the laser without absorbing too much energy.
Optical Sensors: These sensors monitor the position, intensity, and quality of the light beams. They are crucial for maintaining consistent print quality and for system diagnostics.
Windows and Filters: Protective windows and filters shield sensitive components from stray particles or excessive radiation, while also ensuring that the light path is clear and unobstructed.
Calibration Tools: Special tools and software are used for aligning, testing, and calibrating optical components to ensure that they work correctly together within the printer’s system.
Installation and Calibration of Optical Components
Proper Installation: Optical components must be precisely installed to ensure that their alignment meets the strict tolerances required for high-quality printing. This often involves professional setup and alignment tools.
Regular Calibration: Optical systems require regular calibration to account for any shifts due to thermal expansion, mechanical vibration, or wear. Calibration ensures that the focus and positioning of the light beams remain optimal.
Testing and Adjustment: After installation or calibration, comprehensive testing is conducted to verify that the optics produce the correct light intensity and distribution required for the printer’s specific tasks.
Maintenance and Optimization of Optical Components
Regular Cleaning: Optical components should be kept clean from dust, resin splashes, or powder residues, as these can scatter or block light, leading to print defects. Special cleaning solutions and protocols are used to avoid damaging sensitive optics.
Inspection for Wear and Damage: Lenses and mirrors are inspected regularly for signs of wear, such as scratches or thermal damage, which can significantly impact their performance.
Replacement Schedules: Optical components have a limited lifespan, especially in high-intensity environments. Implementing a scheduled replacement plan helps prevent sudden failures.
Environmental Controls: Maintaining environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and cleanliness helps preserve the condition and effectiveness of optical components.
Challenges and Solutions
Thermal Management: High-energy beams can cause significant heating of optical components, potentially leading to distortions. Cooling systems or heat-resistant materials may be necessary to manage these thermal effects.
Coating Degradation: Over time, the reflective or anti-reflective coatings on mirrors and lenses can degrade. Using high-quality coatings and scheduling regular replacements can mitigate this issue.
Alignment Drift: Mechanical and thermal stresses can cause alignment shifts in optical components. Implementing robust mounting solutions and frequent recalibrations can help maintain alignment.
Optical components are critical for the precision and efficiency of 3D printers that utilize light or laser technology. The performance of these components directly affects the quality, speed, and versatility of the printing process. Effective management, including regular maintenance and calibration of optical components, is essential for maximizing the capabilities of 3D printers and ensuring consistent, high-quality outcomes in printed products.