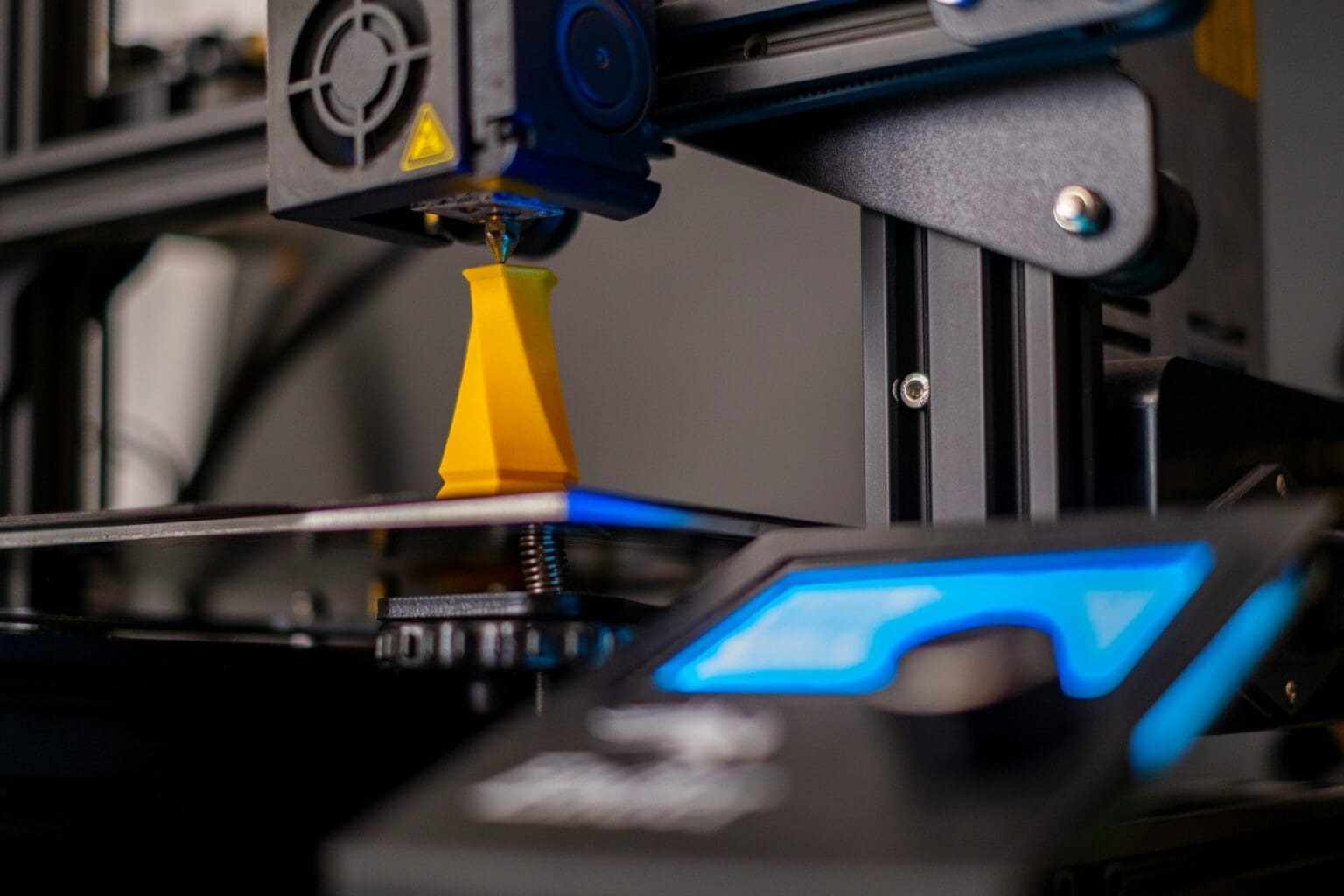
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), also known as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), is one of the most popular and widely used 3D printing technologies. It offers a cost-effective, versatile, and user-friendly solution for producing prototypes and finished products alike. This technology works by extruding thermoplastic filaments through a heated nozzle, laying down material layer by layer to build a three-dimensional object from the bottom up. Understanding the components of an FDM 3D printer is essential for both users and designers to optimize its functionality and maintain its performance. This post will explore the key components of an FDM 3D printer, detailing their roles and importance in the printing process.
Core Components of an FDM 3D Printer
1. Frame and Structure: The frame holds all other components of the printer and provides stability during printing. It can be made from various materials such as acrylic, aluminum, or steel. The rigidity of the frame affects the print quality; a more stable frame reduces vibrations during printing, leading to smoother surfaces on the printed objects.
2. Print Bed: The print bed is where the printed objects adhere during the printing process. It can be heated or non-heated. Heated beds help to prevent warping and ensure better adhesion of the first layer, which is crucial for the success of the print. Materials commonly used for print beds include glass, aluminum, and buildtak.

3. Extruder Assembly: The extruder is responsible for feeding filament to the hot end. There are two main types of extruders in FDM printers:
- Direct Drive Extruder: Places the stepper motor directly above the hot end, providing more direct control and allowing for more consistent flow of material.
- Bowden Extruder: Separates the motor from the hot end, reducing the weight on the print head and potentially increasing print speed. However, this setup can complicate the printing of flexible materials.

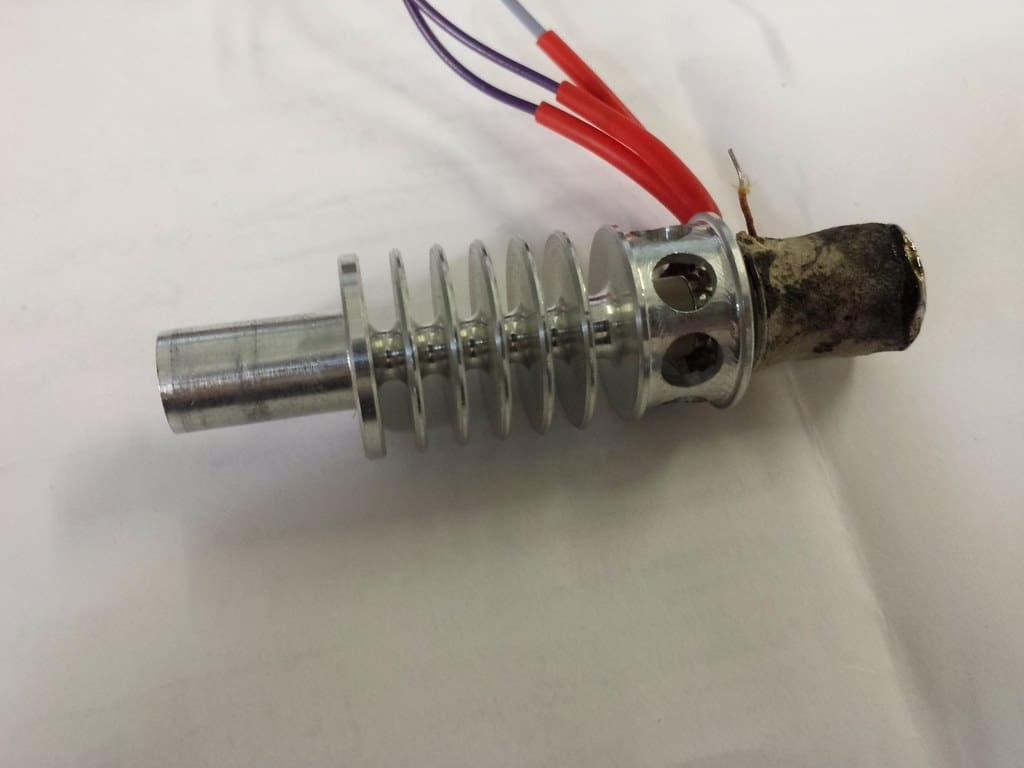
4. Hot End: The hot end is the component that heats up and melts the filament. It consists of a heating block, a nozzle, and a thermistor that controls the temperature. The nozzle, which comes in various diameters, determines the layer height and the precision of the print.

5. Cooling System: Cooling fans are crucial in an FDM printer. They solidify the extruded plastic immediately after it exits the nozzle, which is essential for achieving fine detail and preventing deformations in overhanging sections of the print.
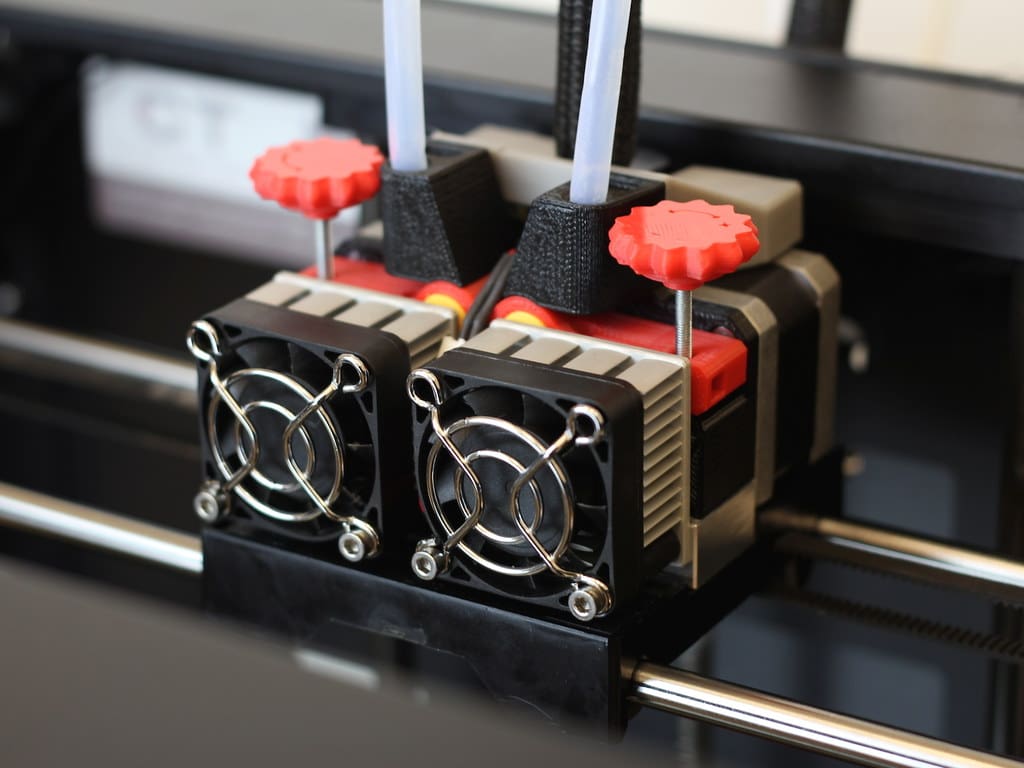
6. Stepper Motors: These motors drive the movement of the print head and the print bed. Precision in stepper motor control is vital for accuracy in 3D printing, as it directly affects the positioning and movement of the print head along the X, Y, and Z axes.
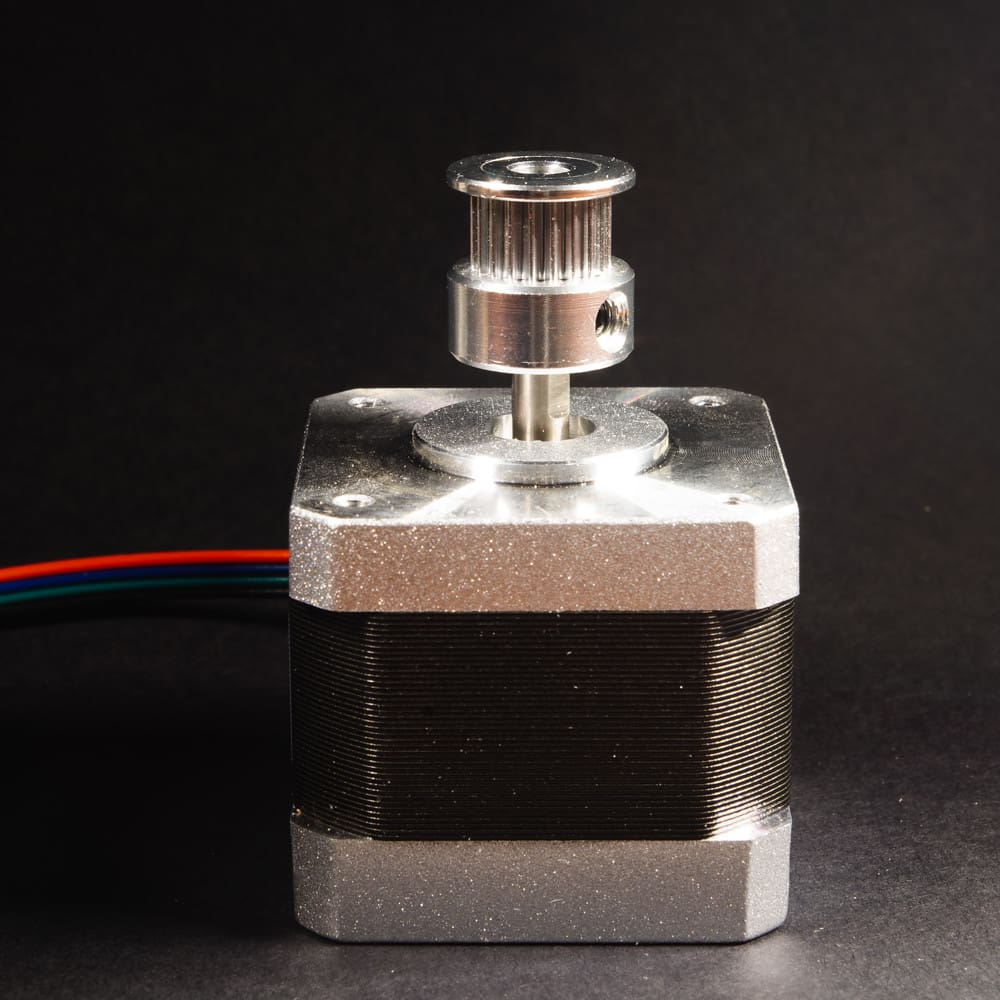

7. Belts and Pulleys: These components transfer the movement from the stepper motors to the print head and print bed. The quality and tension of the belts are important to maintain accurate movements and prevent any slipping during printing.
8. Controller Board: The brain of the 3D printer, the controller board, manages all electronic components of the printer, including motors, sensors, and temperature control. It interprets the G-code—the detailed set of instructions that guide the printer on how to create the model—from the connected computer or SD card.
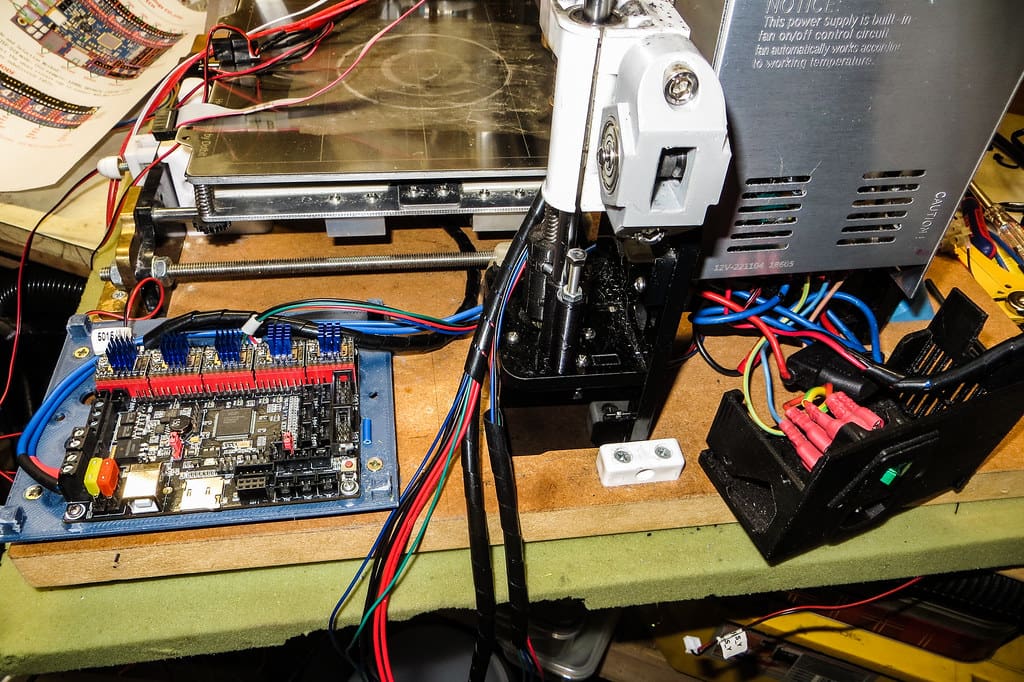
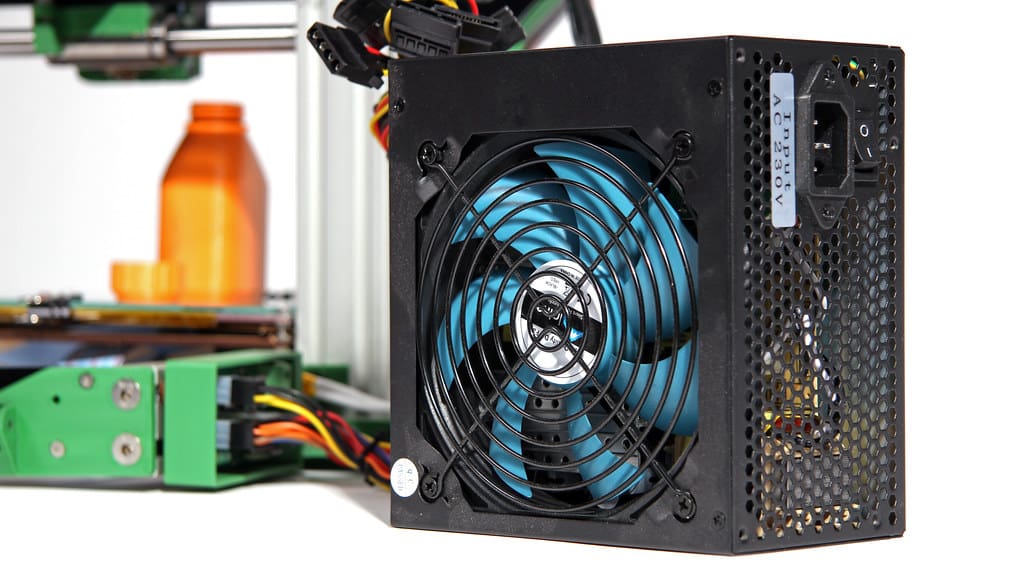
9. Power Supply: The power supply unit (PSU) provides the necessary power to the printer, particularly for heating the hot end and the heated bed. Ensuring an adequate and stable power supply is crucial for maintaining consistent performance throughout the printing process.

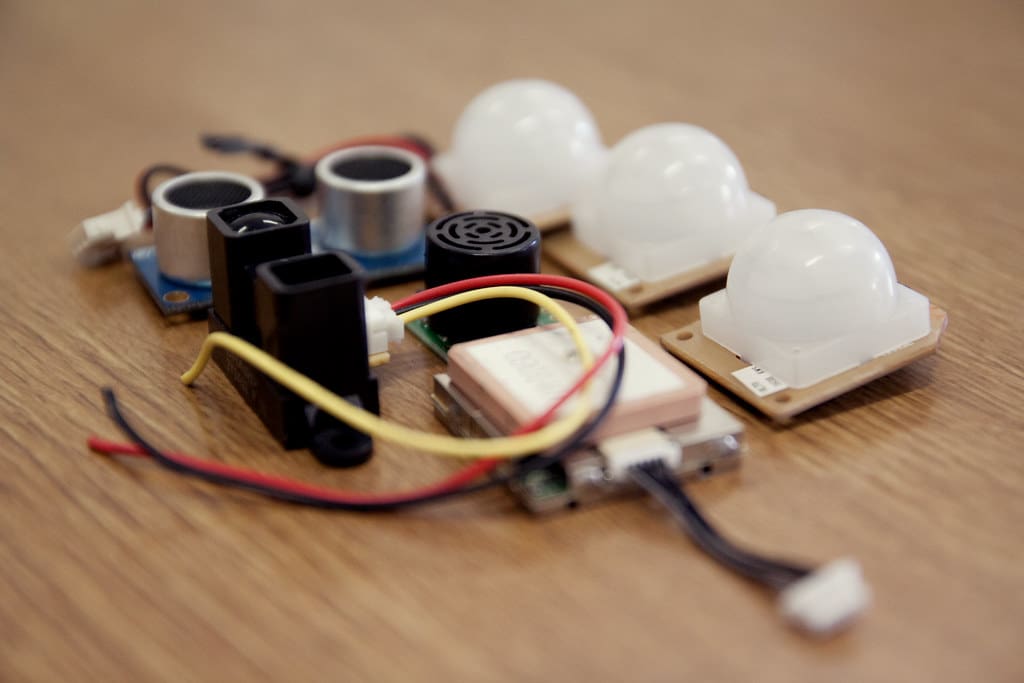
10. Sensors and Calibration Tools: Sensors in FDM printers can include thermistors for temperature monitoring, endstops to limit the movement of the axes, and sometimes even sensors for automatic bed leveling. These tools are essential for maintaining the printer’s performance and ease of use.

Each component of an FDM 3D printer plays a critical role in its operation and overall performance. From the sturdy frame that supports the machine to the precise extruder that deposits the filament, understanding these components helps users and technicians optimize their use of the technology, troubleshoot issues, and maintain the printer effectively. As the technology evolves, so too do the components, with ongoing innovations aimed at improving print quality, speed, and user-friendliness. For anyone interested in 3D printing, a thorough knowledge of the machine’s inner workings is invaluable, not only for operating the printer but also for enhancing and customizing it to meet specific printing needs.