The craft of making musical instruments is an ancient art, deeply rooted in tradition and skilled craftsmanship. However, in recent years, 3D printing technology has begun to significantly influence this field, introducing new possibilities for instrument design, manufacturing, and customization. This innovative approach not only offers a fresh perspective on traditional manufacturing techniques but also opens up new avenues for creativity and expression in music.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Musical Instruments
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has been utilized in various industries for rapid prototyping and complex part production. Its application in musical instrument manufacturing is a relatively recent development, spurred by advancements in 3D printing technologies and materials that can meet the demands of musical performance. Today, musicians and makers are exploring the potential of 3D printed instruments, from classical violins and guitars to unique, custom-designed creations that challenge traditional acoustic concepts.

Advantages of 3D Printing in Musical Instruments
Innovative Designs: 3D printing allows for the creation of complex, intricate shapes that are often impossible to achieve with conventional woodworking or metalworking techniques. This capability enables instrument designers to experiment with novel structural configurations that can enhance sound quality and playability.
Customization: Musicians often seek instruments tailored to their specific needs and preferences. 3D printing offers unprecedented customization options, including adjustable features, ergonomic designs tailored to the musician’s physique, and aesthetic modifications that reflect personal style.
Material Diversity: Modern 3D printers can work with a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, and composite materials. Each material brings different acoustic properties, allowing for the exploration of new sounds and tonal qualities that expand the musical palette.
Cost-Effective Prototyping: Developing new musical instruments traditionally requires extensive time and resources. 3D printing significantly reduces these costs by streamlining the prototyping process, allowing for more rapid iteration and testing of design ideas.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Musical Instruments
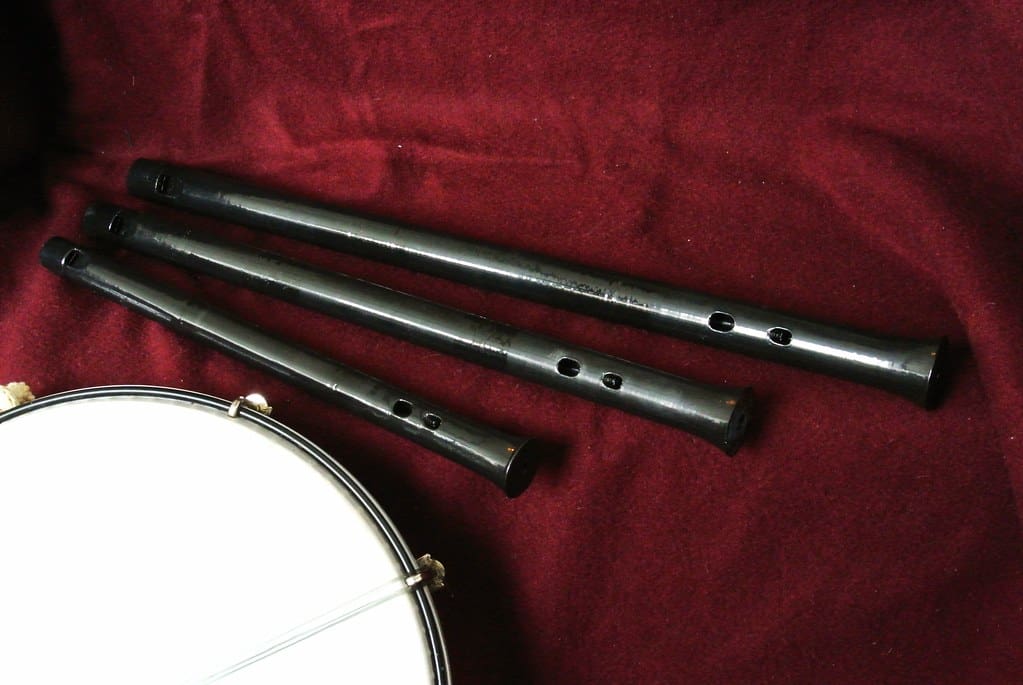
Wind Instruments: Flutes, clarinets, and other wind instruments have been successfully produced using 3D printing. These instruments can be designed to optimize airflow and resonance chambers more precisely than traditional methods, potentially improving sound quality and ease of playing.
Stringed Instruments: Violins, guitars, and ukuleles are among the stringed instruments that have seen innovative applications of 3D printing. Not only can the bodies of these instruments be printed, but intricate details like fretboards and tuning pegs can also be precisely manufactured to enhance performance and visual appeal.
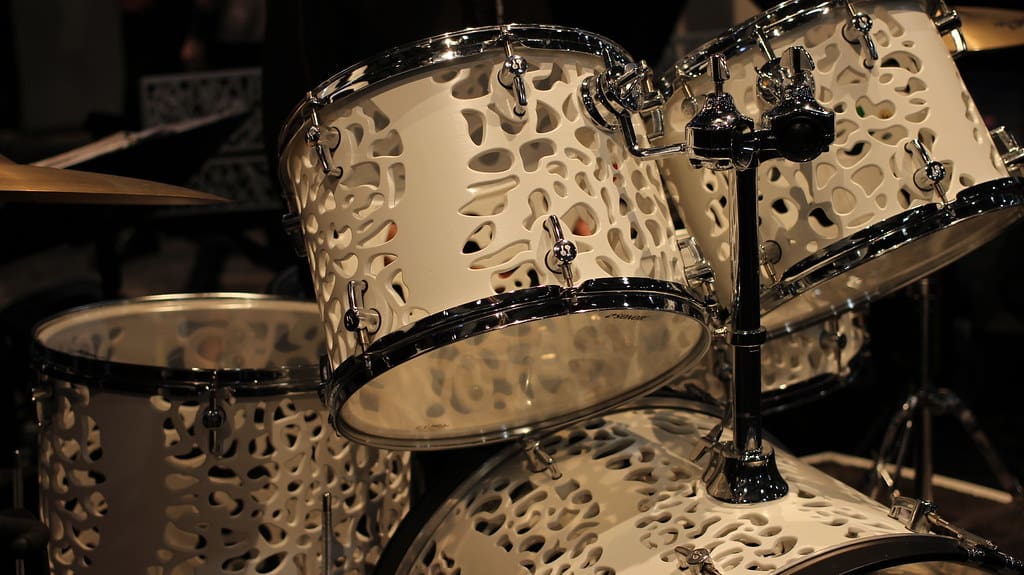
Percussion Instruments: Drums and other percussion instruments benefit from the structural strength and lightweight properties of 3D printed materials, allowing for durable, consistent, and sonically interesting designs.
Experimental Instruments: Perhaps one of the most exciting aspects of 3D printing in musical instruments is the creation of entirely new types of instruments. Designers can experiment with shapes, sizes, and materials to create unique sounds and performance experiences that were previously unimaginable.
Challenges in 3D Printing for Musical Instruments
Despite the exciting possibilities, there are several challenges to the widespread adoption of 3D printing in musical instrument manufacturing:
Acoustic Properties: Matching the rich, nuanced tones of instruments made from traditional materials like wood can be difficult. Ongoing research and experimentation are necessary to improve the acoustic performance of 3D printed instruments.
Material Limitations: While there is a wide range of materials available for 3D printing, finding materials that meet the durability, aesthetic, and tonal requirements of high-quality musical instruments is still a challenge.
Perception and Acceptance: Traditionalists in music often value the craftsmanship and history associated with classic instrument manufacturing. Overcoming skepticism from musicians and consumers about the quality and authenticity of 3D printed instruments is essential.

Future Directions in 3D Printing for Musical Instruments
The future of 3D printing in musical instruments looks promising, with continuous advancements in printer technology, materials, and design software expected to overcome current limitations. As these technologies mature, the potential for 3D printed instruments to become more commonplace and accepted increases. Additionally, the ongoing exploration of new materials and hybrid manufacturing processes (combining traditional and additive manufacturing) may lead to further innovations in instrument design and performance.
3D printing is set to continue its transformative impact on the field of musical instrument manufacturing, offering exciting opportunities for innovation and customization. As the technology evolves, it promises to broaden the horizons of what is possible in music production, enabling artists and makers to explore new sounds, forms, and expressions. The harmonization of traditional craftsmanship with modern manufacturing through 3D printing not only preserves the art of instrument making but also propels it into a new era of technological integration and creative potential.