Municipal engineering, which focuses on the planning, construction, and maintenance of urban infrastructure, is undergoing a transformation thanks to the adoption of 3D printing technology. This innovative approach is not only enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of projects but also providing unprecedented flexibility in the design and implementation of urban structures. From bridges and roads to public buildings and utilities, 3D printing offers municipal engineers new tools to address the challenges of modern urban development.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Municipal Engineering
Traditionally, municipal engineering projects have been characterized by high costs, long timelines, and significant material waste. However, the advent of 3D printing technology has begun to change this landscape dramatically. By allowing for precise, automated construction of complex designs at reduced costs, 3D printing is proving to be a game-changer for cities looking to innovate their infrastructure and improve public services.
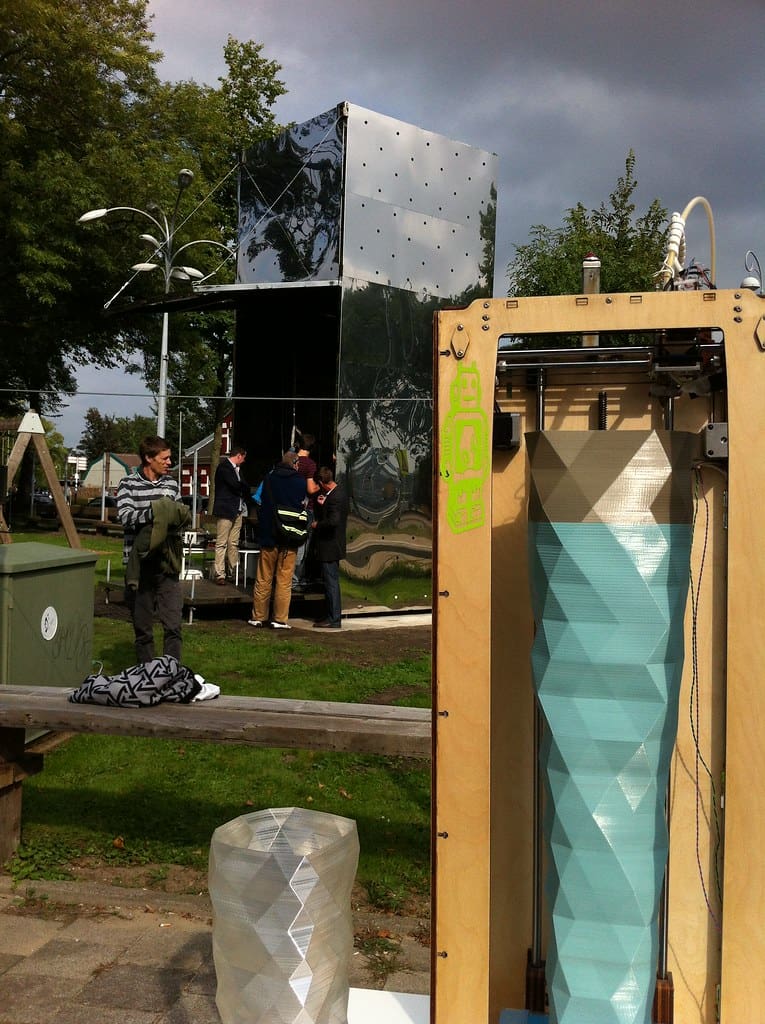

Advantages of 3D Printing in Municipal Engineering
Cost Efficiency: 3D printing significantly reduces the cost of construction by minimizing waste and decreasing the need for labor. Projects can be completed faster and at lower cost, freeing up resources for other critical urban needs.
Design Flexibility: With 3D printing, engineers are no longer constrained by the limitations of traditional construction methods. They can create structures with complex, organic shapes that are both aesthetically pleasing and functionally superior.
Speed of Construction: One of the most significant benefits of 3D printing in municipal projects is the ability to accelerate construction timelines. Structures that would typically take months to build can be completed in a matter of days or weeks.
Sustainability: 3D printing promotes sustainability through efficient use of materials and the potential to use recycled materials in construction. This technology aligns well with the growing emphasis on sustainable development in urban planning.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Municipal Engineering
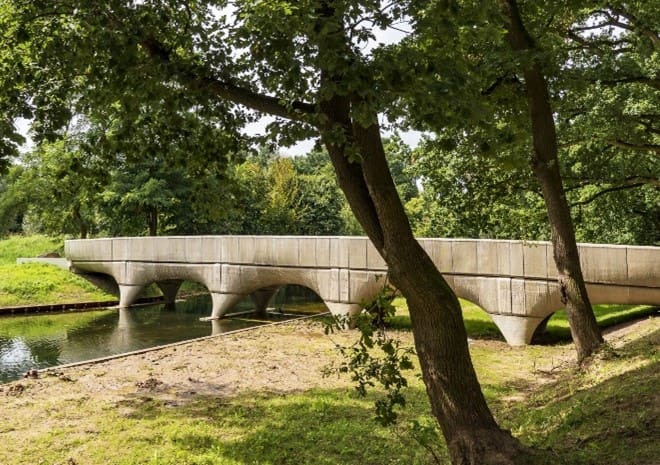
Infrastructure Development: 3D printing is being used to construct durable and efficient infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and tunnels. For instance, the first 3D-printed concrete bridge in the Netherlands showcases the potential for faster and more cost-effective infrastructure development.
Public Buildings and Facilities: Municipalities are exploring the use of 3D printing to build public facilities such as schools, libraries, and community centers. These structures can be designed to meet specific community needs while also incorporating innovative architectural elements.
Water and Sewage Systems: 3D printing can create complex components for water and sewage systems, including pipes and junctions that are optimized for flow and durability. This application has the potential to significantly improve the efficiency and reliability of municipal water services.
Disaster Relief and Temporary Housing: In the event of natural disasters, 3D printing can be rapidly deployed to construct temporary housing and other critical infrastructure. This quick-response capability is invaluable in minimizing the impact of disasters on affected populations.
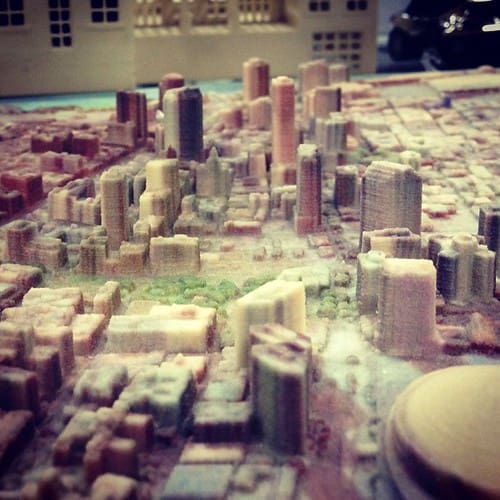

Challenges in 3D Printing for Municipal Engineering
Despite its benefits, integrating 3D printing into municipal engineering projects presents several challenges:
Material Limitations: While 3D printing technology has advanced, the materials available for use are still evolving. Ensuring the long-term durability and safety of printed structures is crucial, particularly for infrastructure that must withstand heavy use and environmental stresses.
Regulatory Hurdles: Municipal projects are heavily regulated, and current building codes and standards may not adequately cover 3D-printed constructions. Updating these regulations to include 3D printing standards is necessary to facilitate broader adoption.
Public Perception and Acceptance: Gaining public trust in 3D-printed structures is essential. Demonstrating the reliability and safety of these innovations is key to their acceptance and widespread use.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Municipal Engineering
The future of 3D printing in municipal engineering looks promising, with continuous advancements in printer technology and materials. The next generation of 3D printing is likely to bring even greater precision, efficiency, and material diversity, further enhancing the capabilities of municipal engineers.
As urban populations continue to grow, the integration of 3D printing into municipal projects could be crucial in addressing the complex challenges of urbanization. This technology offers the potential to create smarter, more sustainable cities that are better equipped to serve their residents.
3D printing holds transformative potential for municipal engineering, offering solutions that are efficient, innovative, and sustainable. As this technology continues to evolve, it will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of urban infrastructure. Embracing 3D printing can help cities meet the demands of modern urban living, providing high-quality, cost-effective, and timely infrastructure solutions.