Biochemical engineering is a branch of chemical engineering that deals with the design and construction of unit processes that involve biological organisms or molecules. It plays a pivotal role in industries like pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, and biotechnology. The integration of 3D printing technology into biochemical engineering is transforming traditional methods by enabling the creation of custom apparatuses, complex bioreactor designs, and tailored enzyme matrices. This innovation enhances process efficiency, product customization, and environmental sustainability in biochemical manufacturing.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Biochemical Engineering
Originally utilized for rapid prototyping in manufacturing sectors, 3D printing has gained traction in biochemical engineering as a valuable tool for creating highly specialized equipment and structures. The technology allows for the precise fabrication of components that can be tailored to specific biochemical processes, enabling enhancements in reaction efficiency, handling of sensitive biomaterials, and integration of complex process flows in smaller footprints.
Advantages of 3D Printing in Biochemical Engineering
Customization and Complexity: 3D printing allows engineers to design and fabricate structures with complex geometries that are often required for efficient biochemical reactions, such as intricately shaped bioreactor internals that optimize media flow and improve mass transfer.
Rapid Development and Testing: The ability to quickly produce bespoke equipment and modifications accelerates the iterative process of design, testing, and scaling in biochemical engineering, significantly reducing development timelines and costs.
Material Efficiency: 3D printing contributes to sustainability by minimizing waste through precise material usage and enabling the production of lighter and stronger components that reduce the overall material footprint.
Innovation in Biocatalyst Design: The technology permits the creation of tailored enzyme immobilization supports with optimized surface areas and porosities, enhancing catalytic activities and stability, and enabling easier recovery and reuse of biocatalysts.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in Biochemical Engineering
Custom Bioreactors: 3D printing is used to construct bioreactors with customized features that address specific process requirements, such as variable compartment sizes, integrated sensors, and optimized flow paths that are not feasible with conventional manufacturing methods.
Enzyme Immobilization Systems: The design and production of novel supports for enzyme immobilization benefit from 3D printing, which can create structures that maximize enzyme loading and accessibility, thereby enhancing reaction rates and efficiencies.
Prototyping Process Equipment: From filtration systems to mixer components, 3D printing allows for the rapid prototyping of process equipment in biochemical engineering, facilitating quick adjustments and optimizations based on operational feedback.
Packaging and Delivery Systems: In pharmaceutical and food industries, 3D printing can develop packaging materials and systems that respond to environmental triggers to release contents at controlled rates or at specific times.
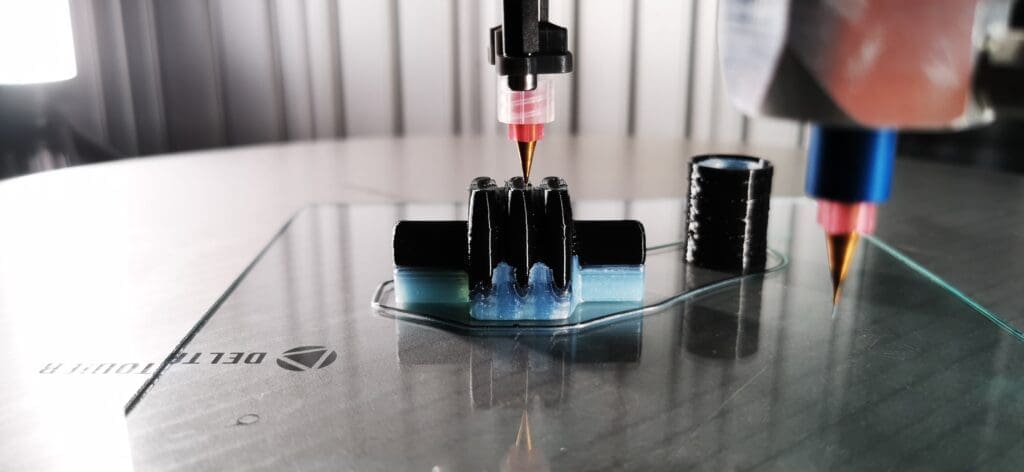

Challenges in 3D Printing for Biochemical Engineering
Material Compatibility: Finding materials that can withstand the harsh conditions of biochemical processes, including high temperatures, pressures, and corrosive substances, while maintaining structural integrity and biocompatibility, is challenging.
Scale-Up: While 3D printing is excellent for prototyping and small-scale production, scaling these processes to industrial levels often involves significant challenges in terms of print time, cost, and material properties.
Regulatory and Safety Standards: Equipment and products developed through 3D printing must meet stringent regulatory standards, particularly in the pharmaceutical and food sectors, where safety and efficacy are critical.
Technical Expertise: The intersection of 3D printing technology with biochemical engineering requires a deep understanding of both fields to effectively design and produce functional components.
Future Directions in 3D Printing for Biochemical Engineering
The future of 3D printing in biochemical engineering looks promising, with continuous advancements in printer technologies, materials, and software expected to address current limitations. Innovations in biocompatible and durable materials, along with improvements in printing resolution and speed, are likely to expand the applications and efficiency of 3D printed tools and equipment in this field.
3D printing is set to continue its transformative impact on biochemical engineering, providing innovative solutions that streamline processes, enhance product customization, and improve environmental sustainability. As the technology evolves, it promises to enable more sophisticated, efficient, and cost-effective production methods in biochemical industries, revolutionizing traditional practices and fostering sustainable development.