Vehicle engineering is at a pivotal point of transformation, largely influenced by the integration of 3D printing technologies. Known for its capacity to revolutionize manufacturing processes, 3D printing is enabling vehicle engineers to push the boundaries of design, performance, and sustainability in automotive production. From passenger cars to commercial vehicles and racing applications, 3D printing offers a range of benefits that enhance the functionality and efficiency of automotive designs.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Vehicle Engineering
Initially utilized for rapid prototyping within the automotive industry, 3D printing has quickly evolved into a tool for manufacturing end-use components. This transition has been supported by significant advancements in 3D printing technologies and materials, allowing for the production of parts that meet or exceed the performance requirements of traditional manufacturing methods. Today, vehicle engineering leverages 3D printing not just for creating models, but for producing functional parts that are integral to the operation and structure of the vehicle.
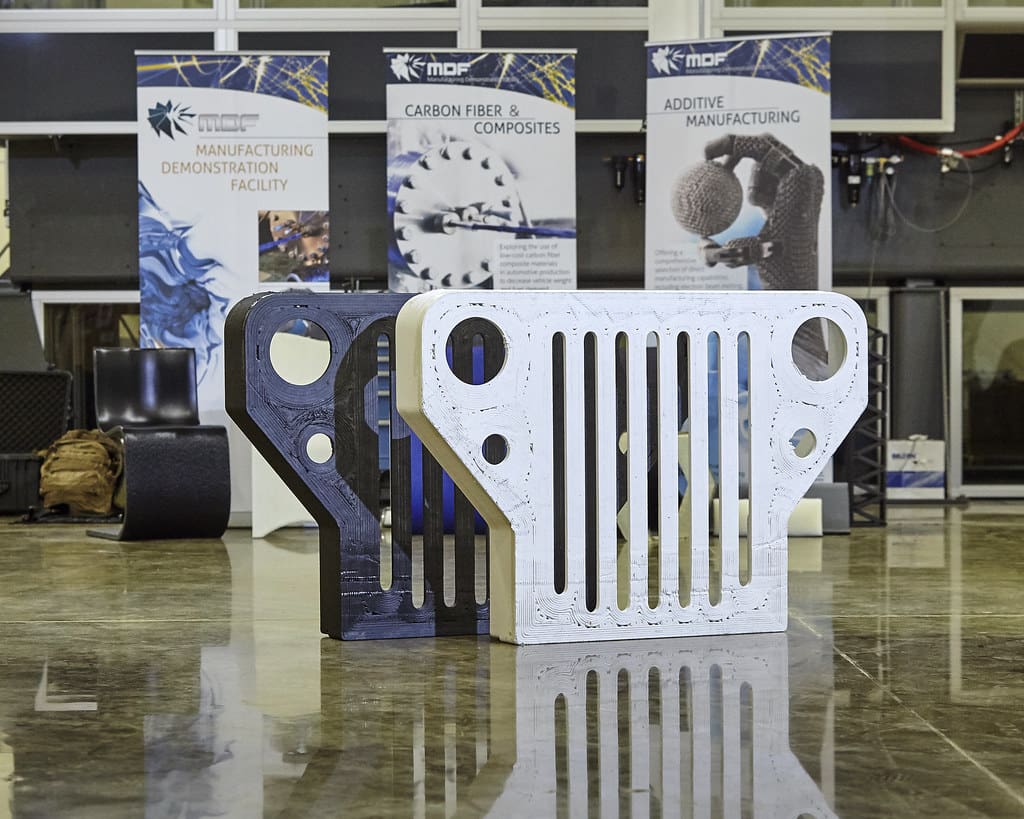

Advantages of 3D Printing in Vehicle Engineering
Complex Geometries and Lightweighting: 3D printing excels in creating complex, intricate shapes that are often too challenging or expensive to fabricate using conventional methods. This capability is particularly beneficial for developing lightweight components through geometrical optimizations and lattice structures, which are crucial for enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
Customization and Flexibility: 3D printing allows for high levels of customization without significant cost increases. This is advantageous for manufacturing bespoke components for luxury vehicles, custom builds, or prototypes that require specific performance attributes.
Reduced Time to Market: By facilitating rapid prototyping and reducing the need for multiple iterations in tooling, 3D printing significantly shortens the development cycle of new vehicles. This accelerates the innovation process, allowing manufacturers to respond more quickly to market demands and technological advancements.
Sustainability: With its additive approach, 3D printing minimizes waste by using only the material necessary to build a part. This efficiency is aligned with the automotive industry’s move towards more sustainable manufacturing practices.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Vehicle Engineering
Engine Components: High-performance engine parts such as pistons, cylinders, and heat exchangers are being produced with 3D printing. These components often benefit from the technology’s ability to produce lightweight designs that maintain high strength and heat tolerance.
Custom Interiors: 3D printing allows for the production of customized interior components, such as dashboard elements, door handles, and air vent grilles. These parts can be tailored to the specific aesthetic or functional requirements of a vehicle.
Prototypes and Tooling: The technology is extensively used to create prototypes and tooling for automotive parts testing. This not only includes structural components but also detailed elements like lighting casings and complex electronic housing.
Specialty Vehicle Parts: For vehicles that require unique solutions, such as race cars or custom performance vehicles, 3D printing can produce parts that meet very specific engineering demands. This includes everything from aerodynamically optimized components to lightweight chassis elements.

Challenges in 3D Printing for Vehicle Engineering
Despite its numerous advantages, several challenges remain in the widespread adoption of 3D printing in vehicle engineering:
Material Limitations: The range of materials suitable for high-performance automotive applications is still expanding. Finding materials that can consistently withstand the stresses and environmental conditions associated with automotive use is crucial.
Scale and Efficiency: While 3D printing is effective for small production runs and prototyping, scaling up to mass production can be economically and logistically challenging with current technology.
Quality and Consistency: Ensuring the quality and consistency of 3D printed parts across large production volumes is essential. This includes maintaining precision in dimensional accuracy and material properties.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Vehicle Engineering
The future of 3D printing in vehicle engineering looks promising, with ongoing advancements in printer technology, materials science, and digital design expected to address current challenges. As these technologies mature, 3D printing is likely to become more integrated into mainstream vehicle manufacturing, potentially leading to a significant shift in how cars are designed and built.
3D printing is poised to continue its transformative impact on vehicle engineering, offering new levels of design freedom, efficiency, and customization. As the technology evolves, it will enable vehicle manufacturers to create more innovative, sustainable, and performance-oriented vehicles. This aligns with the industry’s broader goals of reducing environmental impact and enhancing consumer satisfaction.