3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has dramatically transformed the landscape of healthcare over the past decade. This technology’s ability to create customized, precise, and cost-effective solutions is revolutionizing medical procedures, prosthetics, and even pharmaceuticals. From creating tailor-made organs and tissues to personalized medical devices and tools, 3D printing in healthcare is not just an innovative trend but a fundamental shift in medical practice.
The Evolution of 3D Printing in Healthcare
The first significant applications of 3D printing in healthcare began in the early 2000s with the fabrication of custom prosthetics and dental implants. Since then, the technology has expanded to include a vast range of medical applications, each leveraging the unique ability of 3D printers to produce complex, customized shapes at a reduced cost. Today, 3D printing is used in multiple areas of healthcare, significantly impacting patient care and treatment outcomes.
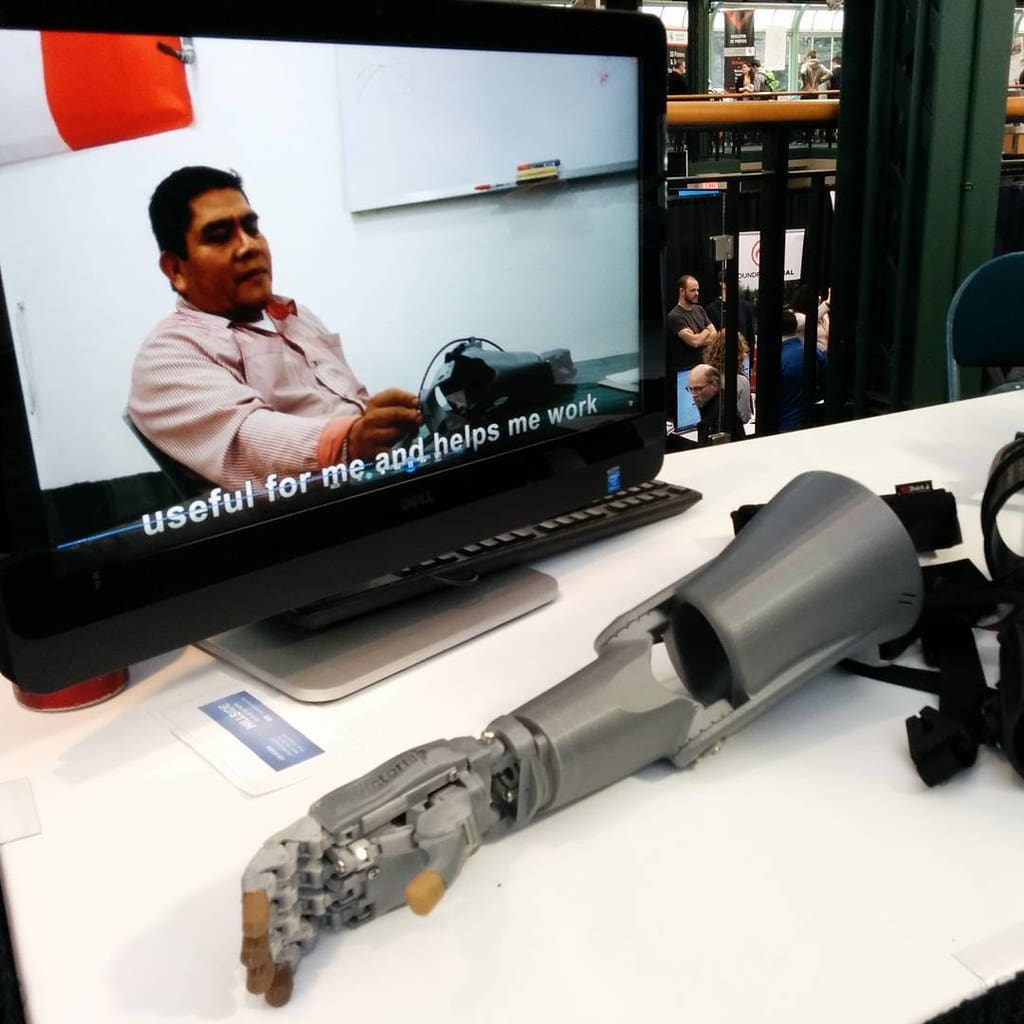

Advantages of 3D Printing in Healthcare
Customization: One of the most significant benefits of 3D printing in healthcare is the ability to produce patient-specific implants and devices. This customization ensures a better fit, improved comfort, and enhanced performance of medical implants.
Speed: In emergency medical situations, 3D printing can produce tools and implants much faster than traditional manufacturing methods. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, 3D printing was crucial in quickly supplying PPE and other medical necessities.
Cost-Effectiveness: Reducing the cost of medical devices and prosthetics makes healthcare more accessible. 3D printing minimizes waste by using only the necessary material for each item, significantly reducing the cost of production.
Innovation: 3D printing encourages innovation by allowing doctors and researchers to prototype new medical devices quickly. This rapid prototyping can accelerate the development and testing of innovative medical solutions.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Healthcare
Prosthetics and Orthotics: Custom prosthetics are one of the earliest and most life-changing applications of 3D printing in healthcare. Tailored to each patient’s unique physiology, 3D-printed prosthetics are not only more comfortable and functional but also much more affordable.
Dental Applications: From crowns and bridges to orthodontic devices, 3D printing is extensively used in dentistry. It allows for faster turnaround times and precise adaptations to individual patients, improving both aesthetic and clinical outcomes.
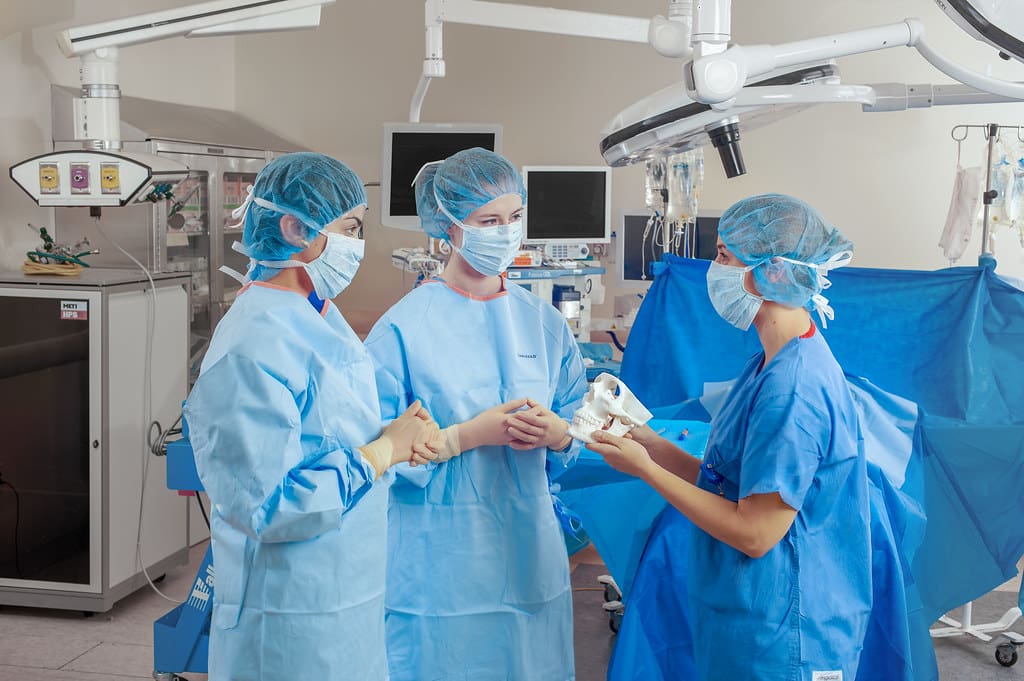
Surgical Planning and Tools: Surgeons utilize 3D printing to create exact replicas of patient-specific anatomy, aiding in pre-surgical planning and increasing the success rate of operations. Moreover, surgical tools customized for specific procedures or patients can be produced on demand.
Tissue and Organ Fabrication: One of the most promising areas of 3D printing is in bioprinting tissues and organs. While still largely experimental, the potential to print functional human tissues and organs could solve the organ shortage crisis and reduce transplant rejection by using the patient’s own cells.
Pharmaceuticals: 3D printing is beginning to change how medications are formulated and delivered, allowing for dosages to be personalized to each patient’s specific needs. This can optimize drug release profiles and improve patient compliance.
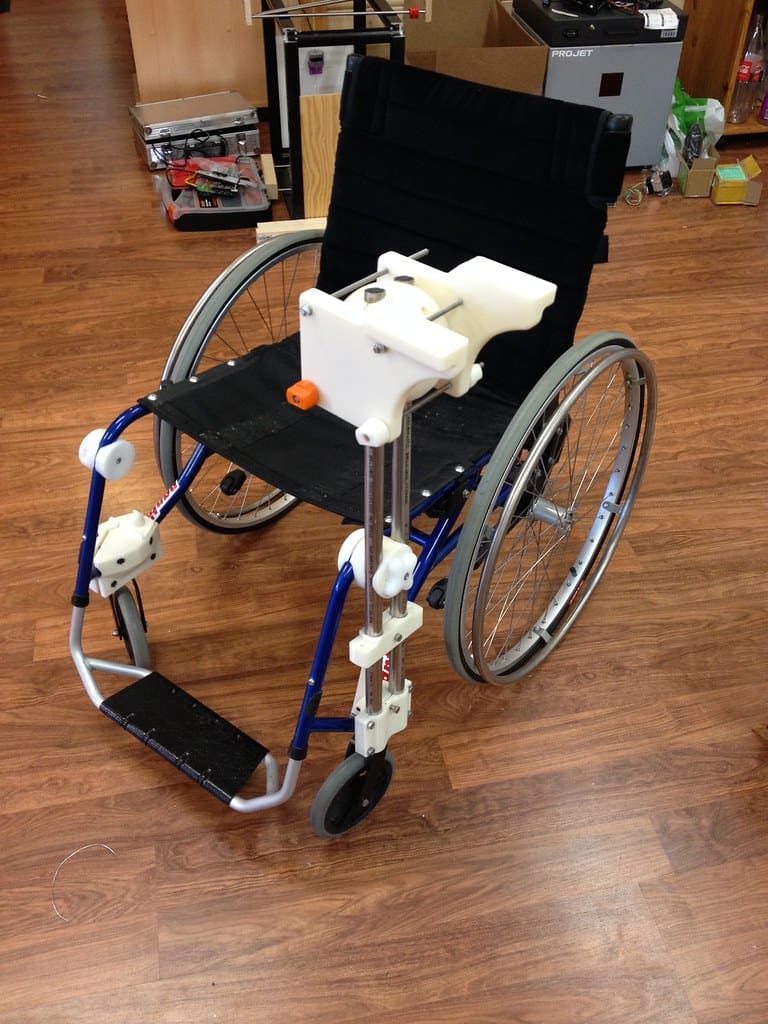

Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its advantages, 3D printing in healthcare faces several challenges. Regulatory hurdles are significant, as each new medical device must undergo rigorous testing and approval processes. The variability in 3D printing materials and processes also poses challenges in standardizing quality and performance.
Looking ahead, the future of 3D printing in healthcare is incredibly promising. Advances in material science will likely lead to the development of new bio-compatible materials. Additionally, as the technology matures and becomes more widespread, its costs are expected to decrease, making 3D-printed medical solutions more accessible.
3D printing is set to continue its expansion across the healthcare sector, providing innovative solutions that enhance patient care, reduce costs, and improve the efficiency of medical treatments. As this technology evolves, it holds the potential to fundamentally change nearly every aspect of healthcare, from routine medical procedures to complex surgeries and treatments. Embracing 3D printing technologies can lead to a new era of personalized, efficient, and accessible healthcare solutions, marking a significant milestone in the ongoing evolution of medical care.