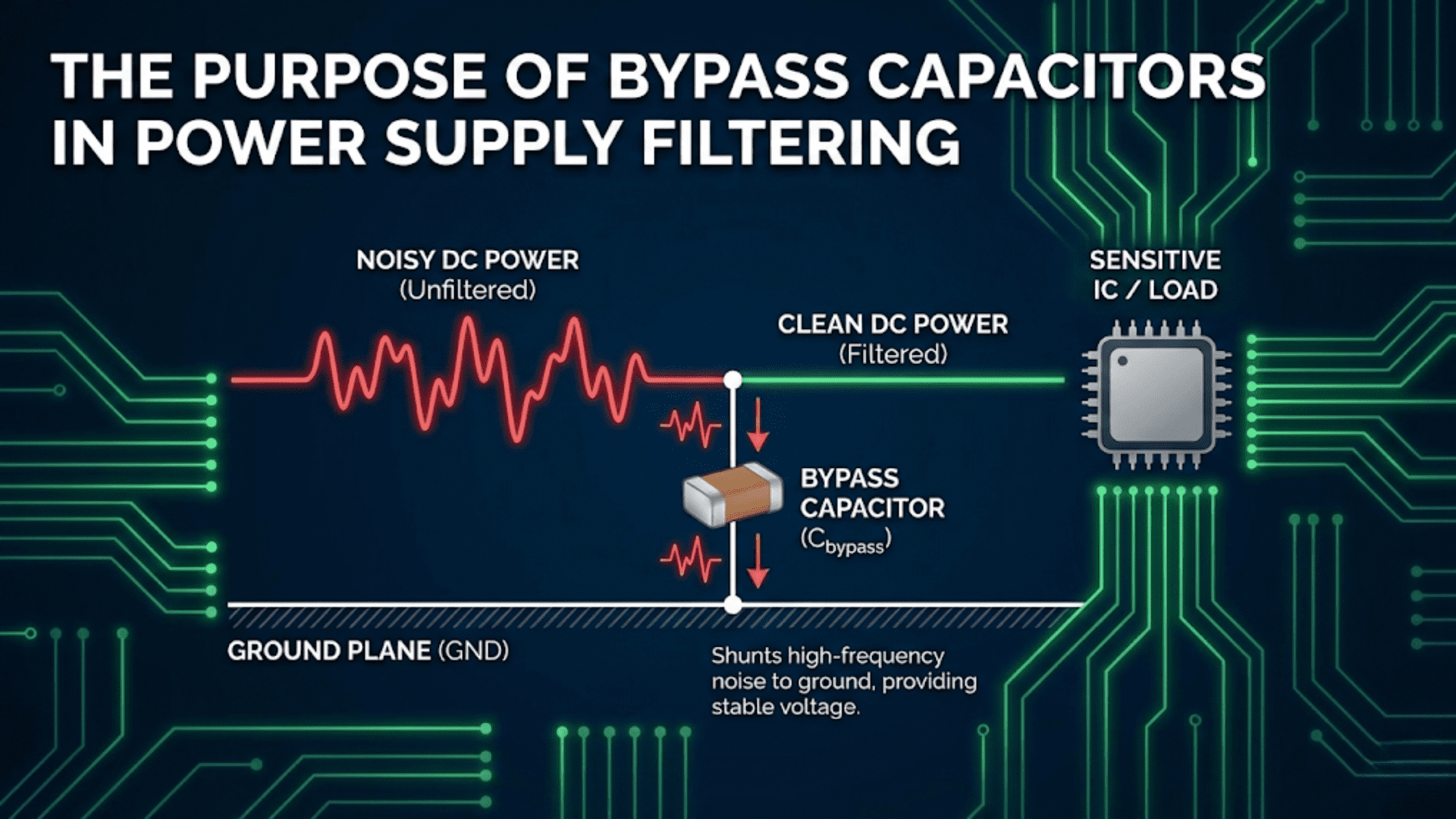
Engineering management involves the application of business strategies and practices to the engineering sector, aiming to streamline processes, optimize resource allocation, and enhance productivity. The integration of 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, into engineering management has opened new avenues for improving project delivery, reducing costs, and fostering innovation. This technology has become a pivotal tool in the hands of engineering managers, transforming traditional manufacturing and design processes across various industries.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Engineering Management
Initially utilized primarily for prototyping, 3D printing has evolved to play a crucial role in direct manufacturing, supply chain optimization, and even end-use production. Its rapid adoption across engineering disciplines is driven by its ability to produce complex components on-demand, reduce lead times, and cut manufacturing costs. As 3D printing technology continues to mature, it increasingly supports engineering management’s core objectives by enhancing operational efficiencies and product development.

Advantages of 3D Printing in Engineering Management
Rapid Prototyping and Iteration: 3D printing accelerates the prototype development process, allowing engineering managers to quickly test and refine ideas. This rapid iteration capability is crucial for agile product development and innovation.
Cost Reduction: By minimizing the need for expensive tooling and reducing material waste, 3D printing helps lower production costs. It also allows for cost-effective low-volume production and custom manufacturing, which are particularly beneficial for specialized engineering applications.
Supply Chain Simplification: 3D printing enables on-site production of parts, potentially reducing the need for large inventories and minimizing logistics costs. This capability can simplify supply chains and reduce the vulnerability of production processes to external disruptions.
Customization and Flexibility: Additive manufacturing allows for easy customization of parts with minimal additional cost, supporting engineering managers in delivering tailored solutions to meet specific project requirements or customer needs.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Engineering Management
Facility Management: 3D printing is used to produce replacement parts and components for machinery and equipment quickly and locally, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Construction and Infrastructure Projects: In the construction sector, 3D printing can be utilized to create complex components required for specific applications, such as custom fixtures or architectural models, enhancing the speed and efficiency of construction projects.
Product Development: Engineering managers use 3D printing to develop new products by prototyping them for market testing. This application is crucial in industries such as consumer electronics, automotive, and aerospace, where innovation is a key competitive advantage.
Risk Management: 3D printing enhances risk management by allowing for thorough testing and iteration of parts before full-scale production begins, reducing the potential for costly recalls or redesigns.

Challenges in 3D Printing for Engineering Management
Material Limitations: While 3D printing offers a range of material options, the suitability of these materials for specific engineering applications can be limited. Ensuring that materials meet the required specifications for strength, durability, and other operational conditions is essential.
Skill Gaps: Effective integration of 3D printing into engineering management requires specific skills and knowledge, both in additive manufacturing technologies and in digital design. Bridging the skill gap through training and development is necessary for maximizing the benefits of 3D printing.
Scale and Efficiency: While 3D printing is ideal for prototyping and small-batch production, scaling it for large-scale manufacturing can be challenging and may not always be cost-effective compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
Regulatory and Standardization Issues: Navigating the regulatory landscape for 3D printed products, particularly in highly regulated industries like aerospace and healthcare, requires careful attention to compliance and quality standards.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Engineering Management
The future of 3D printing in engineering management is promising, with ongoing advancements in printer technologies, materials, and digital modeling tools. Future trends may include the development of faster, more cost-effective printing technologies that can handle a wider range of materials. Additionally, increased automation and integration with other digital manufacturing technologies will likely enhance the efficiency and scalability of 3D printing applications.
3D printing is set to continue revolutionizing engineering management practices by offering innovative solutions that enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and accelerate product development. As the technology progresses, it promises to unlock new possibilities for managing engineering projects and operations, making it an indispensable tool in the arsenal of modern engineering managers. With ongoing advancements, 3D printing will increasingly influence how engineering teams design, plan, and execute projects across various sectors.