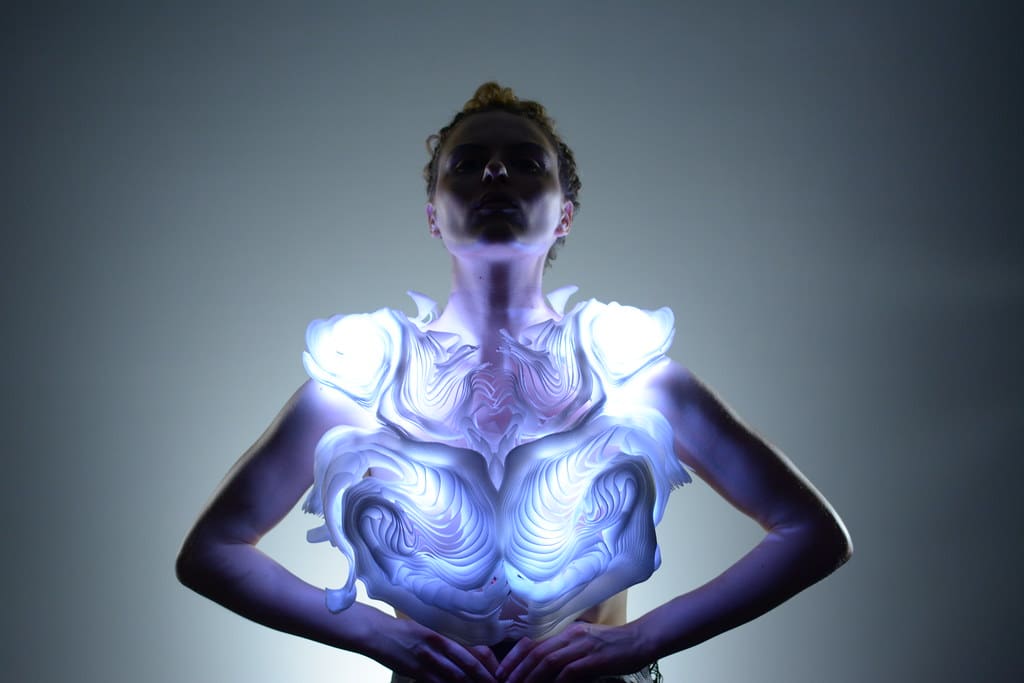
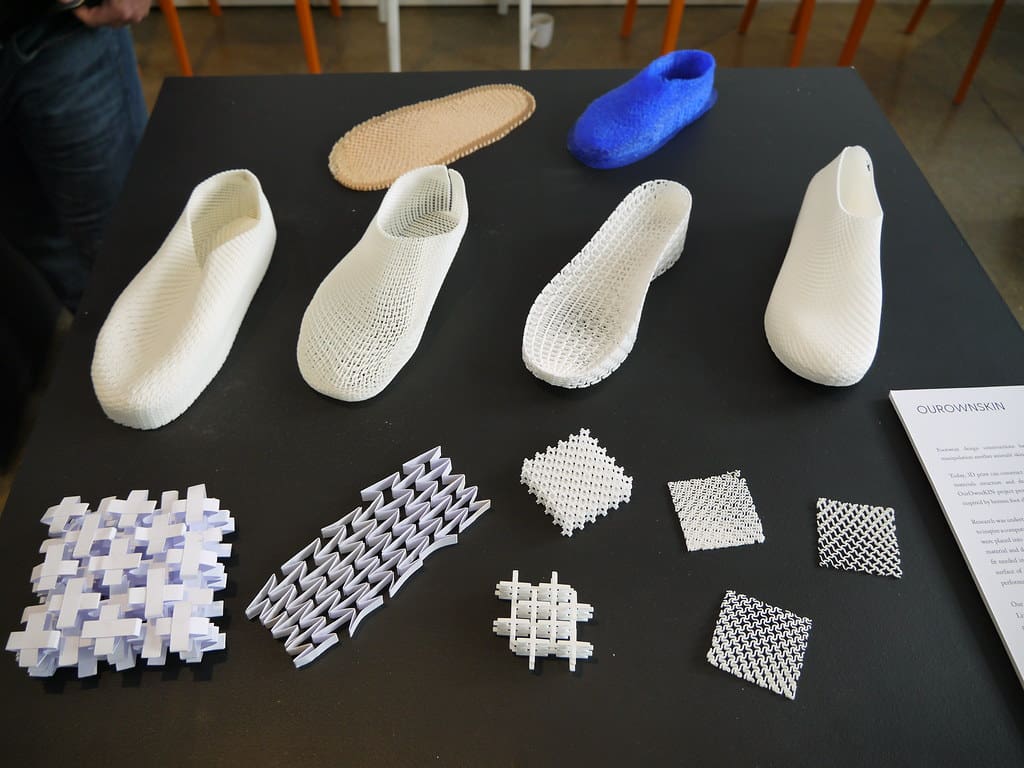
3D printing is steadily gaining traction in the clothing industry, offering a fresh perspective on fashion design and manufacturing. This technology allows designers to transcend traditional fabrication limits, enabling unprecedented levels of customization, intricate detailing, and a significant step towards sustainable fashion. As the industry grapples with environmental concerns and shifts towards more personalized consumer experiences, 3D printing emerges as a key technology.
Advantages of 3D Printing in Clothing Production
The adoption of 3D printing in clothing brings numerous advantages:
Customization and Fit: 3D printing offers unparalleled opportunities for customization, allowing garments to be tailored to individual body shapes. This ensures a perfect fit, enhancing both the comfort and style of the wearer, a leap forward in personalization that traditional methods struggle to match.
Design Freedom: This technology enables designers to explore complex, often avant-garde structures that are challenging or impossible to create with conventional textile techniques. 3D printing fosters a new level of creativity in fabric patterns, garment structure, and integration of non-textile elements.
Sustainability: One of the most compelling aspects of 3D printing is its potential to minimize waste. Traditional cut-and-sew methods result in substantial fabric waste, whereas 3D printing utilizes only the material needed to construct the garment. Moreover, there’s potential for using recycled materials to further enhance the environmental benefits.
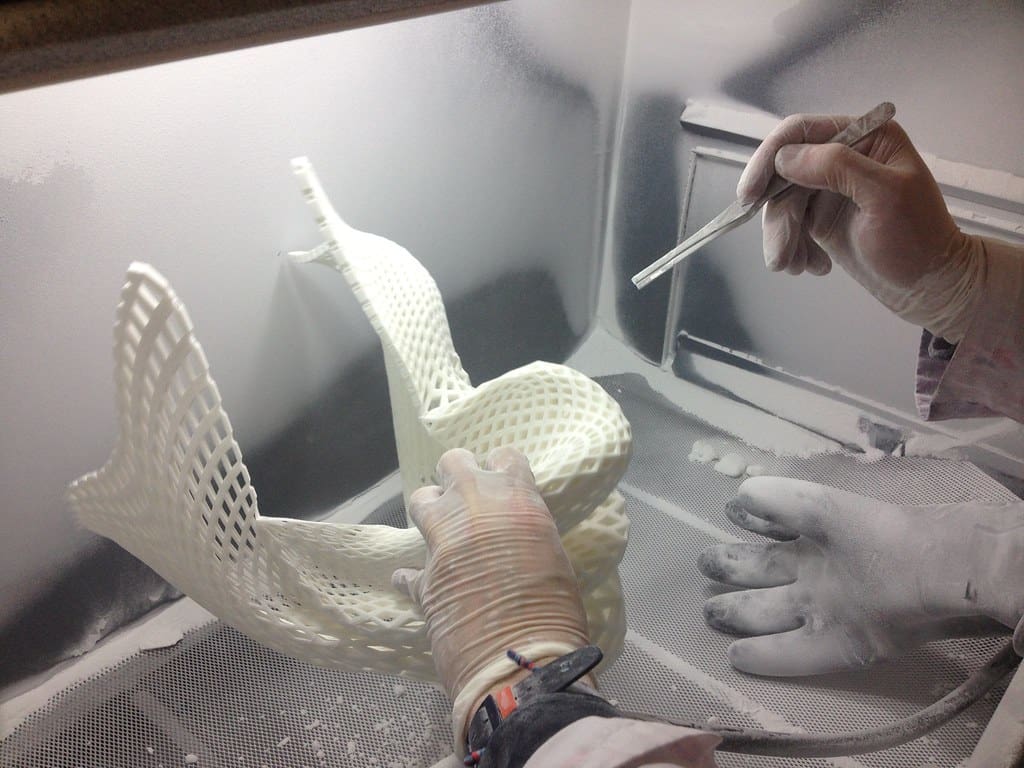

Key Applications of 3D Printing in the Clothing Industry
3D printing finds various applications across the fashion sector:
High Fashion and Haute Couture: Designers in the high fashion realm employ 3D printing to produce striking, intricate runway pieces that often serve as trendsetters. These garments showcase the elaborate capabilities of 3D printing, from sculptural forms to intricate lattice structures that textiles cannot replicate.
Sportswear and Performance Apparel: In sportswear, 3D printing is used to develop garments with specific performance enhancements such as aerodynamic features, optimized breathability, and precisely placed support or flexibility.
Footwear: The footwear industry benefits greatly from 3D printing, especially in customizing shoes for optimal fit and performance. Companies are now offering shoes with 3D printed insoles and midsoles tailored to the wearer’s foot contours and movement style.
Prototyping and Sample Testing: 3D printing accelerates the design process by enabling quick production of prototypes and samples, allowing for rapid iteration and refinement before final production. This not only speeds up the development cycle but also reduces costs associated with sample production.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its potential, 3D printing in the clothing industry faces several challenges:
Material Limitations: Current materials used in 3D printing, such as certain plastics and resins, may not always provide the comfort and wearability required for everyday clothing.
Production Speed and Cost: While 3D printing is excellent for prototyping and custom pieces, its speed and cost-efficiency at a mass production scale are currently less competitive than traditional textile manufacturing.
Market Adoption: Consumer acceptance of 3D printed garments is still evolving, with concerns about the aesthetics, comfort, and durability of printed materials compared to conventional fabrics.
Future Trends in 3D Printing for the Clothing Industry
Looking ahead, the future of 3D printing in clothing promises exciting developments:
Material Innovations: Advances are expected in the development of new printable materials that are more flexible, comfortable, and akin to traditional textiles in feel and durability.
Mainstream Adoption: As the technology matures and becomes more cost-effective, it is likely to be adopted more widely across the fashion industry, potentially becoming a standard tool for both mass production and bespoke fashion.
Integration with Wearable Technology: The potential for integrating sensors and other electronic components directly into garments could open new possibilities for smart clothing that not only looks unique but also performs specific functions, from health monitoring to changing color or pattern in response to environmental stimuli.
3D printing is poised to revolutionize the clothing industry by fostering greater innovation, customization, and sustainability. As this technology continues to evolve, it offers exciting opportunities for the future of fashion, challenging designers and manufacturers to rethink the boundaries of what’s possible in clothing production. Embracing 3D printing could well be crucial for the next generation of fashion industry leaders.