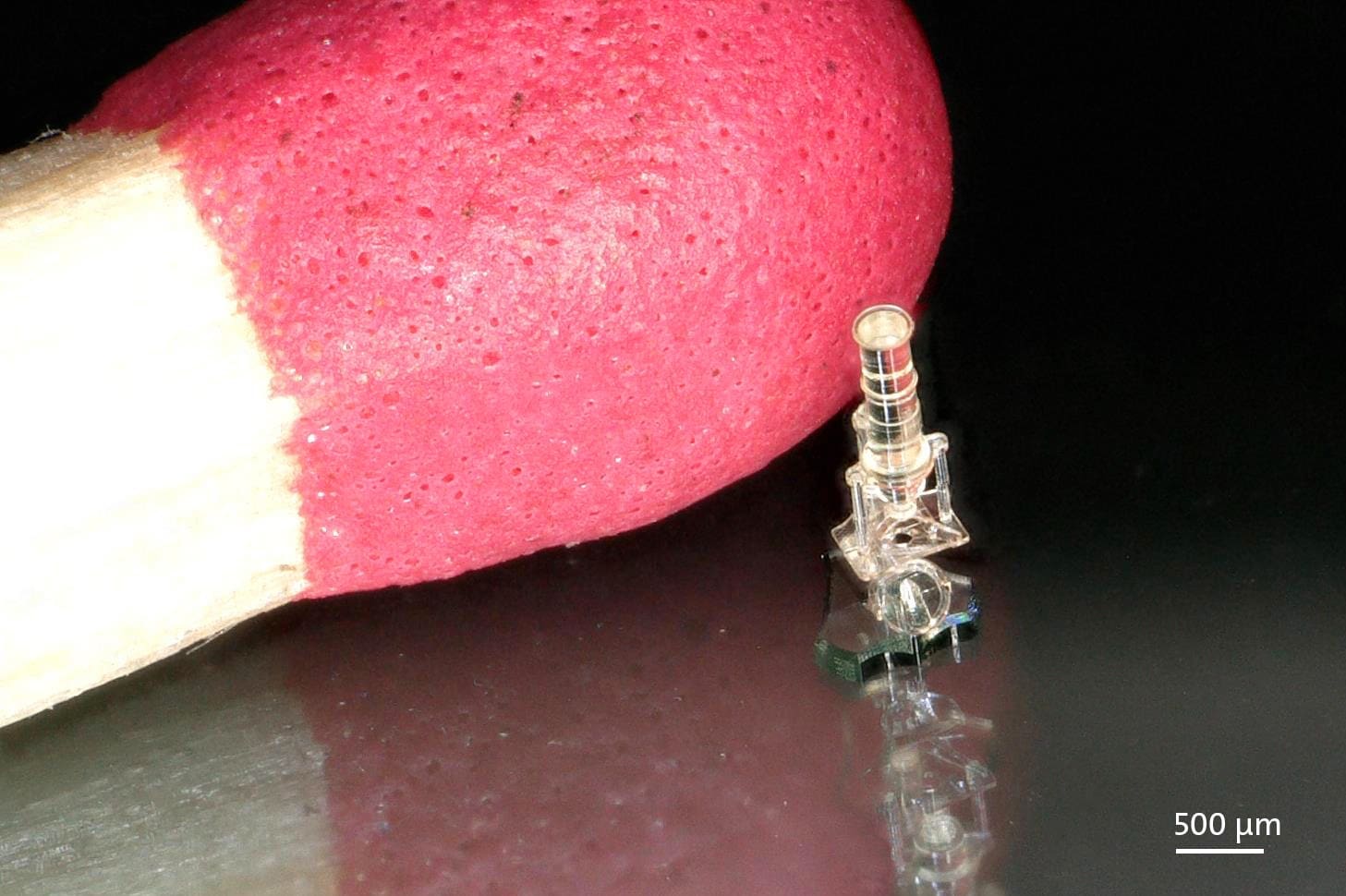
Nanotechnology involves manipulating matter at the molecular and atomic levels, typically within the scale of 1 to 100 nanometers. As a field poised to revolutionize areas ranging from medicine to materials science, nanotechnology’s integration with 3D printing is opening up new avenues for innovation. This combination allows for the precise fabrication of structures at the nanoscale, which can lead to breakthroughs in drug delivery systems, electronics, and new materials. The adoption of 3D printing technologies in nanotechnology — often referred to as nano 3D printing — promises to enhance the capabilities and applications of both fields dramatically.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Nanotechnology
3D printing at the nanoscale, also known as nanofabrication, initially revolved around prototyping microdevices and has evolved to enable the direct manufacturing of nanostructured materials and devices. Innovations in 3D printing technologies, such as two-photon polymerization, have allowed researchers and engineers to produce features as small as 100 nanometers, facilitating the creation of complex nanostructures that were previously difficult or impossible to build.
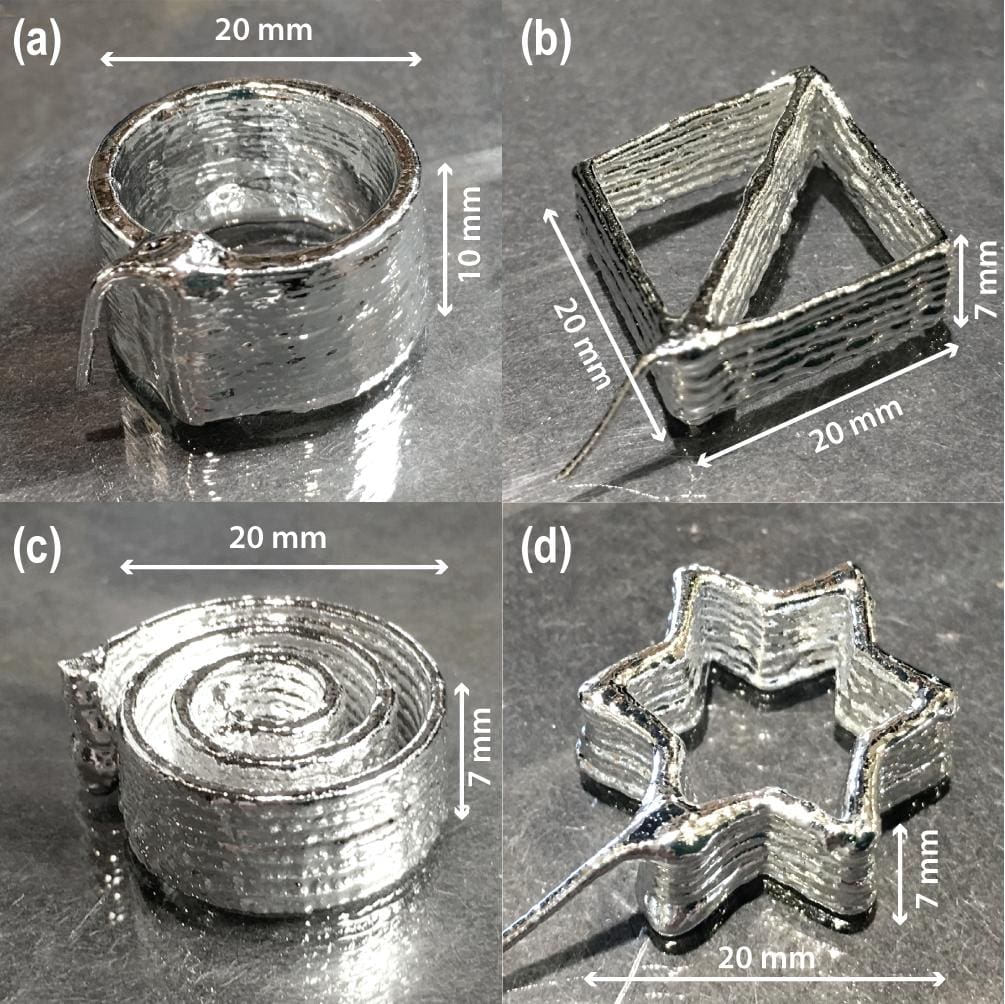
Advantages of 3D Printing in Nanotechnology
Precision and Complexity: Nano 3D printing allows for the creation of highly complex structures with precise control over shape and size at the nanoscale, essential for applications in electronics, photonics, and biomedical engineering.
Customization and Flexibility: This technology enables the bespoke fabrication of nanostructures tailored to specific functions, such as targeted drug delivery vehicles or specific photonic crystals, enhancing their performance and functionality.
Rapid Prototyping and Development: Nano 3D printing facilitates the quick development and testing of nanoscale devices, significantly speeding up the research and development process in nanotechnology.
Integration of Multiple Materials: Advanced nano 3D printing techniques can handle multiple materials in a single build process, allowing for the fabrication of complex devices with integrated functionalities.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Nanotechnology
Drug Delivery Systems: Nano 3D printing is used to create precise drug delivery mechanisms capable of targeting specific cells or tissues in the body, improving the efficacy and reducing the side effects of treatments.
Sensors and Actuators: The ability to produce nanoscale sensors and actuators is crucial for the development of advanced diagnostic tools and intelligent systems in robotics and aerospace.
Energy Storage and Conversion: Nanostructured materials fabricated via 3D printing can significantly enhance the performance of batteries and solar cells by optimizing their surface area and electron transport properties.
Biomedical Implants and Devices: Nano 3D printing can produce scaffolds for tissue engineering with features that mimic the extracellular matrix, promoting cell growth and tissue regeneration.
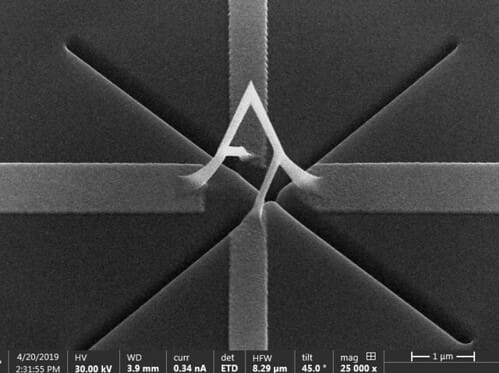
Challenges in 3D Printing for Nanotechnology
Despite its transformative potential, nano 3D printing faces several significant challenges:
Resolution and Accuracy: While great strides have been made, pushing the limits of resolution and accuracy further into the nanoscale remains a technical challenge that is crucial for broader applications.
Material Limitations: The range of materials suitable for nano 3D printing is currently limited, particularly when it comes to materials that can be precisely manipulated at the nanoscale and exhibit desired properties such as conductivity or biocompatibility.
Scalability: Scaling nano 3D printing processes from laboratory prototypes to industrial production is a major hurdle, involving issues of speed, cost, and the replication of precise nanostructures reliably.
Regulatory and Ethical Concerns: As with many aspects of nanotechnology, there are ongoing debates and concerns about the environmental, health, and ethical implications of manufacturing and using nanomaterials, which must be addressed as the technology develops.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Nanotechnology
The future of 3D printing in nanotechnology is promising, with ongoing research focused on overcoming current limitations and expanding capabilities. Innovations in printer designs, novel nano-inks, and hybrid fabrication techniques that combine top-down and bottom-up approaches are likely to enhance the precision, versatility, and applications of nano 3D printing.
3D printing is set to revolutionize nanotechnology by providing tools to build complex nanostructures with unprecedented precision and customization. As this technology continues to evolve, it will unlock new possibilities in various fields, leading to innovations that could reshape industries from healthcare to energy. The integration of 3D printing and nanotechnology not only exemplifies the cutting edge of modern engineering but also highlights the potential for significant advancements in both fields.