PolyJet 3D printing stands out in the realm of additive manufacturing for its exceptional ability to produce high-resolution, multi-material objects with precise detail and smooth finishes. Similar to how an inkjet printer works, PolyJet technology layers photopolymer resins and cures them instantly using UV light, enabling the creation of complex geometries and intricate designs that are difficult to achieve with other 3D printing technologies.
How PolyJet Printing Works
The core of PolyJet printing lies in its precision. The process begins with a jetting head, akin to those used in traditional inkjet printing, which deposits tiny droplets of photopolymeric resin onto a build tray. Each droplet is only a few microns in diameter, allowing for extremely detailed features and a smooth surface finish. After a layer of resin is deposited, it is immediately cured by ultraviolet light. This process repeats layer by layer, building the object from the bottom up.
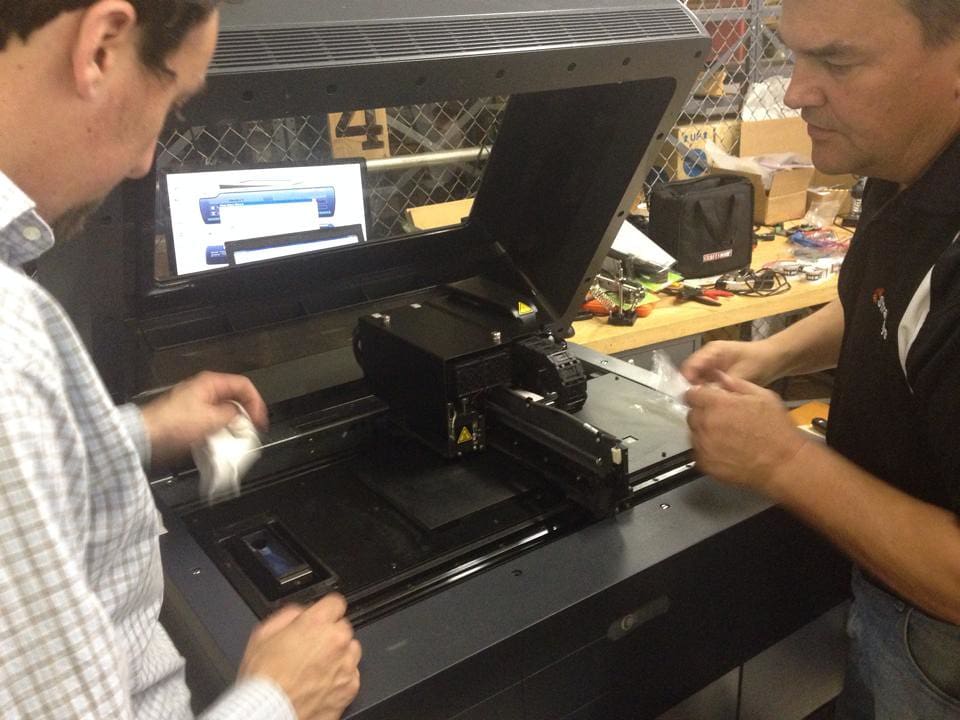

One of the unique features of PolyJet is its ability to print with multiple materials simultaneously. This includes a variety of colors and material properties, from rigid to flexible, all within a single print cycle. As a result, designers can create models that have a range of textures and mechanical properties without the need for painting or assembly.
Advantages of PolyJet 3D Printing
Precision and Detail: With resolutions as fine as 16 microns, PolyJet is ideal for applications where detail is paramount, such as in medical modeling or consumer product design.
Material Versatility: The technology supports over 500 different materials, allowing for prints that can include diverse properties such as transparency, flexibility, and various colors in one object.
Speed: PolyJet is notably fast in the setup and printing process, making it highly suitable for rapid prototyping environments where time is of the essence.
Applications of PolyJet 3D Printing
PolyJet technology is employed across various sectors:
Consumer Goods and Electronics: For creating realistic prototypes of devices with fine details and smooth surfaces that closely mimic the final product.
Medical Devices: Used in the production of models for surgical planning and medical training, where anatomical precision is required.
Education: Helps in creating detailed models that aid in teaching complex subjects such as biology, chemistry, and engineering.
Considerations and Limitations
Despite its advantages, PolyJet does have some limitations:
Cost: The high cost of PolyJet printers and their materials can be prohibitive for smaller businesses or individual designers.
Post-Processing: While the parts have a high-quality finish, removing support material and additional curing can be necessary, adding time to the overall manufacturing process.
Material Properties: The materials used in PolyJet printing generally do not have the same strength or temperature resistance as those used in traditional manufacturing, which may limit their use in functional applications.
The Future of PolyJet Printing
Advancements in PolyJet technology continue to enhance its appeal. Ongoing developments aim to expand the range of materials with improved functional properties and to increase the printing speed, making it even more efficient. As these improvements unfold, PolyJet is expected to find new applications in areas currently dominated by traditional manufacturing methods.
PolyJet 3D printing offers unmatched capabilities in the production of detailed, high-quality prototypes and models. Its ability to combine multiple materials into a single print makes it a valuable tool in industries requiring precision and customization. As the technology evolves, it holds the potential to transform how products are designed and prototyped, pushing the boundaries of innovation in various fields.