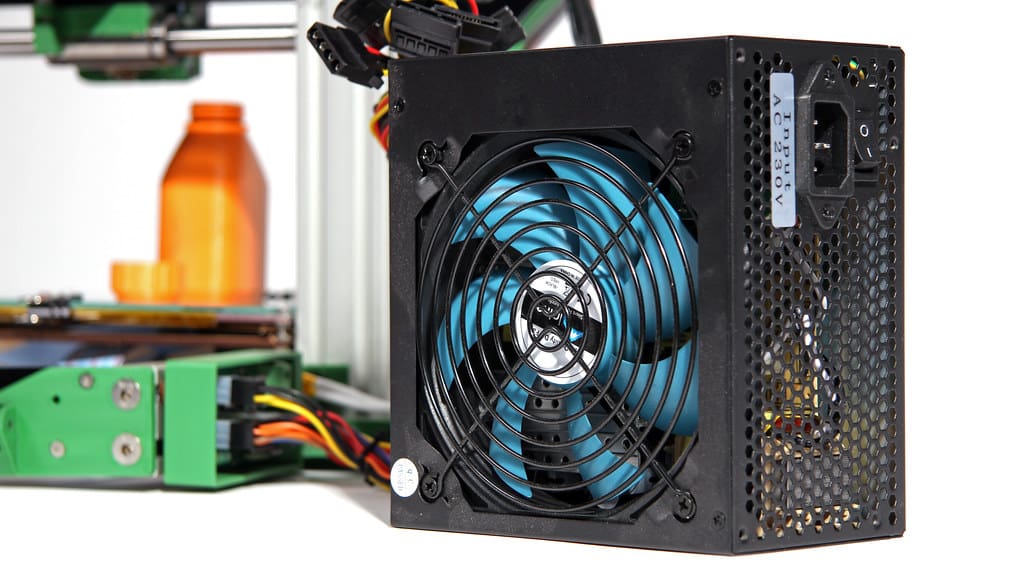
The power supply in a 3D printer is a critical component that often goes unnoticed despite its fundamental role in ensuring the smooth and effective operation of the printer. It converts mains AC (alternating current) to low-voltage regulated DC (direct current) power, which is safe and necessary for the delicate electronic components and motors within the printer. This article explores the importance, types, and considerations of power supplies in 3D printing, highlighting their impact on the overall functionality and reliability of the printer.
Importance of the Power Supply in 3D Printing
Stability: The power supply stabilizes the electrical current, ensuring that the printer operates without fluctuations that can lead to failures or inaccuracies in print quality.
Safety: It provides protection against electrical hazards such as short circuits, overvoltage, and overcurrent, which are crucial for the safe operation of electronic equipment.
Efficiency: A good power supply is efficient, converting electricity without excessive waste as heat. This efficiency not only saves energy but also reduces the thermal stress on the printer components.
Capability: The power supply must be capable of handling the total load required by the printer, including the motors, heated bed, hotend, and control electronics, to ensure that the printer can perform to its maximum capacity.
Components of a 3D Printer Power Supply
Transformer: Converts the high voltage AC from the mains to a lower voltage suitable for the printer’s needs.
Rectifier: Changes the AC to DC, as DC is necessary for the steady operation of the printer’s electronics and motors.
Filter: Smoothes out the DC current to eliminate any AC residue or voltage spikes that could potentially harm the printer’s electronic components.
Regulator: Maintains a constant voltage output regardless of changes in load or input voltage, which is vital for the consistent performance of the printer.
Types of Power Supplies Used in 3D Printers
ATX Power Supplies: Originally designed for personal computers, ATX power supplies are commonly used in DIY 3D printers due to their availability, affordability, and reliability. They often include features such as fan cooling and various protection mechanisms.
Dedicated 3D Printer Power Supplies: These are specifically designed for use in 3D printers, with ratings to handle typical loads of popular printer models. They are usually compact, enclosed units that prioritize efficiency and stability tailored for 3D printing.
Adjustable Power Supplies: Some advanced 3D printers utilize adjustable power supplies that allow users to modify the output characteristics based on different operational needs, such as changing the heat bed temperature more quickly.
Switching Power Supplies: These are now more common in 3D printers due to their efficiency and the ability to handle a wide range of input voltages and outputs. Switching power supplies are lighter and more compact than traditional transformer-based supplies.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper Sizing: Ensuring that the power supply is adequately rated for the printer’s maximum power consumption is crucial. It should provide enough current for the heated bed, which is often the most power-consuming component, in addition to the motors and hotend.
Ventilation: Power supplies generate heat, and adequate ventilation is essential to prevent overheating. Placement in areas with good airflow and, if necessary, additional cooling fans can help maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Regular Checks: Visual inspections for signs of wear, damaged cables, or connections and listening for unusual noises can help catch issues early before they lead to failures during printing.
Dust and Debris: Keeping the power supply clean and free from dust will prevent potential shorts and overheating. This is particularly important in environments with high particulate matter, such as workshops.
Safety and Upgrades
Safety Features: Features such as overcurrent protection, short circuit protection, and thermal shutdown are important for the safety of both the printer and its operator. Ensuring that the power supply complies with safety standards is crucial.
Upgrades: As printers are upgraded and possibly draw more power, it might become necessary to upgrade the power supply to a unit that can handle increased loads. This is especially true if adding significant components like a larger heated bed or additional extruders.
The power supply is a vital backbone of any 3D printer, ensuring that all other components receive the stable, reliable power they need to function correctly. Understanding the role of the power supply, the types available, and the key considerations for its maintenance and upgrade can significantly impact the performance and longevity of a 3D printer. Properly managing this often-overlooked component can lead to safer, more efficient, and more reliable printing outcomes, ensuring that the printer operates at its best at all times.