3D printing has emerged as a transformative technology in the realm of design and manufacturing, offering the potential to reduce costs dramatically while increasing accessibility to high-quality products. Known for its versatility and efficiency, 3D printing enables both designers and consumers to create complex products without the hefty price tag associated with traditional manufacturing methods. This technology is particularly impactful in developing regions and among startups and small businesses where budget constraints often limit access to advanced manufacturing resources.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Low-Cost Design
Initially utilized primarily for prototyping in high-tech industries, 3D printing has expanded its reach, becoming a crucial tool in a variety of sectors including consumer goods, healthcare, and education. As printer technology has evolved and become more affordable, it has opened up new possibilities for low-cost design and production, even in settings that traditionally lack access to expensive manufacturing infrastructure.

Advantages of 3D Printing in Low-Cost Design
Reduction of Manufacturing Costs: 3D printing significantly cuts costs by eliminating the need for expensive molds and reducing material waste. This is achieved through additive processes, where material is only deposited where it is needed.
Enhanced Design Flexibility: Without the constraints of traditional manufacturing, designers can experiment with complex, intricate designs that would be too costly to produce otherwise. This flexibility allows for innovation in product design and functionality.
Rapid Prototyping and Iteration: Designers can quickly produce prototypes to test and refine their products, which is particularly valuable in a low-cost design context. Rapid prototyping speeds up the development process and helps avoid the costs associated with multiple iterations in traditional manufacturing.
Customization at No Extra Cost: 3D printing enables customization during the manufacturing process without additional costs. Products can be tailored to individual needs and preferences, enhancing customer satisfaction and value.
Local Production: 3D printers allow for local manufacturing, reducing the logistics costs and environmental impact associated with shipping products from distant manufacturing locations.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Low-Cost Design
Affordable Housing: 3D printing is being used to construct low-cost housing quickly and efficiently, particularly in areas facing housing crises or after natural disasters. These homes can be printed with local materials, further reducing costs and environmental impact.
Medical Devices and Prosthetics: In healthcare, 3D printing offers a cost-effective way to produce medical devices and prosthetic limbs. Devices can be customized to the patient at a fraction of the cost of traditional methods, making medical care more accessible in under-resourced areas.
Educational Tools: 3D printing allows schools and educational programs to create custom learning materials and scientific models affordably. This technology can democratize access to high-quality educational resources, especially in low-income regions.
Consumer Products: From household items to personal gadgets, 3D printing enables entrepreneurs and designers to develop and market products at a low initial investment, making it easier to start small businesses and test market responses without significant financial risk.
Sustainable Products: 3D printing promotes sustainability through efficient material use and the potential to use recycled materials. Producing sustainable products at low cost can make eco-friendly choices more accessible to a broader audience.
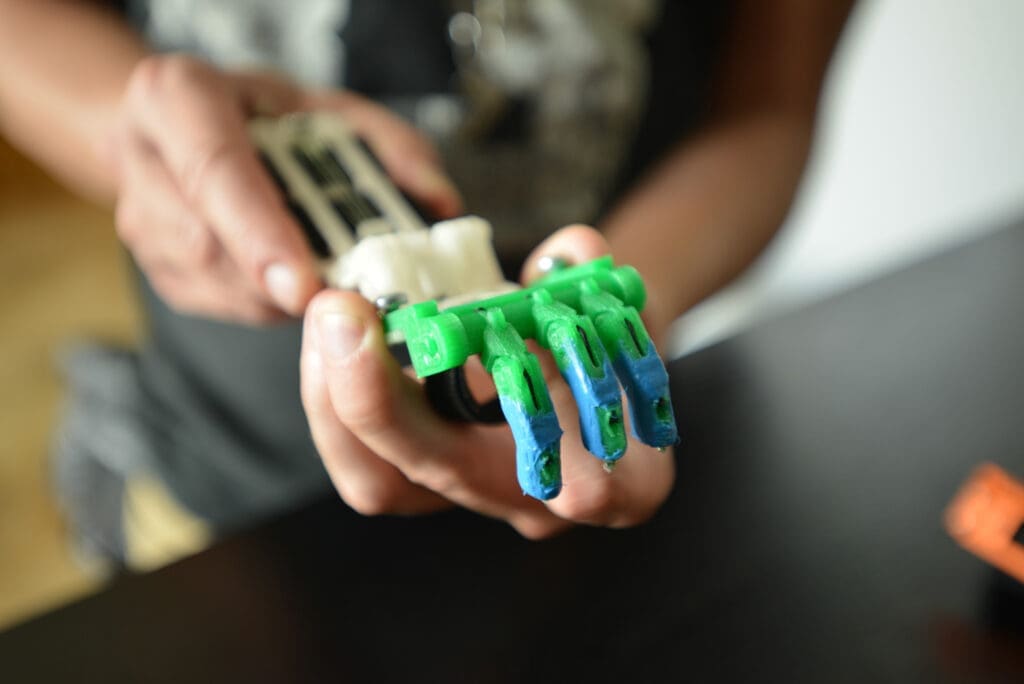

Challenges in 3D Printing for Low-Cost Design
Material Limitations: While 3D printing technology has advanced, the range of affordable printing materials is still somewhat limited, potentially affecting the durability and functionality of low-cost designs.
Quality and Consistency: Ensuring consistent quality in 3D printed products can be challenging, particularly when scaling production. Maintaining high standards in low-cost design requires careful monitoring and quality control.
Technical Expertise: Effective use of 3D printing technology requires specific skills and knowledge, which can be a barrier in regions with limited educational resources.
Infrastructure Requirements: Although 3D printing reduces the need for traditional manufacturing infrastructure, it still requires electricity and internet access, which may not be available in all areas.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Low-Cost Design
As 3D printing technology continues to improve and become more accessible, its impact on low-cost design is expected to grow. Future developments may include more affordable and efficient printers, a wider variety of low-cost materials, and enhanced software that simplifies the design process for non-experts.
3D printing is revolutionizing the concept of low-cost design by making it possible to produce high-quality, customized products at significantly reduced costs. This technology not only supports economic development by enabling local manufacturing but also enhances accessibility to essential goods and services worldwide. As 3D printing technology evolves, it promises to further democratize design and manufacturing, providing exciting opportunities for innovation and growth across various sectors.