Apparel engineering combines the art of fashion design with the science and technology of manufacturing clothing. This field focuses on the technical aspects of clothing production, such as material selection, pattern making, and assembly processes. The advent of 3D printing technology has introduced a new dimension to apparel engineering, enabling designers and manufacturers to transcend traditional boundaries and create clothing that is both innovative and personalized. This technology not only streamlines the production process but also offers unprecedented opportunities for customization and functionality in apparel design.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Apparel Engineering
Originally used for prototyping in industries such as automotive and aerospace, 3D printing has found a compelling application in the fashion industry. It allows for the direct manufacturing of textiles and garments with complex designs that would be difficult or impossible to create using conventional methods. As 3D printing technology has evolved, it has been increasingly adopted by fashion designers and apparel engineers to create intricate patterns, seamless garments, and garments with integrated functionality such as flexibility, breathability, and water resistance.
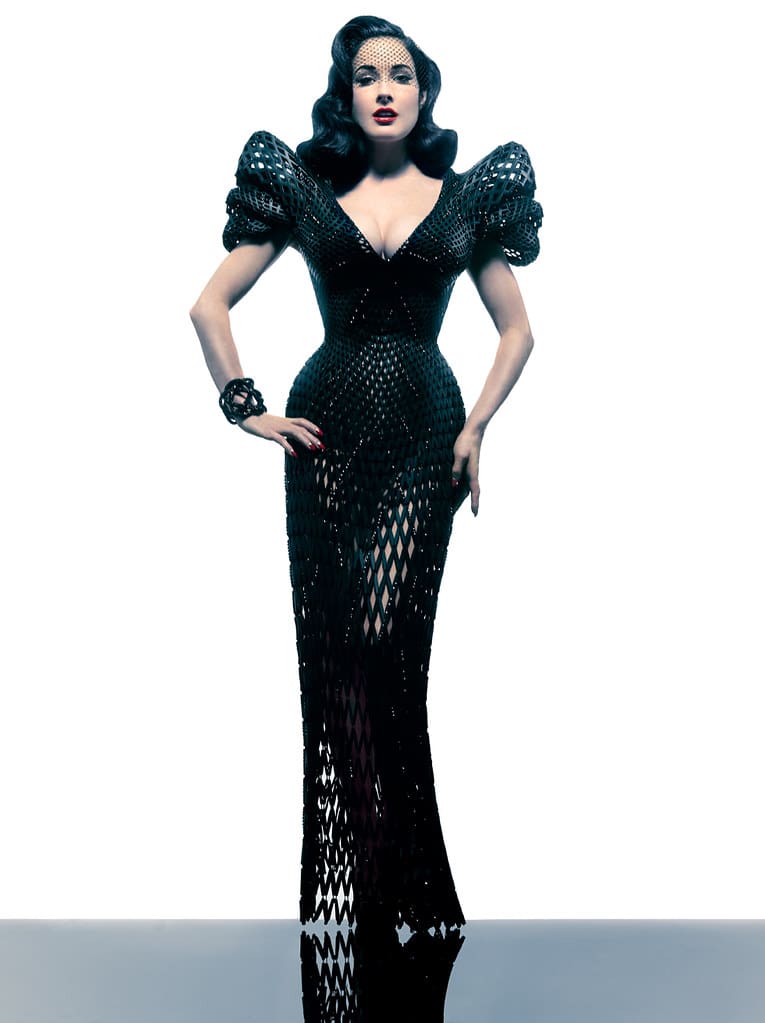

Advantages of 3D Printing in Apparel Engineering
Innovative Design Possibilities: 3D printing enables the creation of complex and detailed designs that are not limited by the constraints of traditional fabric manufacturing and garment assembly techniques. Designers can experiment with structures and shapes that were previously unachievable.
Customization and Personalization: One of the most significant benefits of 3D printing in apparel is the ability to customize garments at no additional production cost. Each piece can be tailored to fit the individual preferences and body measurements of the wearer.
Sustainability: 3D printing reduces waste by using only the amount of material necessary to produce a garment, unlike traditional garment manufacturing, which involves cutting from large pieces of fabric and often results in significant material waste.
Speed and Flexibility in Production: Apparel engineers can quickly move from design to production, reducing lead times and enabling rapid response to market trends. This agility is particularly beneficial in an industry characterized by fast fashion cycles.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Apparel Engineering
High Fashion and Couture: Designers use 3D printing to create intricate, one-of-a-kind couture pieces that showcase the possibilities of combining technology with traditional haute couture craftsmanship.
Performance Wear: In sports and performance apparel, 3D printing is used to fabricate garments with specific properties, such as enhanced aerodynamics, moisture-wicking capabilities, and optimal thermal comfort, tailored to the needs of athletes.
Footwear: 3D printing has revolutionized shoe design and manufacturing, allowing for the creation of shoes with custom-fit and optimized cushioning and support systems.
Prototyping and Fit Testing: 3D printing allows designers and engineers to prototype and refine garments and accessories quickly, ensuring better fit and comfort before mass production begins.

Challenges in 3D Printing for Apparel Engineering
Material Limitations: While there have been significant advancements in printable materials, the range suitable for comfortable, durable clothing is still developing. Current materials used in 3D printed apparel often lack the softness or flexibility desired for everyday wear.
Production Scale and Cost: Scaling 3D printing for mass production remains economically and technically challenging. The cost and speed of 3D printing need further improvement to compete with traditional textile manufacturing methods.
Technical Skills and Integration: Integrating 3D printing into traditional apparel manufacturing processes requires a shift in skills and understanding. Training and development are necessary for designers and engineers to fully leverage this technology.
Market Acceptance: Despite its potential, there is still a need for greater market acceptance of 3D printed apparel. Consumer awareness and appreciation of the benefits of 3D printed garments need to be fostered.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Apparel Engineering
The future of 3D printing in apparel engineering is promising, with ongoing innovations likely to enhance the practicality and appeal of 3D printed garments. Expected advancements include the development of new flexible, comfortable materials that can meet consumer expectations and improvements in printing technologies that reduce costs and increase production speeds.
3D printing is poised to continue its transformative impact on apparel engineering, offering new tools for innovation and efficiency in garment design and production. As the technology progresses, it promises to further revolutionize the apparel industry, enabling more sustainable practices, personalized fashion, and enhanced functionality. With continued development and integration, 3D printing will increasingly become a fundamental part of apparel engineering, reshaping the way clothing is conceived, produced, and worn.