The realm of sculpture, an art form steeped in tradition, is experiencing a revolutionary transformation with the introduction of 3D printing technology. This innovative approach not only expands the toolkit available to sculptors but also redefines the possibilities for what can be created. 3D printing in sculpture allows artists to transcend traditional constraints of material and scale, facilitating the creation of works that are intricate, personalized, and otherwise impossible to achieve through conventional methods.
The Rise of 3D Printing in Sculpture
3D printing has been embraced by the art community as a powerful medium for sculpture over the last decade. Artists are drawn to 3D printing for its ability to produce precise, repeatable, and complex forms that challenge the limitations of hand-craftsmanship. From small-scale models to large installations, 3D printing has opened new vistas for artistic exploration.
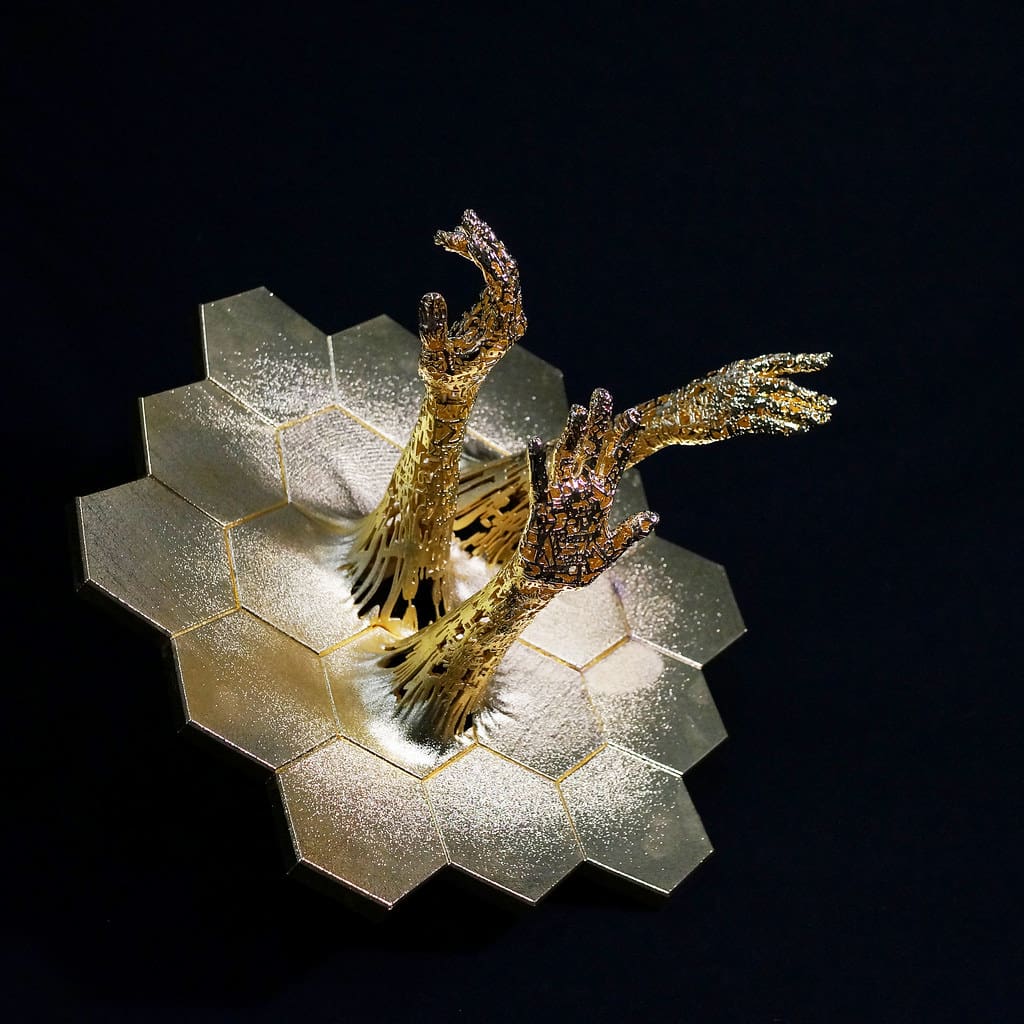

Advantages of 3D Printing in Sculpture
Complex Geometries and Details: One of the most significant benefits of 3D printing is its ability to handle complex geometries and intricate details. Artists can create detailed textures, interlocking parts, and forms that would be challenging or impossible to sculpt by hand or through traditional sculpting methods.
Material Innovation: 3D printing allows the use of a variety of materials, including plastics, resins, metals, and more recently, sustainable and experimental materials. This versatility gives artists the freedom to experiment with different textures, finishes, and structural properties.
Speed and Revision: Sculpture often involves a lengthy process of iteration and refinement. 3D printing streamlines these aspects by allowing quick production of prototypes and easy adjustments to designs. This capability significantly speeds up the creative process and experimentation.
Scalability: Scale is no longer a constraint with 3D printing. Artists can print a sculpture in segments that are assembled into a larger whole, allowing them to achieve monumental sizes not feasible in traditional workshops.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Sculpture
Artistic Exploration and Exhibitions: Many contemporary artists use 3D printing to explore new conceptual and aesthetic ideas. Sculptures created with 3D printing have been featured in major galleries and exhibitions, showcasing the artistic potential of the technology.
Collaborative Projects: 3D printing facilitates collaboration across geographical boundaries. Artists can share digital models and have their works 3D printed anywhere in the world, opening up opportunities for international projects and exhibitions.
Educational Tools: Art schools and universities are increasingly incorporating 3D printing into their curriculum, allowing students to explore the intersections of technology, design, and art. It serves as an excellent tool for teaching the principles of design, geometry, and material properties.
Restoration and Replication: In the realm of art conservation, 3D printing offers solutions for restoring damaged sculptures or creating replicas of valuable pieces. This technology ensures that the integrity of the original work is maintained while making art more accessible to the public.

Challenges and Considerations
Despite its benefits, 3D printing in sculpture faces several challenges. The cost of high-quality 3D printers and the ongoing expenses related to materials can be prohibitive. Additionally, there is an ongoing debate within the art community about the authenticity and craftsmanship of 3D printed works compared to traditional sculpting methods.
Future Trends in 3D Printing for Sculpture
As the technology advances, 3D printing is expected to become more accessible and versatile, further integrating into the mainstream of sculptural practice. Innovations in printer technology and material science will likely enhance the quality and variety of sculptures produced, pushing the boundaries of what is considered possible in the art form.
3D printing is redefining the landscape of sculpture, offering artists unprecedented freedom to explore complex forms and new materials. As this technology continues to evolve, it promises to further expand the creative horizons of sculptors, making it an indispensable part of the artistic process. Embracing 3D printing allows artists to not only preserve traditional sculptural techniques but also to push forward into new realms of creativity and innovation.