Industrial design focuses on the development of products that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing. This field combines elements of art, engineering, and business to create goods that meet specific consumer needs. The advent of 3D printing technology, or additive manufacturing, has significantly influenced industrial design, providing new methods for creating complex and customized products more efficiently and sustainably. This transformative technology allows designers to rapidly prototype, test, and refine their ideas, drastically reducing the time and cost associated with product development.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Industrial Design
Initially utilized for prototyping within engineering sectors, 3D printing has evolved into a tool essential for product development across various industries, including consumer electronics, automotive, and healthcare. This technology allows industrial designers to bypass traditional manufacturing constraints, enabling the creation of designs that were once considered too complex or uneconomical to produce.
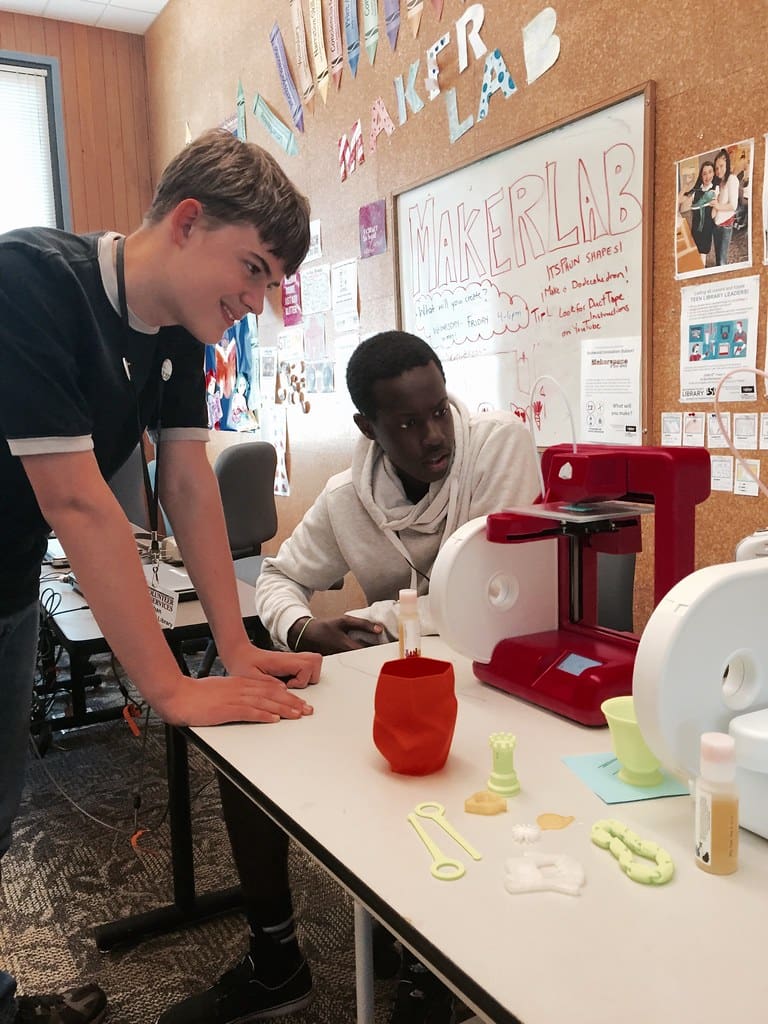

Advantages of 3D Printing in Industrial Design
Rapid Prototyping: One of the most significant advantages of 3D printing is the ability to quickly produce prototypes that designers can use to evaluate the look, feel, and functionality of their products. This rapid prototyping speeds up the iterative process of design, allowing for quick refinements based on testing and feedback.
Complex Geometries and Customization: 3D printing excels at creating parts with complex geometries that traditional manufacturing methods cannot achieve cost-effectively. It also allows for high levels of customization without additional production costs, catering to the growing consumer demand for personalized products.
Cost Reduction: By reducing the need for expensive tooling and minimizing material waste, 3D printing can lower the cost of product development and small-scale manufacturing. This is particularly beneficial for startups and small businesses with limited budgets.
Material Diversity and Functionality: Recent advancements in 3D printing materials have provided designers with a wide array of options, including plastics, metals, and composites that can be tailored to specific product requirements. These materials can include properties such as durability, flexibility, and heat resistance.
Sustainability: 3D printing promotes sustainable manufacturing practices by reducing material waste and enabling the use of eco-friendly materials. The ability to print on demand also decreases overproduction and excess inventory, aligning with environmental sustainability goals.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Industrial Design
Consumer Electronics: Designers utilize 3D printing to create ergonomic and aesthetically unique housings for devices such as smartphones, wearable technology, and headphones. This technology also allows for rapid prototyping of electronic components.
Automotive Parts: In the automotive industry, 3D printing is used to produce lightweight, durable components that can lead to improved vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. Designers also use it to develop customized interiors and complex end-use parts.
Medical Devices: 3D printing enables the design and production of customized medical and healthcare products, including prosthetics, orthotics, and implants tailored to fit individual patients precisely.
Furniture and Home Decor: Industrial designers are increasingly using 3D printing to create unique furniture pieces and home accessories. This approach allows for the exploration of new forms and structures that can redefine traditional aesthetics.
Toys and Games: 3D printing has transformed the toy industry by enabling designers to create complex toys and game components that can be customized to enhance user engagement and experience.
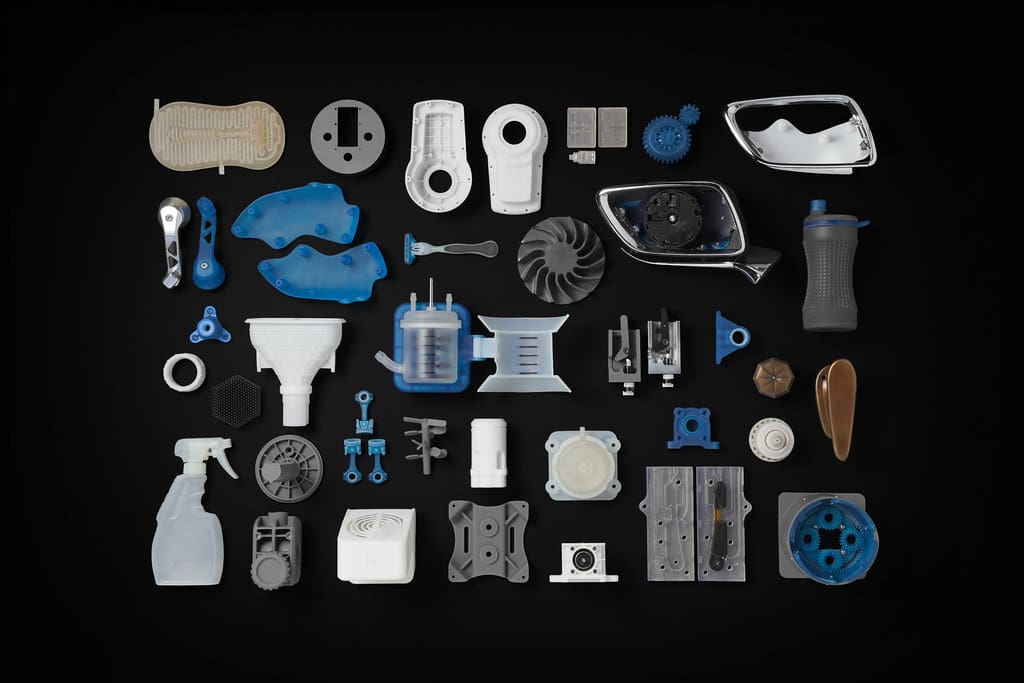

Challenges in 3D Printing for Industrial Design
Strength and Durability: While 3D printed objects can offer complex designs, ensuring they meet the strength and durability required for some commercial applications remains a challenge.
Scale Production Limitations: Although 3D printing is ideal for prototyping and small production runs, scaling up to large volumes can still be cost-prohibitive compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
Surface Finish and Aesthetics: Achieving high-quality surface finishes with 3D printing can require additional post-processing steps, which may increase time and costs.
Technical Skill and Knowledge: Effective utilization of 3D printing technology requires a deep understanding of design principles, material properties, and printing parameters, necessitating ongoing education and training for designers.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Industrial Design
As 3D printing technology continues to advance, its applications in industrial design are expected to broaden. Future innovations may include the development of new materials with enhanced properties, improvements in printing speed and quality, and more efficient post-processing techniques. Additionally, as consumer demand for personalized products increases, 3D printing will likely become an integral part of mass customization strategies in industrial design.
3D printing is revolutionizing industrial design by enabling more rapid, cost-effective, and creative product development. This technology empowers designers to push the boundaries of innovation, creating products that better meet consumer needs and preferences. As 3D printing technologies continue to evolve, they promise to further transform the industrial design landscape, making it more dynamic, responsive, and sustainable.