3D printing, initially seen as a futuristic novelty, has matured into a robust manufacturing tool used across a wide range of industries. From rapid prototyping to advanced production processes, 3D printing has revolutionized how products are designed, tested, and manufactured, offering unparalleled flexibility and enabling innovation at every turn. This versatility has made it an invaluable asset in fields as diverse as aerospace, medicine, fashion, and beyond.
Industrial Manufacturing
The ability of 3D printing to simplify complex assemblies into single processes has had a transformative impact on industrial manufacturing. In aerospace, companies like Boeing and Airbus use 3D printing to produce parts that are lighter, reducing aircraft weight and saving on fuel costs. These components often feature intricate internal structures that could only be made with 3D printing, combining strength with minimal weight.
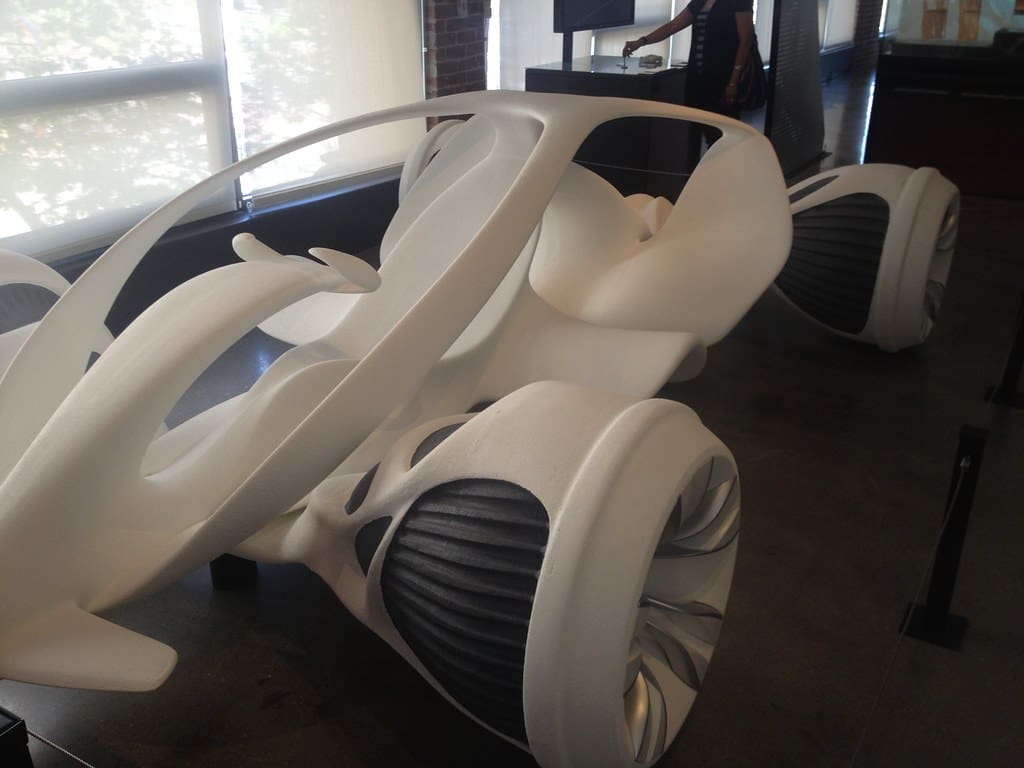

Automotive manufacturers harness 3D printing for both prototyping and production. Companies like BMW and Tesla are integrating 3D printed parts into their vehicles to customize interiors and even optimize parts such as brackets and ductwork. The technology allows for a rapid turnaround from design to production, enabling quicker responses to market changes and reducing downtime in manufacturing processes.
Healthcare
Perhaps no industry has been transformed by 3D printing as profoundly as healthcare. Prosthetics and implants are customized to individual patients, improving comfort and functionality. This customization is critical in areas like pediatric orthopedics, where devices need frequent adjustment and replacement as children grow.
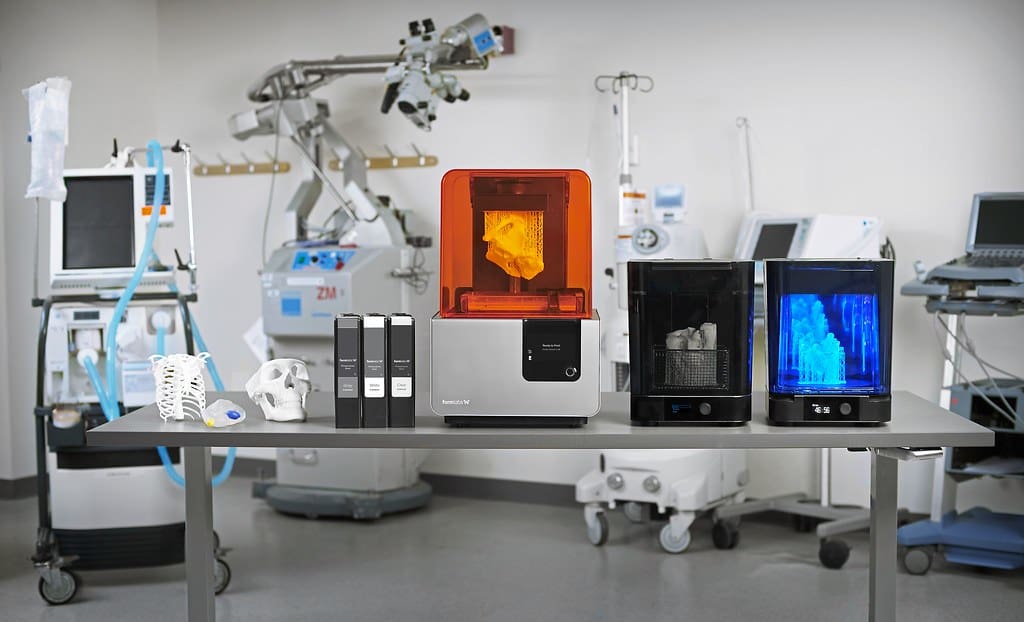

Dental applications are particularly prolific, with 3D printing used to create everything from crowns and bridges to orthodontic devices. This technology reduces waiting times and costs, while increasing the comfort and aesthetic outcomes for patients.
Moreover, 3D bioprinting is on the frontier of medical science, with researchers working towards printing functional human tissues and organs. While still in the developmental phase, this could potentially address the critical shortage of organ donors in the future.
Consumer Products
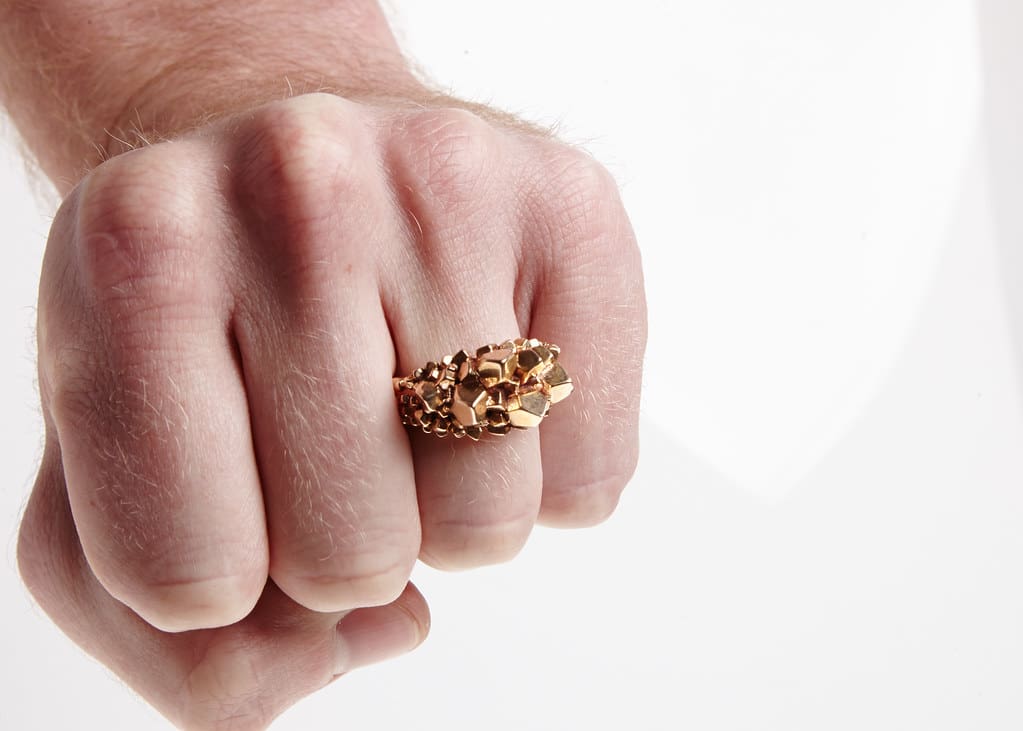
In the consumer products sector, 3D printing allows for the mass customization of goods, from personalized footwear that fits perfectly to bespoke jewelry designed to the consumer’s specifications. Eyewear brands offer frames tailored to the unique contours of the customer’s face, improving comfort and style. Even in home decor, 3D printing enables designers to create unique, complex pieces that reflect individual styles and preferences.

Construction and Architecture
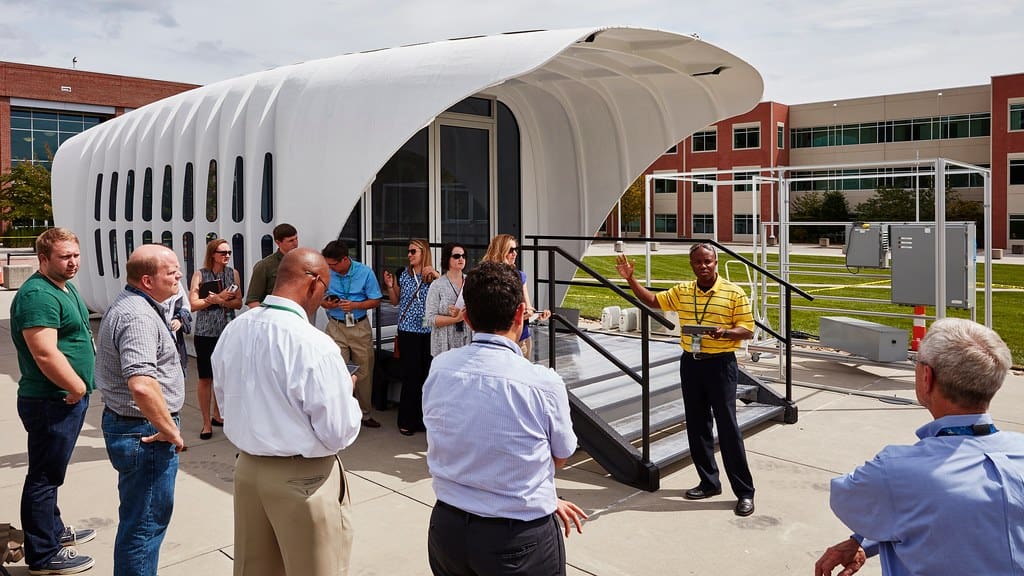
In construction, 3D printing is being used to produce everything from residential homes to commercial buildings, offering a faster, more sustainable method of construction. The technology has been particularly embraced for creating complex architectural features that would be too costly or impossible to achieve with traditional construction methods. Companies like ICON are using 3D printing to build homes in significantly less time than conventional methods, and at a fraction of the cost, providing durable housing solutions in underprivileged areas.

Education and Research
Educational institutions are increasingly incorporating 3D printing into their curriculums, from elementary schools to universities. This hands-on learning tool enhances the educational experience, allowing students to bring their ideas to life. In universities, 3D printing is used for more advanced applications, such as architectural models, engineering prototypes, and historical preservation.
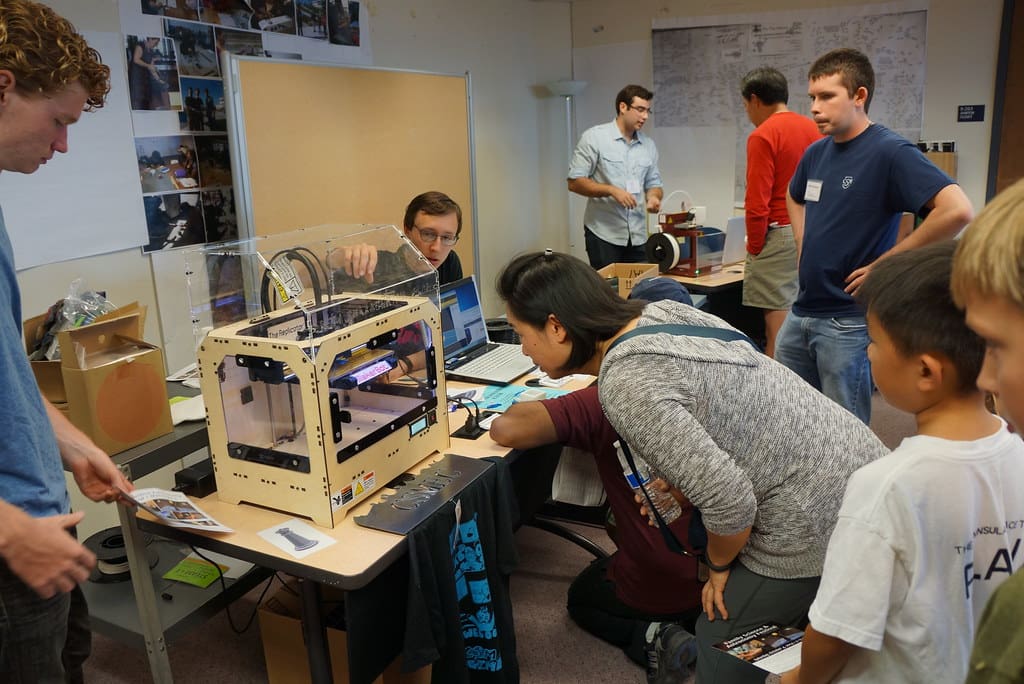

Researchers also leverage 3D printing for experimental setups and custom apparatus, often at a lower cost and with faster turnaround than traditional fabrication methods would allow. This accessibility is enabling groundbreaking studies in fields from archaeology to zoology.
Art and Design
The impact of 3D printing on the art and design world has been revolutionary, enabling artists and designers to explore complex geometries and new forms of expression. This has been evident in both fine art, where sculptors create pieces that were previously impossible, and in fashion, where designers like Iris van Herpen produce intricate garments that are as much engineering feats as they are works of art.

Challenges and Future Potential
Despite its many advantages, 3D printing is not without its challenges. Issues such as the cost of printers, the need for skilled operators, and the environmental impact of waste materials need addressing. However, continuous advancements in technology are helping to overcome these barriers, making 3D printing more accessible and sustainable.
The future of 3D printing promises even greater integration into industrial processes, enhanced material properties, and, ultimately, the closer realization of fully customized mass production.
3D printing has already changed the landscape of manufacturing, healthcare, design, and more. As the technology progresses, its potential seems almost limitless, promising to further disrupt and transform how we create, build, and design. For businesses and creatives alike, embracing 3D printing is not just about keeping up with the times—it’s about staying ahead of the curve in an increasingly competitive world.