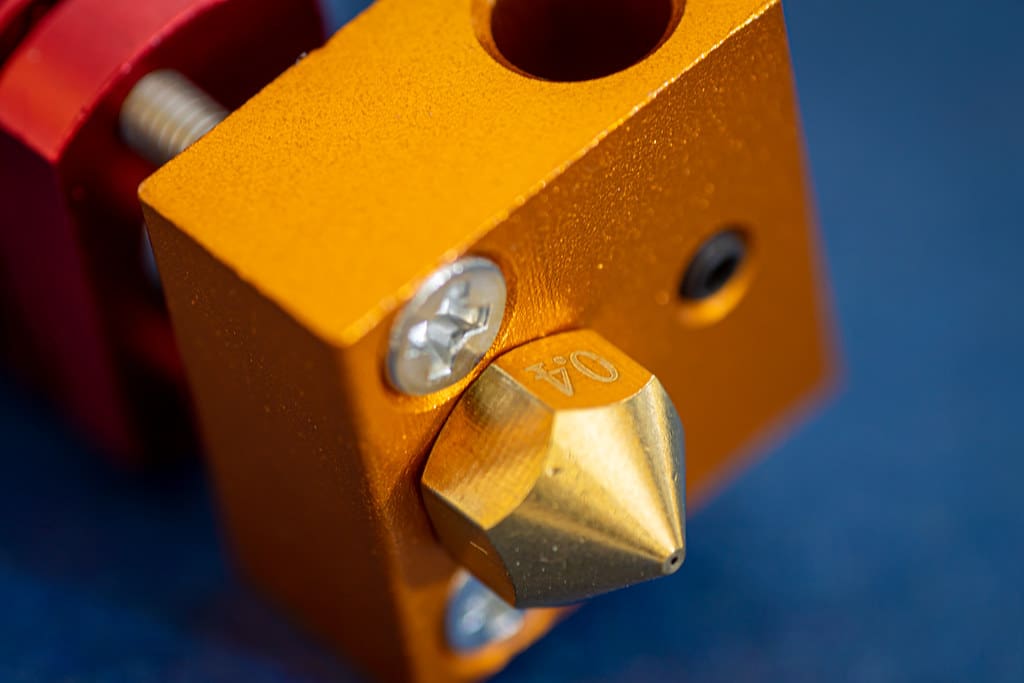
The print head of a 3D printer is a crucial component that significantly influences the quality, speed, and versatility of the printing process. Serving as the point of material application, whether it’s a filament in FDM, resin in SLA, or powder in SLS printers, the print head dictates how material is laid down layer by layer to create the final object. This article explores the complexity of print heads across various 3D printing technologies, discussing their designs, functionalities, and impact on the overall printing process.
Importance of the Print Head in 3D Printing
Precision and Control: The print head’s primary role is to ensure precise and controlled deposition of printing materials. Its accuracy directly affects the print’s resolution, finish, and structural integrity.
Material Handling: Different 3D printing technologies require print heads designed to handle specific materials, from thermoplastics and photopolymers to metal powders. The ability of the print head to process these materials efficiently is vital for expanding the printer’s versatility.
Speed of Operation: The efficiency of the print head also influences the printing speed. Advanced print heads can deposit materials faster while maintaining high-quality output, significantly impacting production throughput.
Adaptability: Some print heads are equipped with features that allow for the adjustment of parameters like flow rate and temperature, enabling them to work with a range of materials and cater to different printing needs.
Types of Print Heads in 3D Printing
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Print Heads:
- In FDM printers, the print head typically includes a heated nozzle that melts the thermoplastic filament. The melted material is extruded through the nozzle’s tip onto the build platform, where it cools and solidifies to form the structure.
Stereolithography (SLA) Print Heads:
- SLA printers use a print head equipped with a UV laser and a system of mirrors (galvanometers) that direct the laser beam across the surface of a photopolymer resin, curing it layer by layer.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) Print Heads:
- SLS print heads consist of a high-power laser and a scanning system that fuses powder particles together. Unlike SLA, SLS does not require resin but works with a variety of powdered materials, including plastics, metals, and ceramics.
PolyJet Print Heads:
- PolyJet technology uses print heads that function similarly to inkjet printers. These print heads jet layers of curable liquid photopolymer onto the build platform, which are then immediately cured by UV light.
Binder Jetting Print Heads:
- In binder jetting, the print head dispenses a liquid binding agent onto a layer of powder material. The binder acts as an adhesive between the powder particles, with subsequent layers built on top to form the object.
Design and Functionality of Print Heads
Nozzle Design:
- The design of the nozzle in FDM print heads is critical for material flow and precision. Nozzles come in various sizes and shapes, influencing print resolution and speed.
Laser and Galvanometer Systems:
- In SLA and SLS printers, the quality and configuration of the laser and the precision of the galvanometer mirrors are crucial for achieving high detail and accuracy in prints.
Inkjet Nozzles:
- PolyJet and binder jetting technologies use inkjet nozzles that must be capable of handling high-viscosity materials and delivering them with consistent accuracy.
Heating and Cooling Systems:
- Many print heads include mechanisms for controlling the temperature of the material being deposited. In FDM, this includes the heating of the nozzle and possibly the material chamber, while cooling systems might be necessary to solidify the material post-deposition.
Maintenance and Optimization
Regular Cleaning and Calibration:
- To maintain optimal performance, print heads require regular cleaning to prevent clogs and buildup, especially in FDM and PolyJet printers. Calibration ensures that material deposition aligns perfectly with the model specifications.
Nozzle Replacement:
- In FDM printers, the nozzle can wear out over time, especially when printing with abrasive materials. Regular inspection and replacement are crucial to maintain print quality.
Software Updates:
- Keeping the printer’s software updated ensures that the print head operates with the latest settings and optimizations, improving performance and compatibility with different materials.
The print head is a vital component in the 3D printing process, significantly impacting the quality, efficiency, and capabilities of the printer. Each type of 3D printing technology demands a specialized print head design tailored to its specific material and operational requirements. Innovations in print head technology continue to drive advancements in 3D printing, enabling more complex, detailed, and reliable prints. Understanding the intricacies of print heads helps users and designers make informed decisions to optimize their printing operations and maintain high standards of production.