In the world of 3D printing, the nozzle is a small yet pivotal component that plays a crucial role in the quality and success of the printing process. Positioned at the very heart of the extrusion mechanism, the nozzle is responsible for depositing the melted material onto the build platform, defining the precision, speed, and quality of the final print. This article delves into the intricacies of the nozzle in 3D printing, exploring its design, materials, maintenance, and how it influences the overall printing process.
Importance of the Nozzle in 3D Printing
Precision of Extrusion: The nozzle determines the amount of material extruded and the precision of its placement. The diameter of the nozzle opening directly influences the resolution of the print; smaller diameters allow for finer details.
Control of Material Flow: A well-designed nozzle ensures smooth and consistent material flow, which is essential for achieving uniform print layers and reducing issues like stringing or blobbing.
Heat Management: The nozzle must withstand and effectively manage high temperatures required to melt various printing materials without degrading over time or altering the properties of the material.
Impact on Print Speed: The size and shape of the nozzle also affect the speed of printing. Larger nozzles can extrude more material at a time, allowing for faster print speeds but at the cost of detail.
Types of Nozzles in 3D Printing
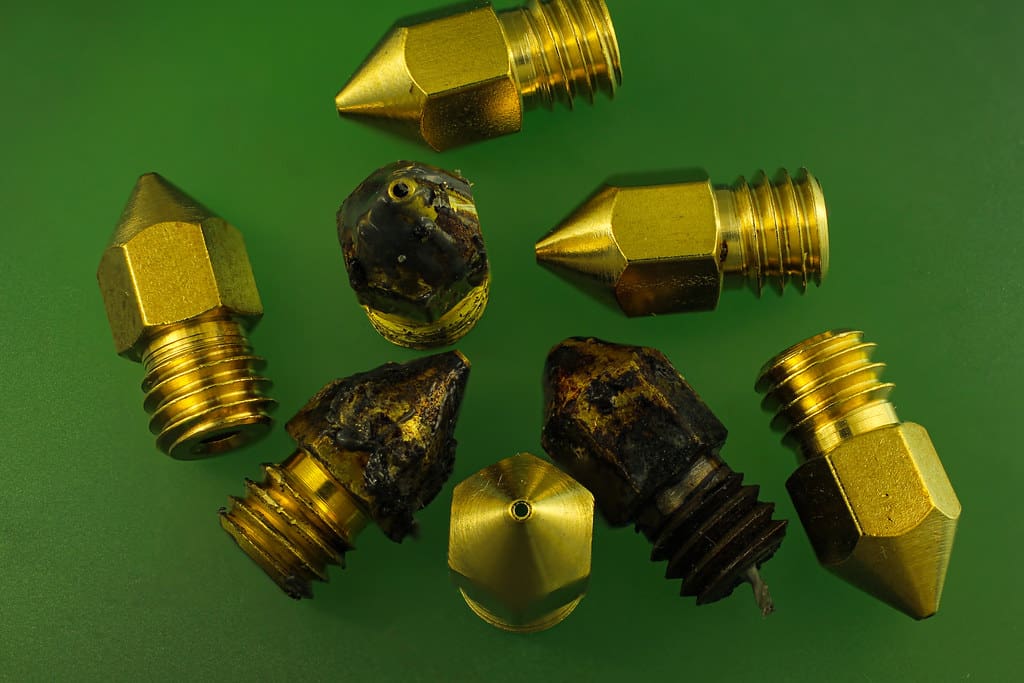
Standard Nozzles: Typically made from brass, standard nozzles are common in most FDM printers. They offer good thermal conductivity and are suitable for basic printing with materials like PLA and ABS.
Hardened Nozzles: For abrasive materials such as carbon fiber-filled filaments, metal-powder-infused filaments, or glow-in-the-dark filaments, hardened nozzles made from stainless steel or treated metals are used to resist wear.
High-Performance Nozzles: Made from premium materials like hardened tool steel or even specialty alloys, these nozzles are designed for high-temperature performance and can handle engineering-grade materials with high melting points.
Multi-Material Nozzles: Some advanced 3D printers feature nozzles capable of handling multiple materials in a single print, allowing for complex models with varying textures, colors, and material properties.
Materials Used for Nozzles
Brass: The most common material for nozzles, brass provides excellent heat conductivity, facilitating smooth and efficient material flow. However, it wears out faster when used with abrasive materials.
Stainless Steel: More durable than brass, stainless steel nozzles are less prone to wear and are better for printing with abrasive materials, though they have poorer thermal conductivity.
Hardened Steel: Ideal for high-strength and abrasive materials, hardened steel nozzles maintain their shape and structure even under harsh printing conditions, ensuring longevity and consistent performance.
Ruby or Sapphire Tips: Some high-end nozzles incorporate ruby or sapphire tips to combine excellent thermal properties with extreme wear resistance, ideal for printing with highly abrasive composites.
Design Features of Nozzles
Nozzle Diameter: Typically ranging from 0.1 mm to 1 mm, the diameter of the nozzle opening determines the minimum layer height and the fineness of detail in the print. Smaller diameters allow for higher resolution but slower printing speeds.
Nozzle Shape: The shape of the nozzle tip can vary, with options like flat, pointed, or volcano-style nozzles, each providing different benefits in terms of print speed and material handling.
Thread Type and Size: Compatibility with the printer’s hot end is crucial, and nozzles come with various thread types and sizes to match specific printer designs.
Maintenance and Care of Nozzles
Regular Cleaning: Nozzles should be cleaned regularly to prevent clogs and buildup, which can affect print quality. This can be done through cold pulls or using cleaning filaments.
Replacement: Over time, nozzles wear down, especially when printing with abrasive materials. Regular inspection and replacement are necessary to maintain print quality.
Calibration: Proper calibration of the nozzle’s distance from the print bed is essential to ensure optimal adhesion and layer formation.
The nozzle is a small but critical component in the 3D printing process, significantly impacting the quality, speed, and capabilities of a printer. Understanding the types of nozzles, their materials, and proper maintenance can help users make informed decisions that optimize their printing projects. Advances in nozzle technology continue to expand the possibilities of 3D printing, pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved with this transformative technology.