Industrial architecture involves the design and development of facilities such as factories, warehouses, and power plants that require specialized considerations for efficiency, functionality, and safety. The adoption of 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is transforming this field by enabling the creation of structures that are both innovative and tailored to specific industrial needs. This technology not only offers significant advancements in the construction process but also enhances the architectural capabilities for industrial applications, promoting greater efficiency and sustainability.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Industrial Architecture
Initially utilized for small-scale models and prototypes, 3D printing has rapidly evolved to accommodate larger structures, including those needed in industrial settings. Today, it is possible to print large-scale components and even entire buildings, making 3D printing a valuable tool in industrial architecture. This shift is fueled by the need for more adaptable and efficient construction methods that can reduce costs, construction time, and environmental impact.
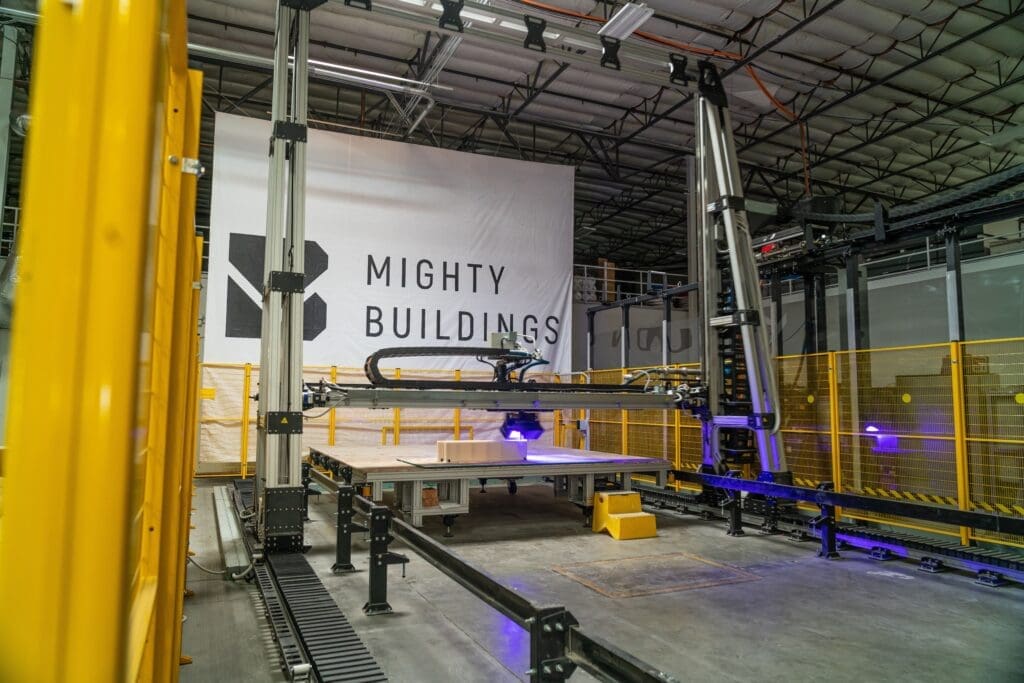

Advantages of 3D Printing in Industrial Architecture
Design Flexibility and Complexity: 3D printing allows architects to explore complex designs that can optimize space utilization and energy efficiency. Customized structures can be created to support specific machinery or operational flows, enhancing overall facility efficiency.
Rapid Construction: The ability to print components and structures on-site significantly reduces construction timelines. This speed is crucial for industrial projects that often operate under tight schedules to commence production.
Cost Reduction: 3D printing reduces the need for manual labor and decreases material waste through precise application, which can lead to substantial cost savings in large industrial projects.
Sustainability: By minimizing waste and allowing for the use of recycled materials, 3D printing contributes to more sustainable construction practices, which is increasingly important in industrial architecture given the typically large scale and environmental impact of industrial facilities.
Customization and Scalability: Additive manufacturing supports the customization of designs at minimal additional costs, making it ideal for industrial facilities that require unique solutions for integration of specific technologies or processes.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Industrial Architecture
Manufacturing Facilities: Customized layouts designed to streamline manufacturing processes can be efficiently realized with 3D printing. This includes the creation of floors and structures designed to bear heavy loads, accommodate high ceilings, or integrate sophisticated ventilation systems.
Warehousing and Logistics: 3D printing can be used to design warehouses that maximize space efficiency and improve logistics. Innovative designs that facilitate easier movement of goods and better storage solutions can be implemented without the constraints of traditional construction methods.
Energy Sector: In the energy industry, 3D printing allows for the construction of facilities with designs that optimize the operation of large and complex machinery, such as in wind farms or hydroelectric plants.
Research and Development Labs: Facilities designed for R&D can benefit from 3D printed features that are customized for specific research activities, including laboratories with specialized containment or ventilation systems.
Challenges in 3D Printing for Industrial Architecture
Material Durability: Ensuring that 3D printed materials meet industrial standards for durability, especially in harsh environments, is critical. The materials used must withstand extreme conditions such as high temperatures, corrosive substances, or continuous vibration.
Regulatory Compliance: Industrial facilities often face strict regulatory requirements. Ensuring that 3D printed buildings comply with these regulations presents a significant challenge.
Scale Limitations: While 3D printing technology is advancing, scaling up to the vast sizes required for some industrial applications remains a technical challenge. Ensuring structural integrity and stability over large spans is crucial.
Integration with Traditional Building Techniques: Combining 3D printing with conventional construction methods to leverage the strengths of both approaches requires innovative construction management and design adaptation.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Industrial Architecture
As 3D printing technology continues to evolve, its applications in industrial architecture are expected to expand, driven by innovations in printing technologies, materials, and design software. Future developments may include enhanced multi-material printing capabilities, faster production speeds, and more robust integration tools for combining 3D printing with traditional construction methods.
3D printing is set to revolutionize industrial architecture by providing new methods for designing and constructing industrial facilities. This technology offers the potential to significantly enhance the efficiency, sustainability, and customization of industrial buildings, aligning with modern demands for faster, more adaptable, and environmentally friendly construction practices. As the technology matures, it promises to play an increasingly vital role in the development of industrial infrastructure, changing the way architects and builders approach industrial projects.