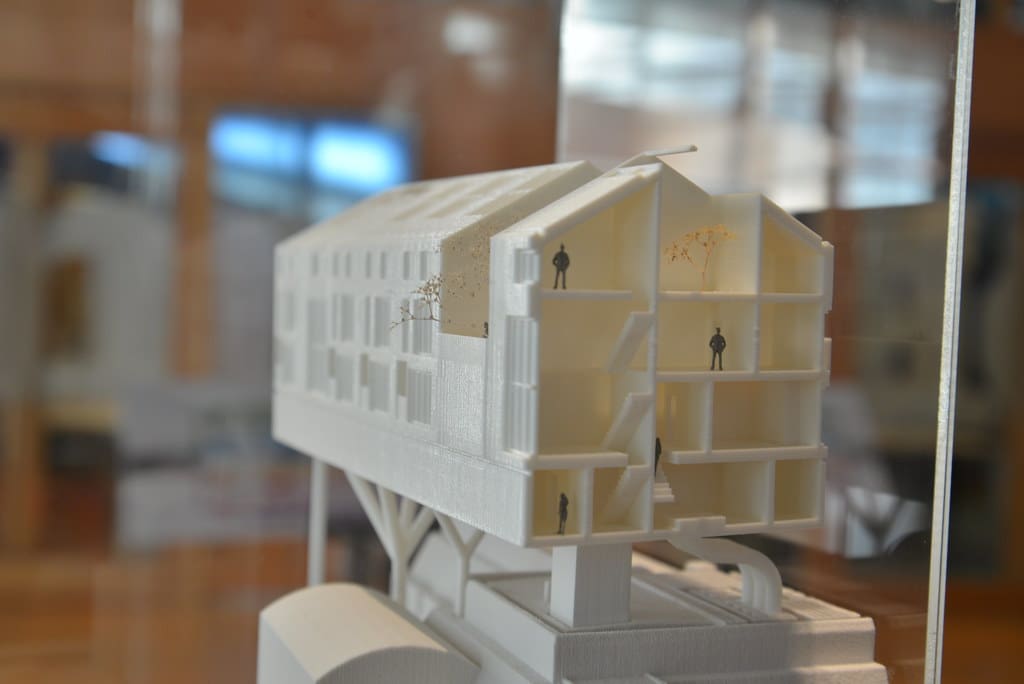
The construction industry is undergoing a transformation, driven by the adoption of new technologies that promise to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and customization. Among these, 3D printing stands out as a particularly transformative technology, offering significant improvements over traditional building methods. This innovative approach to construction—also known as additive manufacturing—enables the precise and rapid production of building components and even entire structures, revolutionizing how buildings are designed, constructed, and maintained.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Building Technologies
Originally used for creating detailed models and prototypes, 3D printing has scaled up to encompass large-scale construction applications. Advances in 3D printing technology now allow for the creation of complex architectural elements, robust structural components, and innovative materials directly on construction sites or in manufacturing settings. This technology is not only reshaping traditional building techniques but also addressing some of the most pressing challenges in construction today, including labor shortages, waste management, and the need for personalized living spaces.

Advantages of 3D Printing in Building Technologies
Speed and Efficiency: 3D printing significantly accelerates the construction process. Components can be produced on-demand and assembled on-site, reducing overall build times and minimizing the need for manual labor.
Design Flexibility: Additive manufacturing enables the creation of complex geometrical shapes that often surpass the capabilities of traditional construction methods. This flexibility allows architects and engineers to explore new creative possibilities and implement designs that incorporate organic shapes and customized features.
Cost-Effectiveness: By reducing the amount of material waste and decreasing reliance on skilled labor, 3D printing can lower construction costs. The precision of 3D printers also means that materials are used more efficiently, further driving down expenses.
Sustainability: 3D printing contributes to more sustainable construction practices by optimizing material usage and reducing waste. Additionally, it facilitates the use of eco-friendly materials, including recycled plastics and composites, further diminishing the environmental impact of building projects.
Enhanced Structural Integrity: New techniques in 3D printing allow for the integration of reinforcement within printed structures, enhancing their strength and durability. This is particularly important in regions susceptible to extreme weather or seismic activity.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Building Technologies
Residential and Commercial Buildings: From single-family homes to office buildings, 3D printing is being used to construct a variety of structures. These buildings often feature unique architectural designs that are both aesthetically pleasing and functional.
Infrastructure Projects: Bridges, tunnels, and other infrastructural components are increasingly being produced using 3D printing techniques, allowing for faster deployment and reduced costs compared to traditional construction methods.
Customized Interior Elements: 3D printing is ideal for creating customized interior design elements, including walls, tiles, and furniture, tailored to specific aesthetic and functional requirements.
Restoration and Renovation: In the realm of architectural conservation, 3D printing offers a valuable tool for reproducing ornate historical elements with high accuracy, aiding in the restoration and preservation of heritage buildings.
Emergency Housing: 3D printing provides a rapid-response solution for creating temporary housing in the aftermath of disasters. These homes can be quickly produced on-site, offering a durable and cost-effective solution for displaced communities.

Challenges in 3D Printing for Building Technologies
Material Limitations: Ensuring that printed materials meet all necessary standards for safety, durability, and weather resistance remains a challenge. The development of new materials suitable for 3D printing in construction is ongoing.
Scale Limitations: While the potential to print large structures exists, the size of printable elements is often constrained by the dimensions of the available 3D printers. Overcoming these limitations requires continuous advancements in printer technology.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues: Integrating 3D printed buildings into existing regulatory frameworks poses significant challenges. Building codes and standards are still catching up with the advancements in 3D printing technology.
Skill Gaps: As 3D printing in construction is still relatively new, there is a notable skills gap in the workforce. Training programs and educational initiatives are crucial to equip professionals with the necessary expertise to leverage this technology effectively.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Building Technologies
The future of 3D printing in building technologies looks promising, with ongoing research and development expected to address current limitations and expand the capabilities of this technology. Innovations in printer design, material science, and digital modeling are likely to further enhance the viability and efficiency of 3D printing in construction, paving the way for more widespread adoption across the industry.
3D printing is poised to revolutionize the building technologies sector by providing more efficient, sustainable, and customizable construction solutions. As the technology continues to evolve, it promises to reshape the landscape of construction and architecture, making it possible to build more complex, durable, and creative structures more quickly and at a lower cost than ever before. The integration of 3D printing into building practices not only supports technological innovation but also promotes environmental sustainability and enhances the adaptability of living spaces to meet future needs.