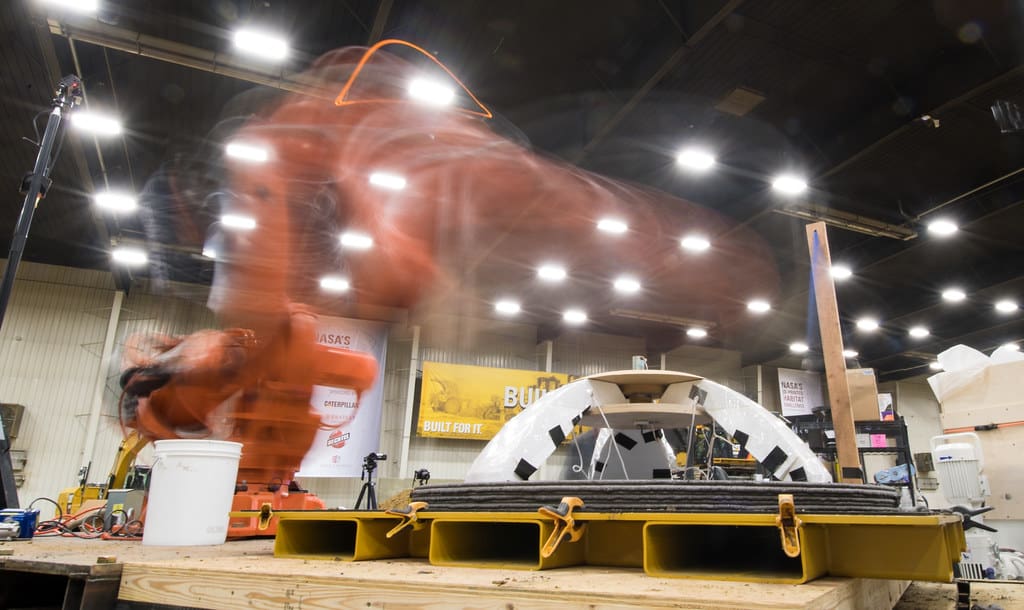
The construction industry is on the cusp of a technological revolution, driven by advancements in 3D printing. This transformative technology, also known as additive manufacturing, has the potential to significantly alter how buildings are designed, constructed, and maintained. With benefits ranging from reduced labor costs to increased sustainability, 3D printing is poised to address some of the most pressing challenges facing the construction sector today.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Construction Technology
Originally used for creating detailed models and prototypes, 3D printing has evolved to support the construction of complex structures and architectural elements. Advances in 3D printing technology have enabled the use of a variety of materials, including concrete, polymers, and metals, allowing for applications that range from small components to entire buildings. As the technology continues to mature, its integration into mainstream construction practices is becoming increasingly feasible.
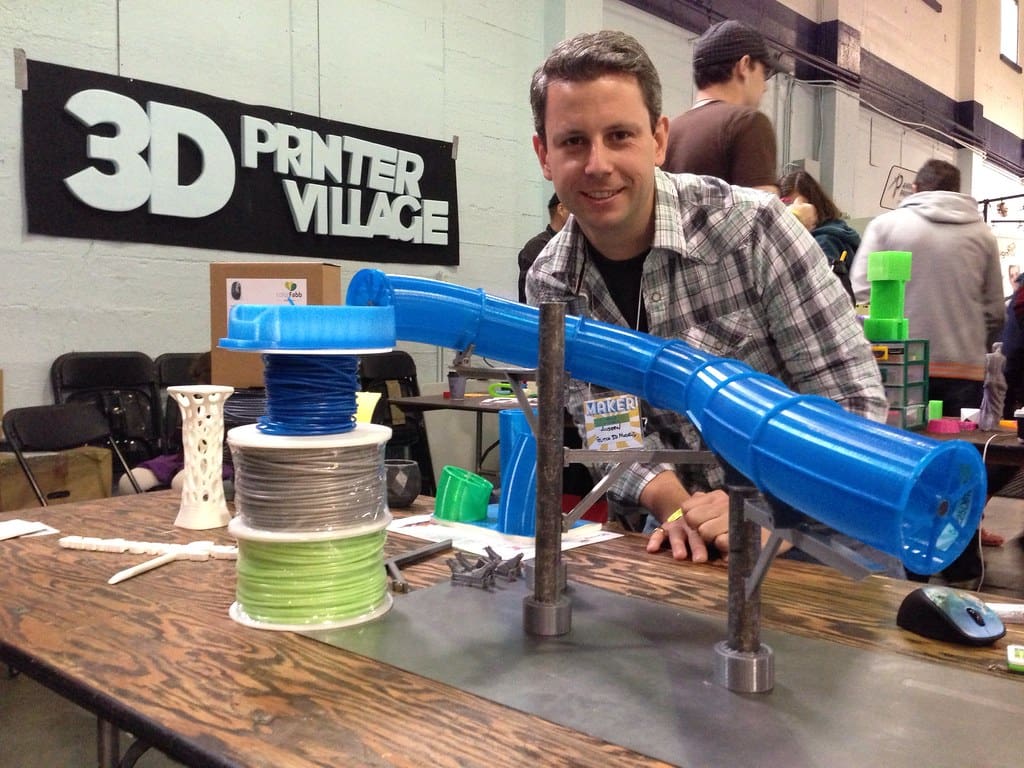

Advantages of 3D Printing in Construction Technology
Cost Efficiency: One of the most significant advantages of 3D printing in construction is the potential for cost reduction. By minimizing waste and optimizing material usage, 3D printing can lower material costs. Additionally, the automation of construction processes reduces labor costs and speeds up construction times.
Design Flexibility: 3D printing allows for the creation of complex, customized designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional construction methods. This flexibility enables architects and engineers to explore innovative architectural shapes and structures, enhancing both aesthetics and functionality.
Sustainability: 3D printing contributes to environmental sustainability by reducing waste and enabling the use of recycled or eco-friendly materials. The precise application of materials in additive manufacturing means that only the necessary amount is used, minimizing excess.
Speed of Construction: Buildings can be constructed much faster with 3D printing than with traditional methods. This speed can be particularly beneficial in scenarios requiring rapid shelter, such as disaster relief efforts.
Improved Safety: With automation at the core of 3D printing, the need for human intervention is significantly reduced, lowering the risk of accidents on construction sites.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Construction Technology
Residential and Commercial Buildings: Several companies around the world have successfully demonstrated the use of 3D printing to construct residential homes and commercial buildings, showcasing the technology’s potential to streamline the construction process while reducing costs and environmental impact.
Infrastructure Projects: 3D printing is being explored for its potential in infrastructure development, including the construction of bridges and tunnels. These projects benefit from the quick production times and the ability to create complex geometrical structures that are both strong and lightweight.
Custom Architectural Elements: The technology is particularly well-suited for creating bespoke architectural features that require high levels of detail, such as facades, columns, and interior elements. These components can be tailored to meet specific design requirements, allowing for a high degree of personalization.
Restorations and Replications: 3D printing offers valuable tools for the restoration of historical buildings. Damaged or eroded elements can be precisely replicated and restored, preserving the architectural integrity and historical accuracy of heritage sites.
Temporary Structures: The ability to quickly produce and assemble structures makes 3D printing ideal for temporary constructions, such as event pavilions or emergency housing. These structures can be easily dismantled and recycled, reducing waste.
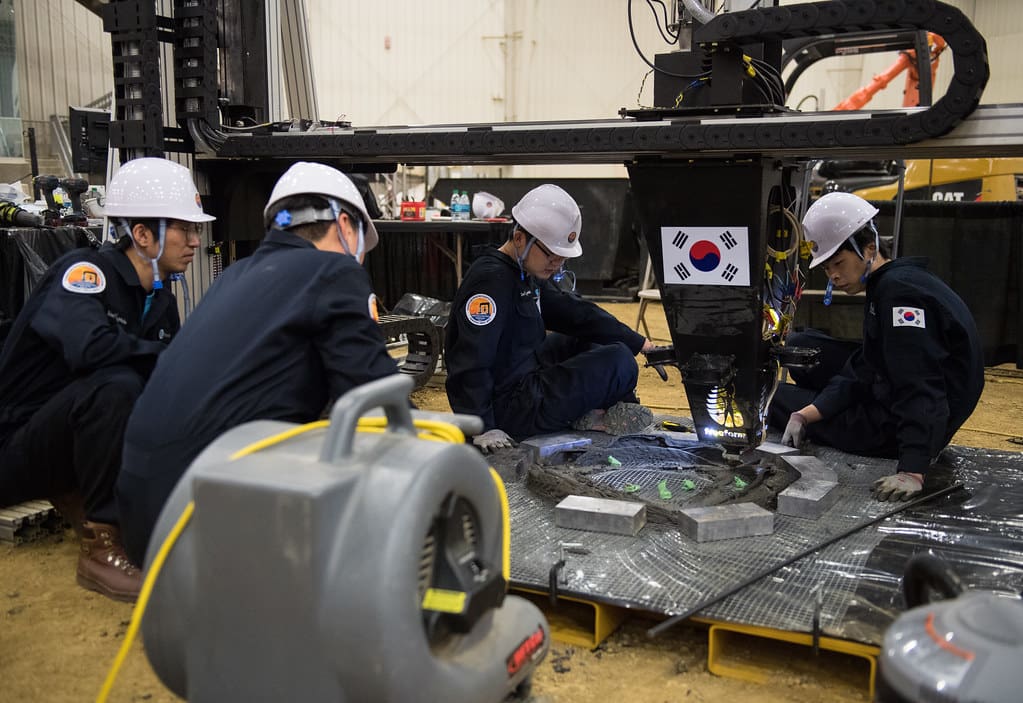

Challenges in 3D Printing for Construction Technology
Material Limitations: While advancements have been made, the range of materials suitable for 3D printing in construction is still limited. Developing materials that are both printable and meet structural requirements is ongoing.
Scale and Accessibility: Scaling 3D printing to larger construction projects presents technological and logistical challenges. Additionally, the accessibility of 3D printing technology is limited in regions lacking the infrastructure to support such innovation.
Regulatory Hurdles: Building regulations have not yet fully caught up with the advancements in 3D printing. Ensuring compliance with local building codes and standards can be a significant barrier to the adoption of 3D printing in mainstream construction.
Skill Gaps: There is a learning curve associated with operating 3D printing equipment and designing for additive manufacturing. Training skilled workers in this new technology is essential for its widespread adoption.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Construction Technology
As 3D printing technology continues to advance, its applications in construction are expected to expand. Future developments may include enhanced printing techniques capable of handling multiple materials simultaneously, improvements in the speed and scale of printing, and more widespread regulatory acceptance.
3D printing is set to revolutionize the construction industry by offering innovative solutions that promise greater efficiency, sustainability, and design flexibility. As the technology matures and overcomes current limitations, it could become a standard practice in construction, fundamentally changing how buildings are made. The potential for 3D printing to transform construction is immense, promising to redefine the landscapes of cities and towns globally while addressing the critical needs of speed, cost, and environmental impact.