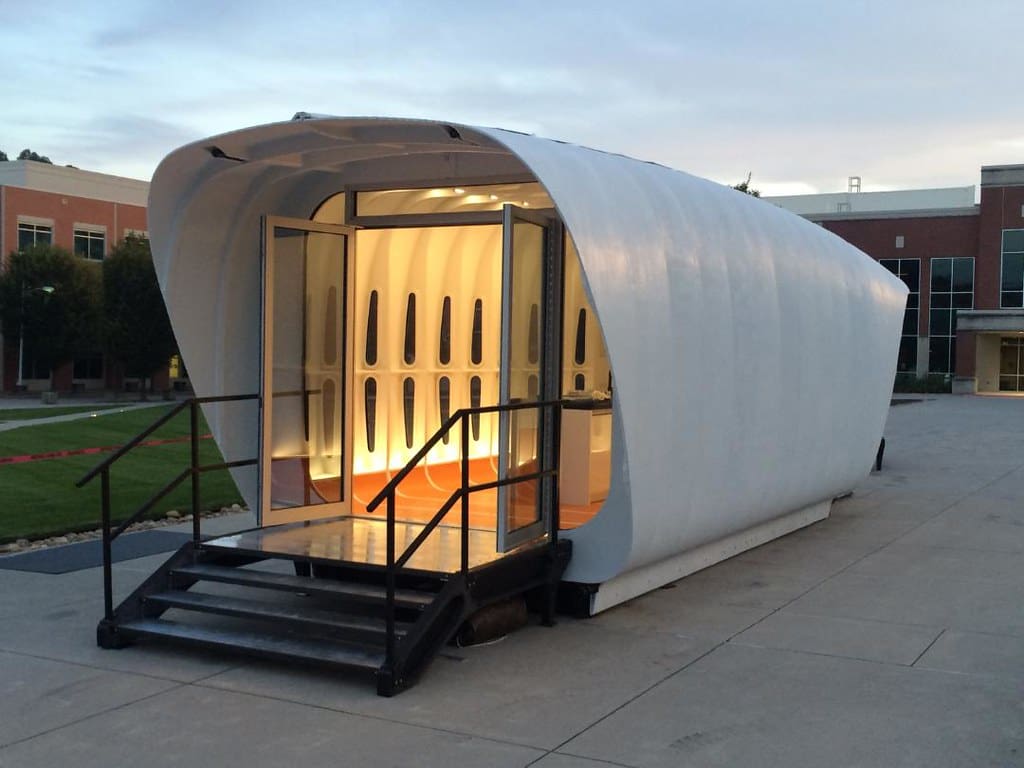
Residential architecture focuses on the design and construction of living spaces, from single-family homes to multi-unit dwellings. With the advent of 3D printing technology, also known as additive manufacturing, the residential construction sector is experiencing a paradigm shift. This innovative approach offers architects and builders the ability to create complex, customized housing solutions quickly and cost-effectively, while also addressing some of the environmental concerns associated with traditional construction methods.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Residential Architecture
Initially used for creating models and prototypes in various industries, 3D printing has matured into a technology capable of producing functional, durable structures. In the realm of residential architecture, 3D printing is being harnessed to construct entire homes, offering a faster, more flexible, and less wasteful approach to building. As the technology continues to evolve, it is becoming increasingly viable for mainstream housing projects, promising to reshape the landscape of residential construction.
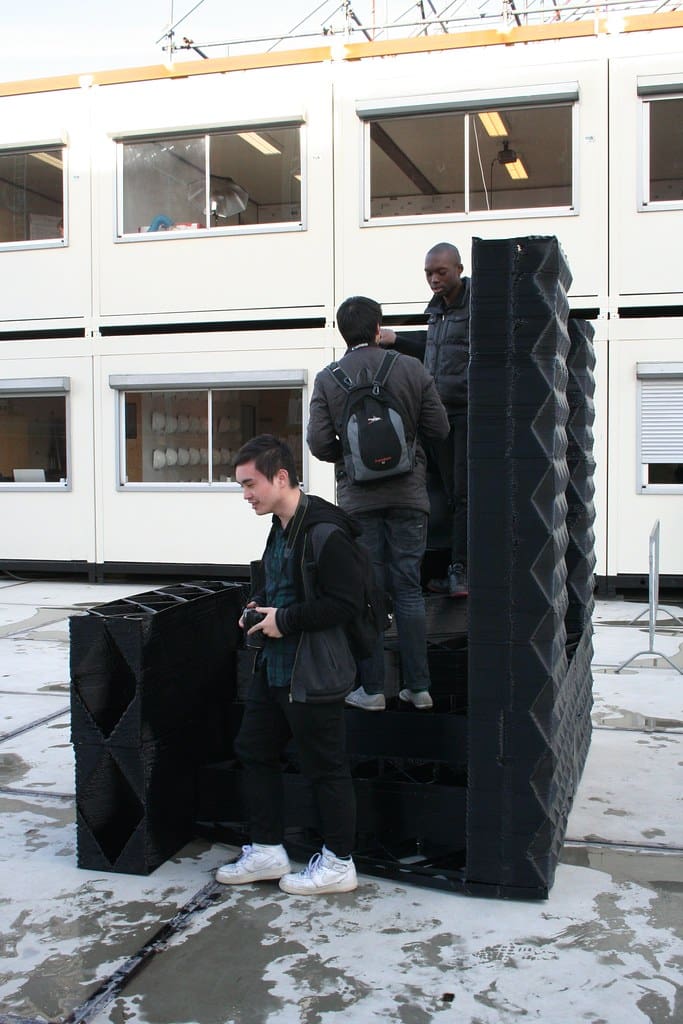

Advantages of 3D Printing in Residential Architecture
Cost Reduction: 3D printing significantly reduces labor costs and material waste, two of the largest expenses in traditional home construction. Automated printing technology requires fewer workers on-site, and precise material application minimizes excess.
Speed of Construction: Homes can be printed in a fraction of the time required for traditional construction methods. This rapid turnaround not only speeds up the building process but also reduces the overall cost of projects.
Design Flexibility: 3D printing allows for greater design flexibility, enabling architects to experiment with complex shapes and forms that would be difficult or expensive to achieve through conventional building methods.
Sustainability: Additive manufacturing contributes to environmental sustainability by reducing waste and often using recycled materials. Additionally, the precision of 3D printing means that materials can be used more efficiently, further reducing the environmental footprint of building.
Customization: With 3D printing, each home can be customized to the specific needs and preferences of its residents without significantly impacting the cost or timeline of the project.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Residential Architecture
Custom Homes: 3D printing is particularly well-suited for constructing custom-designed homes that cater to individual preferences regarding layout, design, and materials.
Affordable Housing: The efficiency and lower costs associated with 3D printing make it an excellent option for affordable housing projects. Quickly produced homes can be a vital response to housing crises in many parts of the world.
Disaster Relief Housing: In the aftermath of natural disasters, 3D printed homes can be rapidly deployed to provide temporary or permanent housing for those affected. These homes can be designed to be more resilient against future disasters.
Extensions and Renovations: 3D printing can be used for expanding or renovating existing structures. This application is useful for seamlessly blending new sections with old, maintaining structural integrity and aesthetic continuity.

Challenges in 3D Printing for Residential Architecture
Material Durability and Longevity: Ensuring that 3D printed materials can withstand various climates and environmental conditions over long periods is crucial. Ongoing research is needed to validate the longevity of such materials.
Regulatory and Building Codes: The integration of 3D printed homes into existing building codes and standards is an ongoing challenge. Regulations need to evolve to accommodate and properly assess the nuances of 3D printed structures.
Public Perception and Market Acceptance: Convincing homeowners and residential developers to adopt 3D printing technology involves overcoming skepticism regarding the durability, safety, and aesthetic appeal of printed homes.
Technical Limitations: While 3D printing technology is advancing rapidly, there are still limitations to the size of structures that can be printed and the types of materials that can be used effectively.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Residential Architecture
The future of 3D printing in residential architecture looks promising, with potential advancements in printer technology, materials science, and design software. Innovations could lead to wider adoption of 3D printing in residential building projects, offering even greater flexibility, efficiency, and sustainability. The integration of smart home technology into 3D printed homes could also enhance the functionality and appeal of these living spaces.
3D printing is set to revolutionize the field of residential architecture by providing new methods for constructing homes that are both innovative and sustainable. As the technology continues to develop, it promises to offer more sophisticated solutions that could transform residential living spaces worldwide. With ongoing advancements and broader acceptance, 3D printing will increasingly become a cornerstone of modern residential architecture, reshaping how homes are designed, built, and perceived.