3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is revolutionizing the automotive industry by offering unprecedented flexibility and efficiency in car design and production. As manufacturers seek to reduce costs, speed up development, and increase customization, 3D printing emerges as a key technology that aligns perfectly with these goals. This innovation is transforming everything from prototyping to production, enabling the automotive sector to respond more swiftly to market changes and consumer preferences.
Advantages of 3D Printing in Automotive Manufacturing
3D printing brings several significant advantages to the automotive industry:
Customization and Complexity: This technology allows for the production of complex components that are often too intricate for traditional manufacturing techniques. It enables a high level of customization, facilitating the creation of features tailored to specific customer requests, particularly in luxury and high-performance vehicles.
Cost Reduction and Efficiency: 3D printing minimizes material waste by using only the amount needed to build parts, unlike traditional subtractive methods that cut away from a larger block. It also allows for just-in-time production of parts, reducing the need for large inventories and thus lowering storage and handling costs.

Speed of Production: The ability to rapidly produce prototypes speeds up the iterative design process significantly. Automotive designers and engineers can develop and test parts much quicker, enabling faster overall vehicle development cycles.
Key Applications of 3D Printing in the Automotive Industry
The applications of 3D printing in the automotive sector are varied and growing:
Prototyping: Automotive companies use 3D printing extensively to prototype new parts. This allows for the physical examination of part designs before they go into mass production, ensuring they meet all specifications and fit with other components correctly.
Production Parts: More and more, 3D printing is not just for prototypes but also for final production parts. For example, companies like BMW and Ford are using 3D printed components in their production cars, particularly for complex or custom elements that are difficult or costly to produce otherwise.
Tooling and Assembly: 3D printing is also revolutionizing the production line itself. Manufacturers are printing custom jigs and fixtures that are used to assemble car parts. These tools are lighter and more ergonomically designed than traditional tools, increasing efficiency and reducing the strain on workers.
Aftermarket and Spare Parts: Automakers are beginning to use 3D printing to offer aftermarket parts. This method is particularly beneficial for producing spare parts for older models, which can be costly to store and may be in low demand.
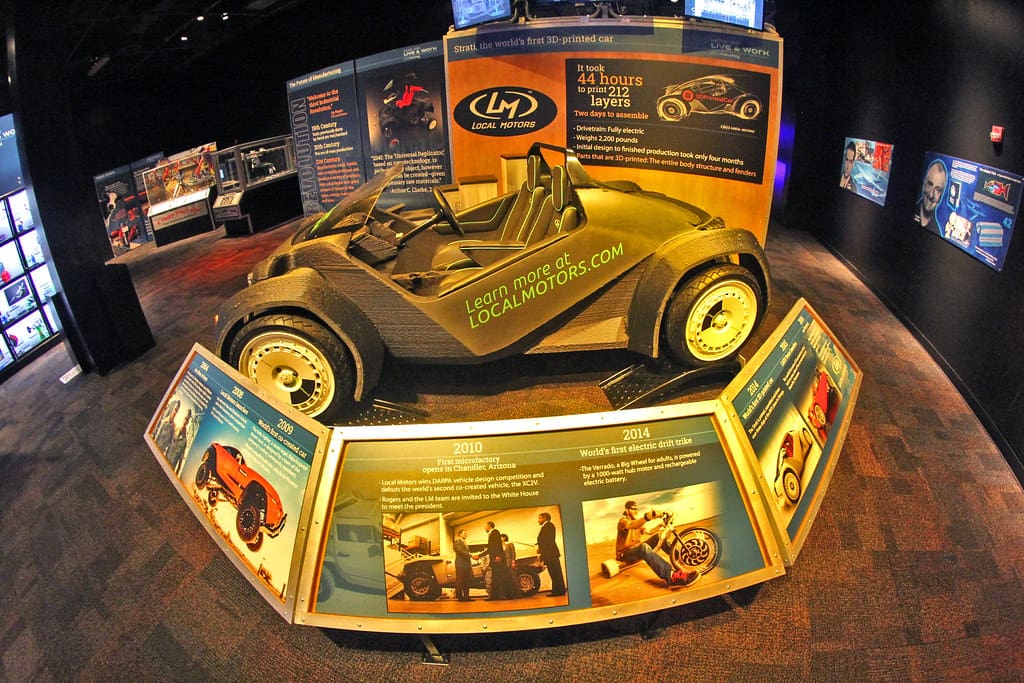

Challenges and Considerations
Despite its many benefits, 3D printing faces several challenges in the automotive industry:
Material Limitations: The range of materials suitable for 3D printing is still expanding. Durability and longevity under automotive stresses are critical factors that must be considered when selecting materials for exterior and structural parts.
Scale and Integration Challenges: Integrating 3D printing into existing large-scale production lines is non-trivial. The automotive industry relies on speed and volume, areas where traditional manufacturing currently has an advantage over 3D printing.
Quality and Regulatory Compliance: All automotive parts must meet strict regulatory standards. Ensuring that 3D printed parts comply with these standards requires rigorous testing and quality control processes.
Future Outlook
The future of 3D printing in the automotive industry looks promising. Technological advancements are expected to expand the material options, improve print speeds, and enhance the precision of 3D printers, making them more suited for large-scale production. Furthermore, as the automotive industry continues to focus on sustainability, 3D printing’s ability to reduce waste and energy consumption makes it an attractive option for eco-friendly manufacturing processes.
3D printing is set to play a pivotal role in the future of automotive manufacturing. By enabling greater customization, reducing costs, and speeding up development, this technology is helping the industry to innovate and adapt in a fast-changing world. As 3D printing technology continues to evolve, its integration into automotive manufacturing processes will likely deepen, offering new opportunities for design and production.