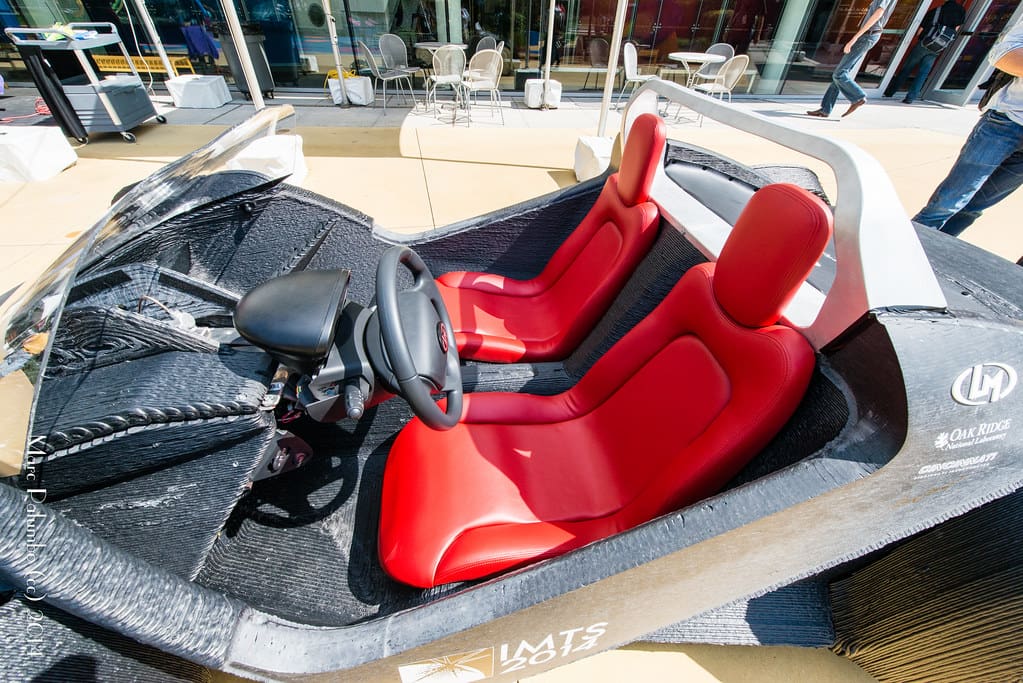
Interior design is an art and science dedicated to making spaces both aesthetically pleasing and functionally optimal. The advent of 3D printing technology has opened up new vistas in interior design, providing unprecedented opportunities to customize designs, enhance spatial functionality, and experiment with new materials and forms. This technology enables designers to transcend traditional limitations, offering unique solutions that can be tailored to individual preferences and space requirements.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Interior Design
3D printing, originally utilized primarily in industrial applications for prototyping, has evolved to become a significant tool in the creative industries, including interior design. It allows for the creation of complex, customized furniture pieces, intricate decorative items, and innovative structural elements within spaces. As the technology continues to advance, its integration into interior design is becoming increasingly sophisticated, enabling designers to offer bespoke solutions that were once thought impractical or overly expensive.
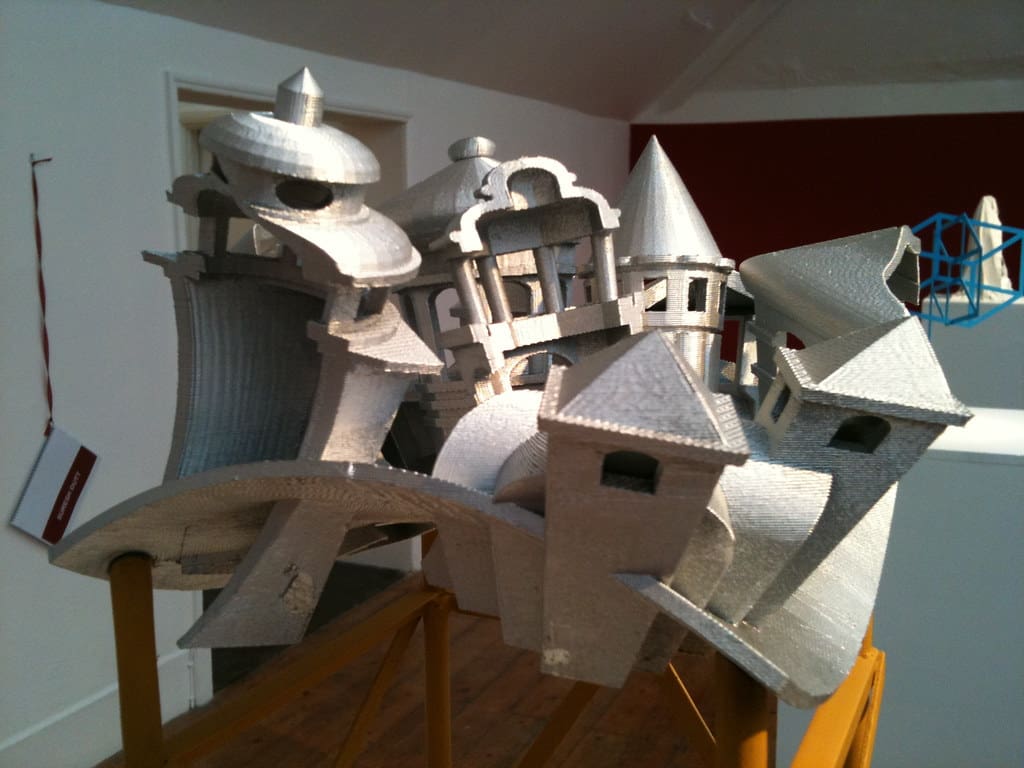

Advantages of 3D Printing in Interior Design
Customization and Personalization: 3D printing allows for the customization of design elements to an extent that traditional methods cannot match. Designers can tailor furniture, fixtures, and decor to the specific dimensions and style preferences of a client, ensuring a perfect fit for the intended space.
Complex Geometrical Designs: The technology enables the production of complex geometric patterns and shapes that can add a unique aesthetic quality to interior spaces. These forms can be designed to interact with light and shadow in ways that enhance the visual dynamics of a room.
Rapid Prototyping: Designers can quickly produce a physical model of a design element, allowing for immediate evaluation and refinement. This accelerates the design process, enabling faster project completion and more effective client presentations.
Material Innovation: 3D printing offers access to a range of novel materials, including composites that can have customized properties such as flexibility, translucency, or enhanced durability. This opens up new possibilities for both functional and decorative elements.
Sustainability: The technology promotes sustainability through efficient material use and the potential to use recycled materials for printing. This reduces waste and can lower the environmental impact of manufacturing new interior design elements.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Interior Design
Furniture Design: Chairs, tables, and other furnishings can be designed and printed to meet specific aesthetic and functional requirements. This includes creating furniture that is ergonomic, fits specific spaces perfectly, or contains integrated technology.
Decorative Elements: From vases and sculptures to intricate wall hangings and ceiling features, 3D printing allows interior designers to create unique decor items that reflect the latest trends or personal tastes of clients.
Functional Art: Designers can merge aesthetics with functionality by creating pieces that are both beautiful and serve a specific purpose, such as acoustically optimized wall panels or light-diffusing fixtures.
Custom Architectural Details: 3D printing can be used to produce customized architectural details such as moldings, trims, and even door frames, which can be designed to seamlessly integrate with the overall design theme of a space.
Textiles and Fabrics: Emerging technologies in 3D printed textiles offer new opportunities for designing soft furnishings with unique properties and designs, such as curtains, cushions, or upholstery with integrated patterns and textures.
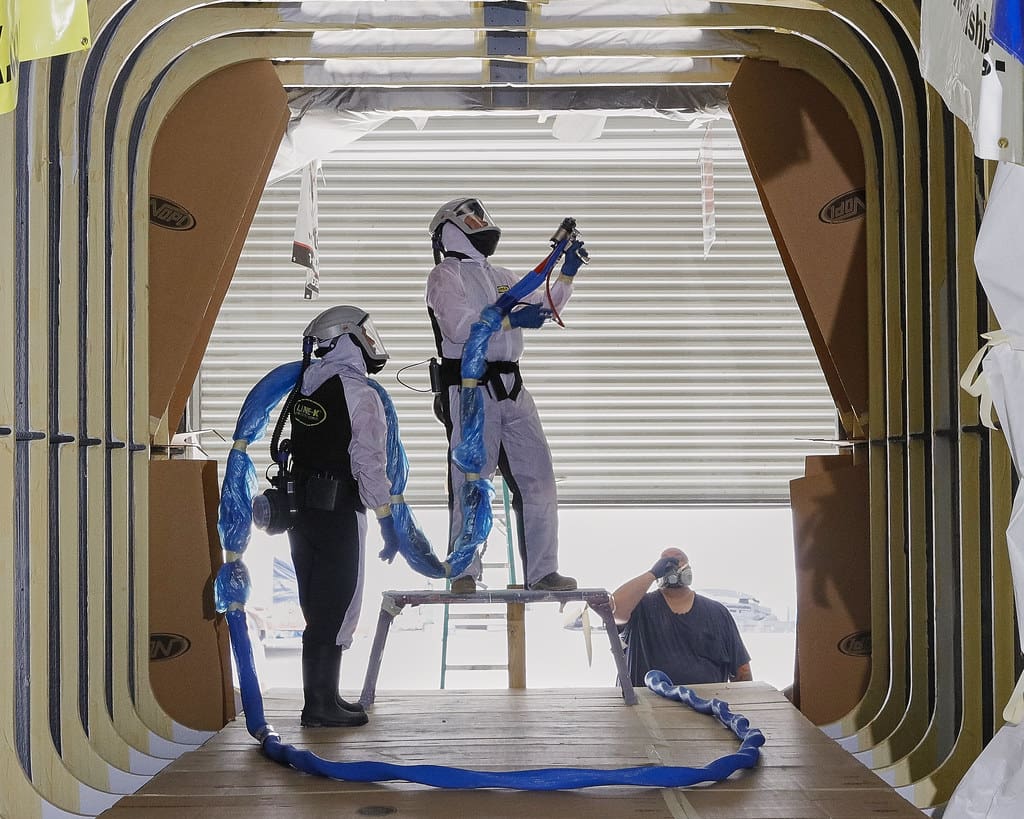

Challenges in 3D Printing for Interior Design
Material Limitations: While there are many innovative materials available, finding materials that combine the desired aesthetic qualities with durability and maintenance requirements can be challenging.
Scale Limitations: The size of printed items is often limited by the dimensions of the 3D printer. Larger items require advanced printers or must be produced in segments and assembled post-printing.
Technical Skill Requirements: Effective use of 3D printing technology requires designers to have specific technical skills, including proficiency in 3D modeling software and an understanding of the printing process.
Cost Considerations: Although 3D printing can reduce certain costs, the initial investment in equipment and ongoing material costs can be significant, particularly for high-end printers capable of producing large items.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Interior Design
As 3D printing technology continues to develop, its applications in interior design are expected to expand. Future advancements may include the ability to print larger items more efficiently, the development of new materials with enhanced properties, and further integration of smart technology into printed design elements.
3D printing is transforming interior design by enabling more personalized, innovative, and sustainable design solutions. As designers continue to explore the potential of this technology, it is likely to become an increasingly integral tool in the creation of modern, customized interior environments. The future of interior design with 3D printing promises not only enhanced aesthetic appeal and functionality but also a broader scope for creativity and innovation in designing spaces.