Transport engineering, a crucial sector that designs, builds, and maintains systems for moving people and goods, is experiencing rapid transformation thanks to 3D printing technology. This innovative approach is revolutionizing the development of transport infrastructure and vehicles by enabling more flexible designs, reducing production costs, and increasing the efficiency of manufacturing processes. As global demand for smarter, more sustainable transportation solutions grows, 3D printing is becoming an essential tool in the transport engineer’s toolkit.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Transport Engineering
Originally used for prototyping in manufacturing, 3D printing has expanded into transport engineering as a key technology for producing parts and systems directly from digital models. The ability to print components on-demand revolutionizes inventory management and reduces the need for large manufacturing spaces, significantly impacting production logistics in transport engineering.

Advantages of 3D Printing in Transport Engineering
Enhanced Design Flexibility: 3D printing allows transport engineers to explore complex geometric designs that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. This capability enables the creation of parts that are optimized for performance with reduced weight and increased strength.
Reduced Time and Costs: 3D printing accelerates the development process from design to production. Engineers can quickly iterate designs and produce prototypes, speeding up the testing phase and reducing the time to market for new transportation solutions.
Increased Material Efficiency and Sustainability: By adding material only where needed, 3D printing minimizes waste compared to subtractive manufacturing processes. The potential to use recycled materials further enhances the sustainability of transport projects.
Customization and On-Demand Production: 3D printing supports the production of customized parts for specific applications without the need for costly tooling changes. This is particularly advantageous for bespoke or limited-run transport solutions.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Transport Engineering
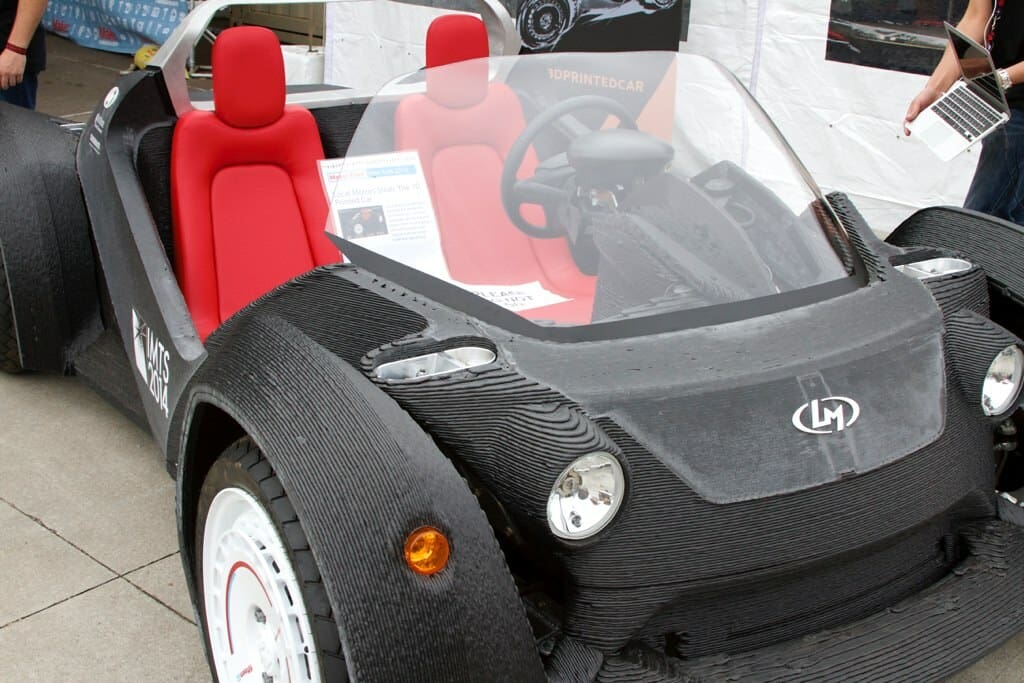
Vehicle Components: From automotive to aerospace, 3D printing is used to produce lightweight, durable components such as brackets, panels, and even critical engine parts. In aerospace, for example, 3D-printed titanium parts are commonplace due to their strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance.
Public Transport Infrastructure: 3D printing is finding applications in the construction of public transport facilities, such as bus stops and railway station components. These structures can be designed to meet exact local requirements and manufactured quickly, reducing construction time and disruption.
Rapid Prototyping for Vehicles: Automotive and aerospace engineers use 3D printing for rapid prototyping of new vehicle designs, allowing for extensive testing and refinement before final production. This not only speeds up the development process but also helps in achieving higher safety and performance standards.
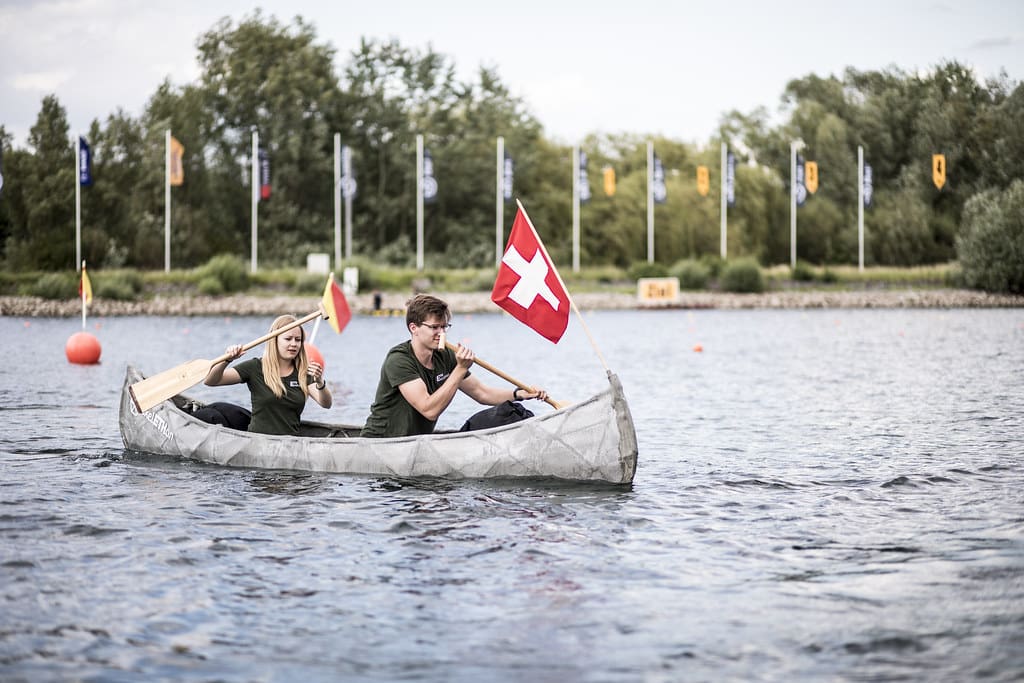
Bridge Construction: Several projects around the world have successfully demonstrated the use of 3D printing in constructing pedestrian and road bridges. These bridges are often made with innovative materials and designs that can be tailored to specific environmental and aesthetic needs.

Challenges in 3D Printing for Transport Engineering
Despite the significant advantages, there are challenges to integrating 3D printing into mainstream transport engineering:
Material Performance: Ensuring that 3D-printed materials can perform under the high stresses and environmental conditions typical in transportation is crucial. Ongoing research is aimed at enhancing the durability and performance characteristics of printed materials.
Scale Limitations: While 3D printing is ideal for small components and prototypes, scaling the technology to produce larger parts, like entire vehicle chassis or major structural sections of aircraft, is still challenging both technically and economically.
Regulatory and Safety Standards: Transport engineering is heavily regulated, and meeting safety standards with new manufacturing methods is a complex process. Certifying 3D-printed parts for use in critical applications involves rigorous testing and validation to ensure they meet all regulatory requirements.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Transport Engineering
The future of 3D printing in transport engineering is promising, with continuous advancements in printer technology, materials science, and digital design tools. Innovations are expected to address current challenges, leading to wider adoption of 3D printing across the transportation sector. Furthermore, the integration of 3D printing with emerging technologies such as AI and IoT could lead to even more efficient and autonomous production processes.
3D printing is set to revolutionize transport engineering by offering innovative solutions that enhance vehicle performance, reduce environmental impact, and streamline production processes. As the technology continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of transportation, making it more sustainable, efficient, and adaptable to changing global needs.