In recent years, 3D printing has emerged as a transformative force in the defense industry, revolutionizing how military equipment is manufactured, maintained, and improved. By enabling on-demand production and reducing dependency on complex supply chains, 3D printing not only enhances operational efficiency but also introduces new capabilities for defense applications. This technology is being increasingly adopted across global defense organizations, signifying a major shift in military manufacturing paradigms.
Enhancing Logistics and Manufacturing
3D printing offers significant logistical advantages by allowing military units to produce parts and equipment directly at or near their point of use. This capability is critical in scenarios where supply lines are compromised or when immediate part replacement is crucial. For example, the U.S. Navy has installed 3D printers on ships, enabling the on-site production of spare parts necessary for ongoing operations, thereby reducing the need for large stocks and minimizing downtime during critical missions.
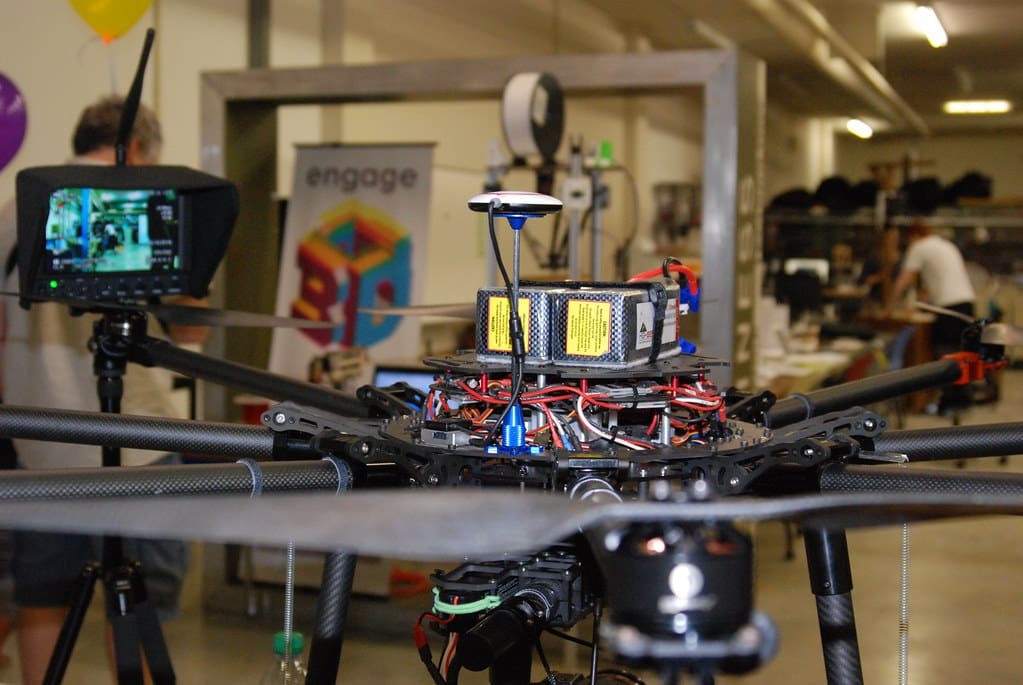

Additionally, the technology simplifies the manufacturing process for complex parts. Components for vehicles, aircraft, and ships that traditionally require extensive tooling and assembly can now be printed in a single process, reducing costs and lead times significantly. This has been particularly transformative in the production of parts with intricate designs that are otherwise too complex or uneconomical to produce using conventional methods.
Innovation in Weapon Systems and Equipment
The defense sector is also leveraging 3D printing to innovate and enhance weapon systems. This technology allows for the creation of parts that are lighter yet more complex than those made through traditional manufacturing, improving the performance and portability of various weapons systems. For instance, 3D printing has been utilized to produce components of missile systems and drones, with designs that optimize aerodynamics and functionality while reducing weight.
Lightweight armor and protective gear are other key areas where 3D printing is making an impact. By using advanced materials and customized designs, military engineers are able to produce armor that provides better protection and comfort for the wearer, potentially improving soldier survivability in combat situations.
Customization for Soldier Safety and Efficiency
One of the most significant benefits of 3D printing in the defense industry is the ability to produce customized equipment tailored specifically to the needs of individual soldiers. This includes ergonomic and protective gear designed according to the unique anatomical data of each service member, such as customized helmets or footwear that provide enhanced comfort and protection.

Moreover, 3D printing facilitates the development of advanced exoskeletons designed to reduce soldier fatigue and increase load-carrying capabilities without compromising mobility. These personalized enhancements are crucial for maintaining high performance and efficiency in field operations.
Research and Development
3D printing accelerates the research and development of new military technologies by enabling rapid prototyping. This allows for faster iteration and refinement of designs, reducing the time from concept to deployment. Collaborations between defense departments and private or academic entities often utilize 3D printing to push the boundaries of what’s possible in military technology, experimenting with new materials and complex structures that were previously unachievable.
Challenges and Considerations
While 3D printing offers numerous advantages, integrating this technology into military applications comes with challenges. High-grade materials suitable for defense applications can be costly and require advanced 3D printing technology. Additionally, security concerns around data sharing and the potential for printing critical components necessitate stringent controls.
Regulatory and ethical considerations also play a significant role, especially in relation to the manufacturing of weapons and the export controls associated with 3D printing technologies.
Future Prospects
Looking forward, 3D printing is expected to continue evolving within the defense industry. Future developments may include enhanced printing technologies capable of handling more diverse materials with greater precision. These advancements could further expand the use of 3D printing in producing more sophisticated and reliable military equipment, potentially transforming strategic capabilities and readiness.
3D printing is set to redefine the landscape of the defense industry significantly. With its capacity to produce high-strength, intricate components on demand, 3D printing not only streamlines manufacturing processes but also opens up new possibilities for military innovation. As this technology continues to mature, its integration into defense strategies will likely become more prevalent, offering enhanced capabilities and operational flexibility across global military forces.